《java基础知识》Java IO流详解
Posted jssj
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《java基础知识》Java IO流详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Java IO概念
1. 用于设备之间的数据传输。
2. Java 将操作数据流的功能封装到了IO包中。
3. 数据流流向分:输入流和输出流,操作对象为文件。
4. 流按照操作数据分:字节流(通用)和字符流。
5. 将计算机语言:二进制数据转换成文件显示到电脑上。
IO包:继承关系图:
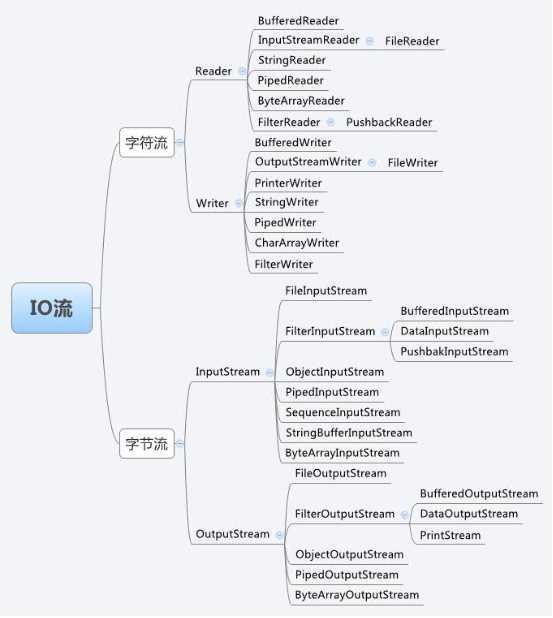
字符流:
Reader :读取字符流,方法见API。
Writer :写入字符流,方法见API。
案例(Writer ):
import java.io.*; public class var public static void main(String[] agrs) Writer writer = null; try writer = new FileWriter("Demo.txt");
// writer = new FileWriter("Demo.txt",true); 文件续写功能,否则会覆盖。 writer.write("今天天气真好!"); writer.flush(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally if(writer != null) try writer.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
运行结果:

案例(Reader):
文件数据:

import java.io.*; public class var public static void main(String[] agrs) Reader reader = null; try reader = new FileReader("Demo.txt"); char[] arr = new char[5]; int red = reader.read(arr); //red是装到数组的长度。 while(red != -1 ) System.out.println(new String(arr,0,red)); red = reader.read(arr); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally if(reader != null) try reader.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
运行结果:

实现一个完整的文件复制。
import java.io.*; public class var public static void main(String[] agrs) Reader reader = null; Writer writer = null; try reader = new FileReader("Demo.txt"); writer = new FileWriter("Dome1.txt"); // char[] arr = new char[5]; int red = 0; //red是装到数组的长度。 while((red = reader.read(arr)) != -1 ) writer.write(new String(arr,0,red)); writer.flush(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally if(reader != null) try reader.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); if(writer != null) try writer.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
运行结果:

优化文件复制案例(缓冲流):
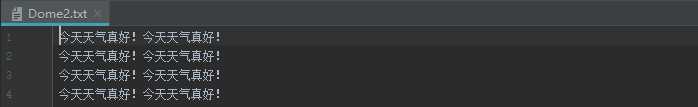
import java.io.*; public class var public static void main(String[] agrs) BufferedReader bufferedReader = null; //缓冲读取流 BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null; //缓冲写入流 try bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Demo.txt")); bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("Dome2.txt")); String str ; while((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null ) bufferedWriter.write(str); bufferedWriter.newLine(); //换行。 bufferedWriter.flush(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally if(bufferedReader != null) try bufferedReader.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); if(bufferedWriter != null) try bufferedWriter.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
运行结果:
上述IO无法处理视频,图片等一些文件,拷贝出来的文件也无法打开,由此我们引出字节流。
字节流:
OutputSteam:写入字节流,方法见API。
InputSteam: 读取字节流,方法见API。
案例(OutputSteam):
public class var public static void main(String[] agrs) FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; try fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("demo.txt"); fileOutputStream.write("今天天气真好,我们去玩吧!".getBytes()); //不需要刷新。 catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally if(fileOutputStream != null) try fileOutputStream.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
运行结果:

案例(InputSteam):
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; public class PublicTest public static void main(String[] args) FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; try fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("demo.txt"); int ch =0; byte[] arr = new byte[fileInputStream.available()]; //正式写代码不要使用fileInputStream.available(),因为文件比较大的时候内存会不够用。 while((ch = fileInputStream.read(arr)) != -1) System.out.println(new String(arr,0,ch)); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally if(fileInputStream != null) try fileInputStream.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
运行结果:

案例:复制一个视频文件
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class PublicTest public static void main(String[] args) FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; try fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("video.avi"); fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("video1.avi"); int ch =0; byte[] arr = new byte[fileInputStream.available()]; //正式写代码不要使用fileInputStream.available(),因为文件比较大的时候内存会不够用。 while((ch = fileInputStream.read(arr)) != -1) fileOutputStream.write(arr); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally if(fileInputStream != null) try fileInputStream.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); if(fileOutputStream != null) try fileOutputStream.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
运行结果:

转换流(键盘输入和控制台输出作为案例):
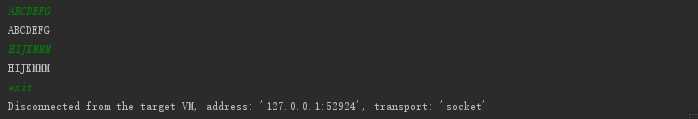
import java.io.*; public class var public static void main(String[] agrs) OutputStream out = System.out; //控制台打印 OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = null; outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(out); // outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(out,"GBK"); 可以指定写的编码 BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter); InputStream in = System.in; //键盘输入流。 InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(in); // InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(in,"BGK"); 同样可以指定编码 BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); try String line = null; while((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) if("exit".equals(line)) break; bufferedWriter.write(line); bufferedWriter.flush(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try if(bufferedWriter != null) bufferedWriter.close(); if(bufferedReader != null) bufferedReader.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
运行结果:
IO流先讲到这里,Java IO流还有很多有意思的类和方法见API。
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/runningTurtle/p/7088125.html
以上是关于《java基础知识》Java IO流详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章