java condition 实现简单的阻塞队列
Posted liumy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java condition 实现简单的阻塞队列相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上一篇文章介绍了condition的使用方法
https://www.cnblogs.com/liumy/p/11563772.html
这一篇文章介绍如何用condition来实现一个简单的阻塞队列 消费者 生产者模式。
消费者 生产者模式就是 生产者生产某些对象,消费者来消费这些对象。其中用对象数组来保存这些对象,既然是数组,在初始化的时候需要指定数组的大小。
在生产者生产的时候需要检查数组是否已经满了,如果满了,那么生产者会被挂起,等到有消费者消费对象时,再进行生产。
当消费者消费的时候,先检查数组是否为空,如果为空会被挂起,等到生产者生产出对象时,再被唤醒,进行消费,这样就简单实现了一个简单的阻塞队列。
下面 上代码。
MyQueue

package com.citi.test.mutiplethread.demo5; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class MyQueue<E> public Object[] obj; private int addIndex; private int removeIndex; private int queueSize; private ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock(); private Condition addCondition=lock.newCondition(); private Condition removeCondition=lock.newCondition(); public MyQueue(int count) obj=new Object[count]; public Object get() return obj[queueSize-1]; public void add(E e) lock.lock(); while(queueSize==obj.length) System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 队列已满,不进行添加、"); try addCondition.await(); catch (InterruptedException e1) // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); obj[addIndex]=e; if(++addIndex==obj.length) addIndex=0; queueSize++; removeCondition.signal(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产之后:"+Arrays.toString(obj)); lock.unlock(); public void remove() lock.lock(); while(queueSize==0) System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 队列为空,不进行移除、"); try removeCondition.await(); catch (InterruptedException e) // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); obj[removeIndex]=null; if(++removeIndex==obj.length) removeIndex=0; queueSize--; addCondition.signal(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费之后:"+Arrays.toString(obj)); lock.unlock();
MyQueueAdd 生产者

package com.citi.test.mutiplethread.demo5; import java.util.UUID; public class MyQueueAdd implements Runnable private MyQueue<String> queue; public MyQueueAdd(MyQueue<String> queue) this.queue=queue; @Override public void run() while(true) queue.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); try Thread.sleep(1000); catch (InterruptedException e) // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); // System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":生产者添加元素"+Arrays.toString(queue.obj));
MyQueueRemove 消费者

package com.citi.test.mutiplethread.demo5; public class MyQueueRemove implements Runnable private MyQueue<String> queue; public MyQueueRemove(MyQueue<String> queue) this.queue = queue; @Override public void run() while(true) queue.remove(); try Thread.sleep(1000); catch (InterruptedException e) // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); // System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":消费者删除:"+Arrays.toString(queue.obj));
TestMyQueue 测试类 生产者大于消费者

package com.citi.test.mutiplethread.demo5; public class TestMyQueue public static void main(String[] args) MyQueue<String> queue=new MyQueue<String>(10); MyQueueAdd add=new MyQueueAdd(queue); MyQueueRemove remove=new MyQueueRemove(queue); new Thread(add).start(); new Thread(add).start(); new Thread(add).start(); new Thread(add).start(); new Thread(remove).start();
下面是执行结果,可以看到当队列为空时,消费者会被挂起,直到有生产者生产出对象,唤醒消费者,消费者再进行消费。因为生产者的个数大于消费者的个数,所以等到数组满了之后,出现队列已满,不进行添加。
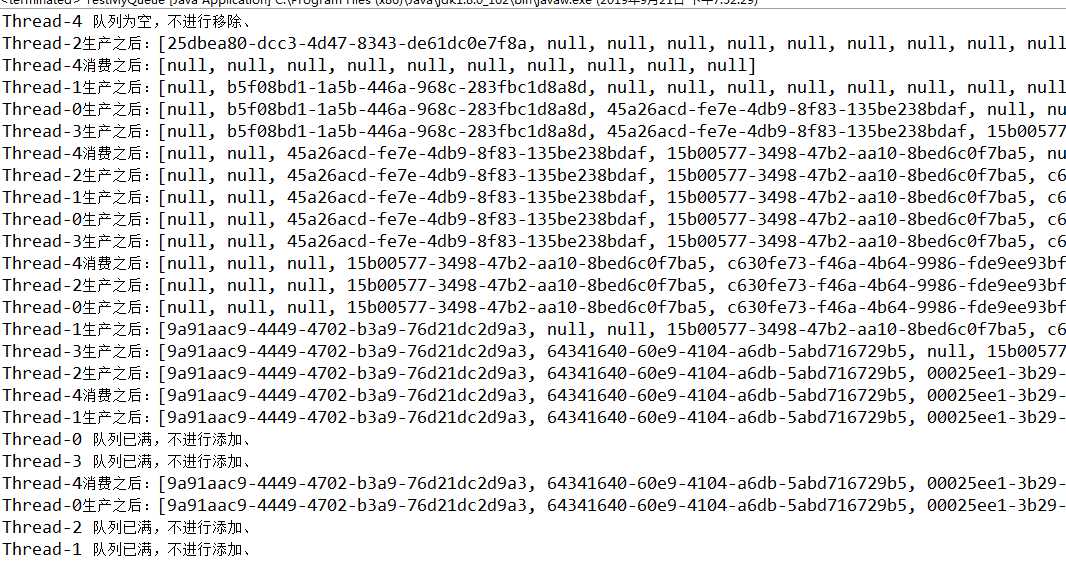
下面将消费者的个数大于生产者的个数
代码

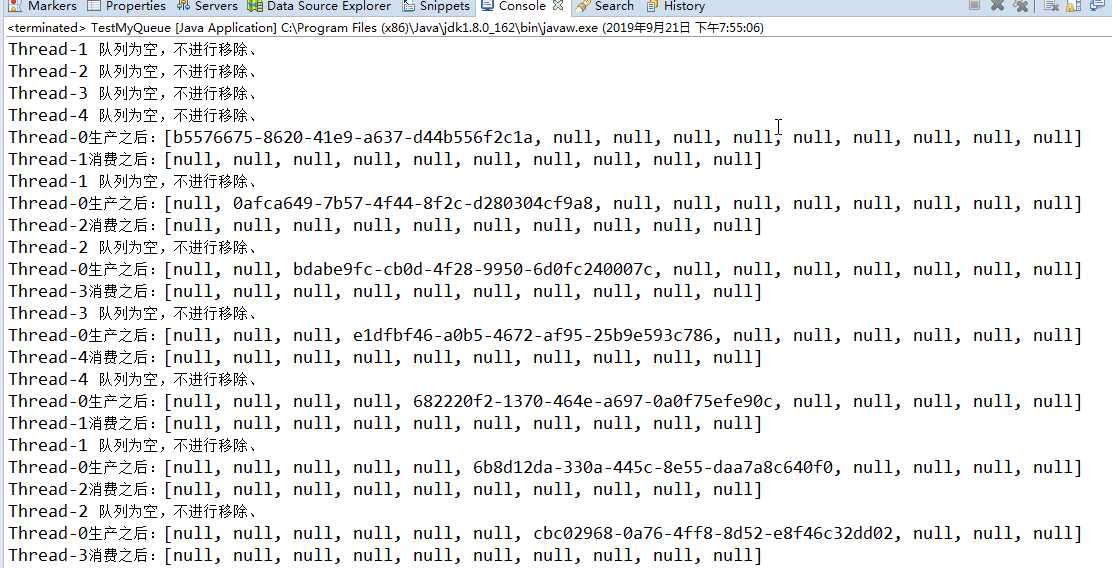
package com.citi.test.mutiplethread.demo5; public class TestMyQueue public static void main(String[] args) MyQueue<String> queue=new MyQueue<String>(10); MyQueueAdd add=new MyQueueAdd(queue); MyQueueRemove remove=new MyQueueRemove(queue); new Thread(add).start(); new Thread(remove).start(); new Thread(remove).start(); new Thread(remove).start(); new Thread(remove).start();
下面是执行结果。
以上是关于java condition 实现简单的阻塞队列的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
