DRF
Posted sima-3
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了DRF相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.postman实现登录
urls.py:
# 登录 url(r‘^v1/login/$‘, views.LoginSessionAPIView.as_view()),
views.py:
from rest_framework.views import APIView from django.contrib import auth class LoginSessionAPIView(APIView): # 登录要禁用认证与权限 authentication_classes = [] permission_classes = [] def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): username = request.data.get(‘username‘) password = request.data.get(‘password‘) if not (username and password): return Response(‘信息有误‘) # user = models.User.objects.filter(username=username).first() # type: models.User # user.check_password(password) user = auth.authenticate(request, username=username, password=password) if not user: return Response(‘登录失败‘) auth.login(request, user=user) return Response(‘登录成功‘)
注 : auth.login(request, user=user) 做了三件事 =>
a.把登录用户的session信息保存到数据库的django_session表中
b.把session_id签发给前台,保存到cookie中
c.把登录的user保存到request.user中
用户登录后做其他的增删改查操作:
session认证中对登录的用户会开启csrftoken认证
系统:session认证
rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication
ajax请求通过认证:
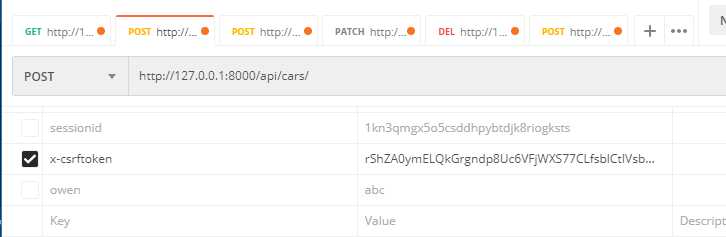
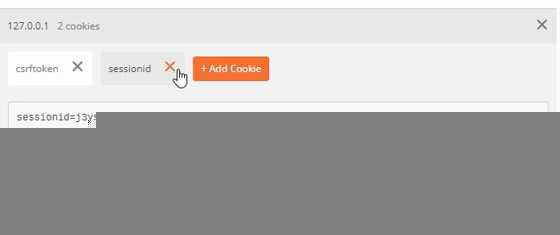
cookie中要携带 sessionid、csrftoken,请求头中要携带 x-csrftoken,后台从META字典中获取
Postman请求header如图:
Postman添加cookie如图:
普通自定义认证类 , 模仿class SessionAuthentication (BaseAuthentication):
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication def authenticate(self, request): auth = 从request中得到 user = 从auth中得到 (session校验中user是由sessionid解析出来的,而jwt校验user是由token字符串解析出来的) if not user: return None return user, auth
二. jwt
jwt:json web tokens 采用json格式在web上传输的 认证字符串
jwt字符串:头.载荷.签名
头:公司基本信息、项目组基本信息、常规加密算法名
载荷:用户信息、过期时间
签名:头、载荷、秘钥
头信息字典,采用base64加密算法.载荷信息字典,采用base64加密算法.头加密串、载荷加密串、服务器秘钥,采用hs256加密算法
base64是可逆加密
hash256是不可逆加密
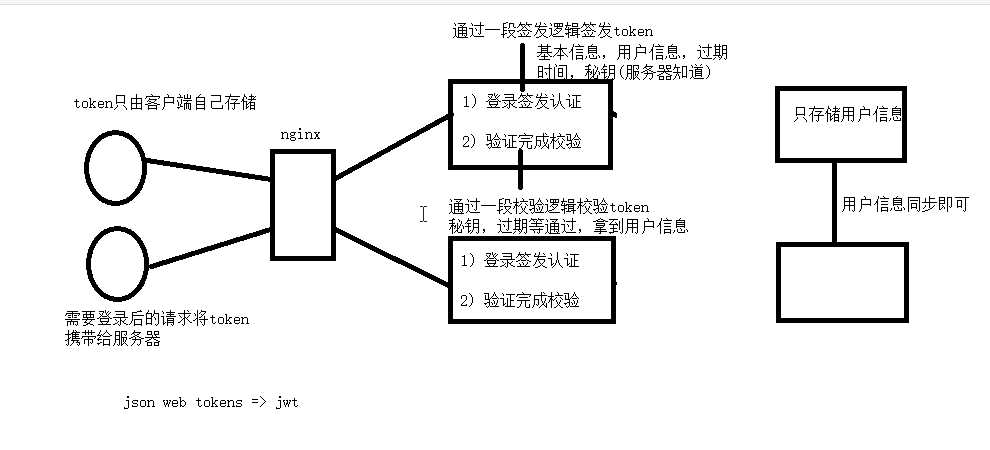
原理图:
安装:
pip install djangorestframework-jwt
1.jwt登录 (取消了认证和权限校验):
urls.py:
from rest_framework_jwt.views import ObtainJSONWebToken, obtain_jwt_token # url(r‘^v2/login/$‘, ObtainJSONWebToken.as_view()), url(r‘^v2/login/$‘, obtain_jwt_token),
源码校验及视图:
校验代码serializers.py(签发,编码形成token):
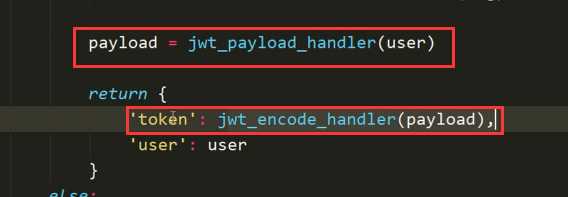
APIView:
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): serializer = self.get_serializer(data=request.data) if serializer.is_valid(): user = serializer.object.get(‘user‘) or request.user token = serializer.object.get(‘token‘) response_data = jwt_response_payload_handler(token, user, request) response = Response(response_data) if api_settings.JWT_AUTH_COOKIE: expiration = (datetime.utcnow() + api_settings.JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA) response.set_cookie(api_settings.JWT_AUTH_COOKIE, token, expires=expiration, httponly=True) return response return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
发送账号密码post请求,成功返回token字符串,错误返回错误信息.
2.自定义jwt登录:
路由:
url(r‘^v3/login/$‘, views.LoginJWTAPIView.as_view()),
视图:
username可能携带的不止是用户名,可能还是用户的其它唯一标识 手机号 邮箱
校验密码,手动通过 user 签发编码形成 jwt-token
import re from utils.response import APIResponse from rest_framework_jwt.serializers import jwt_encode_handler, jwt_payload_handler class LoginJWTAPIView(APIView): authentication_classes = () permission_classes = () def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): # username可能携带的不止是用户名,可能还是用户的其它唯一标识 手机号 邮箱 username = request.data.get(‘username‘) password = request.data.get(‘password‘) # 如果username匹配上手机号正则 => 可能是手机登录 if re.match(r‘1[3-9][0-9]9‘, username): try: # 手动通过 user 签发 jwt-token user = models.User.objects.get(mobile=username) except: return APIResponse(1, ‘该手机未注册‘) # 邮箱登录 等 # 账号登录 else: try: # 手动通过 user 签发 jwt-token user = models.User.objects.get(username=username) except: return APIResponse(1, ‘该账号未注册‘) # 获得用户后,校验密码并签发token if not user.check_password(password): return APIResponse(1, ‘密码错误‘) payload = jwt_payload_handler(user) token = jwt_encode_handler(payload) return APIResponse(0, ‘ok‘, results= ‘username‘: user.username, ‘mobile‘: user.mobile, ‘token‘: token )
3.jwt认证:
rest_framework_jwt.authentication.JSONWebTokenAuthentication
ajax请求通过认证:
请求头中要携带 authorization,值为 jwt+空格+token
路由:
url(r‘^v3/cars/$‘, views.CarV3ModelViewSet.as_view( ‘get‘: ‘list‘, ‘post‘: ‘create‘ )), url(r‘^v3/cars/(?P<pk>.*)/$‘, views.CarV3ModelViewSet.as_view( ‘get‘: ‘retrieve‘, ‘put‘: ‘update‘, ‘patch‘: ‘partial_update‘, ‘delete‘: ‘destroy‘, )),
视图:
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import JSONWebTokenAuthentication class CarV3ModelViewSet(ModelViewSet): authentication_classes = [JSONWebTokenAuthentication] permission_classes = [IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly] queryset = models.Car.objects.filter(is_delete=False) serializer_class = serializers.CarModelSerializer def destroy(self, request, *args, **kwargs): obj = self.get_object() obj.is_delete = True obj.save() return Response(‘删除成功‘)
authonticate方法认证(游客返回None,登录由token字符串反解析为user):
def authenticate(self, request): """ Returns a two-tuple of `User` and token if a valid signature has been supplied using JWT-based authentication. Otherwise returns `None`. """ jwt_value = self.get_jwt_value(request) if jwt_value is None: return None try: payload = jwt_decode_handler(jwt_value) except jwt.ExpiredSignature: msg = _(‘Signature has expired.‘) raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg) except jwt.DecodeError: msg = _(‘Error decoding signature.‘) raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg) except jwt.InvalidTokenError: raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed() user = self.authenticate_credentials(payload) return (user, jwt_value)
get_jwt_value方法获取token值(settings中拿到前缀小写就是jwt,规定前台格式为jwt token字符串):
def get_jwt_value(self, request): auth = get_authorization_header(request).split() auth_header_prefix = api_settings.JWT_AUTH_HEADER_PREFIX.lower() if not auth: if api_settings.JWT_AUTH_COOKIE: return request.COOKIES.get(api_settings.JWT_AUTH_COOKIE) return None if smart_text(auth[0].lower()) != auth_header_prefix: return None if len(auth) == 1: msg = _(‘Invalid Authorization header. No credentials provided.‘) raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg) elif len(auth) > 2: msg = _(‘Invalid Authorization header. Credentials string ‘ ‘should not contain spaces.‘) raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg) return auth[1]
get_authorization_header拿到二进制字符串:
def get_authorization_header(request): """ Return request‘s ‘Authorization:‘ header, as a bytestring. Hide some test client ickyness where the header can be unicode. """ auth = request.META.get(‘HTTP_AUTHORIZATION‘, b‘‘) if isinstance(auth, str): # Work around django test client oddness auth = auth.encode(HTTP_HEADER_ENCODING) return auth
payload签发内容:
payload = ‘user_id‘: user.pk, ‘username‘: username, ‘exp‘: datetime.utcnow() + api_settings.JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA
在settings.py中可找到token的过期时间:300s
‘JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA‘: datetime.timedelta(seconds=300),
4.自定义jwt认证类:
自定义:基于jwt、其它
1)自定义认证类,继承BaseAuthentication(或其子类),重写authenticate
2)authenticate中完成
拿到认证标识 auth
反解析出用户 user
前两步操作失败 返回None => 游客
前两步操作成功 返回user,auth => 登录用户
注:如果在某个分支抛出异常,直接定义失败 => 非法用户
settings.py配置 (修改过期时间和前缀):
# jwt配置 import datetime JWT_AUTH = ‘JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA‘: datetime.timedelta(seconds=30000), ‘JWT_AUTH_HEADER_PREFIX‘: ‘TOKEN‘,
把authentication认证配置换成自定义的jwt认证:
REST_FRAMEWORK = ‘DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES‘: [ # django默认session校验:校验规则 游客 及 登录用户 # ‘rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication‘, # ‘rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication‘, # ‘rest_framework_jwt.authentication.JSONWebTokenAuthentication‘, ‘api.authentications.JWTAuthentication‘, ],
自定义authtications.py (前台发送auth的token,而且不传前缀):
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed import jwt from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import jwt_decode_handler class JWTAuthentication(BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication): # 自定义认证类,重写authenticate方法 def authenticate(self, request): # 认证通过,返回user,auth # 认证失败,返回None auth = request.META.get(‘HTTP_AUTH‘) # 前台用auth携带token if not auth: return None try: payload = jwt_decode_handler(auth) # 出现jwt解析异常,直接抛出异常,代表非法用户,也可以返回None,作为游客处理 except jwt.ExpiredSignature: raise AuthenticationFailed(‘token已过期‘) except: raise AuthenticationFailed(‘token非法‘) user = self.authenticate_credentials(payload) return (user, auth)
视图:
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import JSONWebTokenAuthentication class CarV3ModelViewSet(ModelViewSet): #authentication_classes = [JSONWebTokenAuthentication] permission_classes = [IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly] queryset = models.Car.objects.filter(is_delete=False) serializer_class = serializers.CarModelSerializer def destroy(self, request, *args, **kwargs): obj = self.get_object() obj.is_delete = True obj.save() return Response(‘删除成功‘)
5.自定义权限类:
系统:
1)AllowAny:允许所有用户,校验方法直接返回True
2)IsAuthenticated:只允许登录用户
必须request.user和request.user.is_authenticated都通过
3)IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly:游客只读,登录用户无限制
get、option、head 请求无限制
前台请求必须校验 request.user和request.user.is_authenticated
4)IsAdminUser:是否是后台用户
校验 request.user和request.user.is_staff is_staff(可以登录后台管理系统的用户)
自定义:基于auth的Group与Permission表
1)自定义权限类,继承BasePermission,重写has_permission
2)has_permission中完成
拿到登录用户 user <= request.user
校验user的分组或是权限
前两步操作失败 返回False => 无权限
前两步操作成功 返回True => 有权限
查看所有用户路由:
# 权限: 只有管理员分组成员才可以查看所以用户信息 url(r‘^users/$‘, views.UserListAPIView.as_view()),
视图:
from rest_framework.generics import ListAPIView from .permissions import AdminPermission class UserListAPIView(ListAPIView): queryset = models.User.objects.filter(is_active=True) serializer_class = serializers.UserModelSerializer # 登录的用户必须是自定义管理员分组成员 permission_classes = [AdminPermission]
自定义permissions.py:
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission class AdminPermission(BasePermission): # 继承BasePermission,重写has_permission def has_permission(self, request, view): # 有权限,返回True # 无权限,返回False user = request.user if not user: return False # 用户是 管理员 分组 (管理员分组是Group表中的一条自定义记录) if not user.groups.filter(name=‘管理员‘): return False # 登录的用户必须是自定义管理员分组成员 return True
6.admin添加用户密文密码及其他信息:
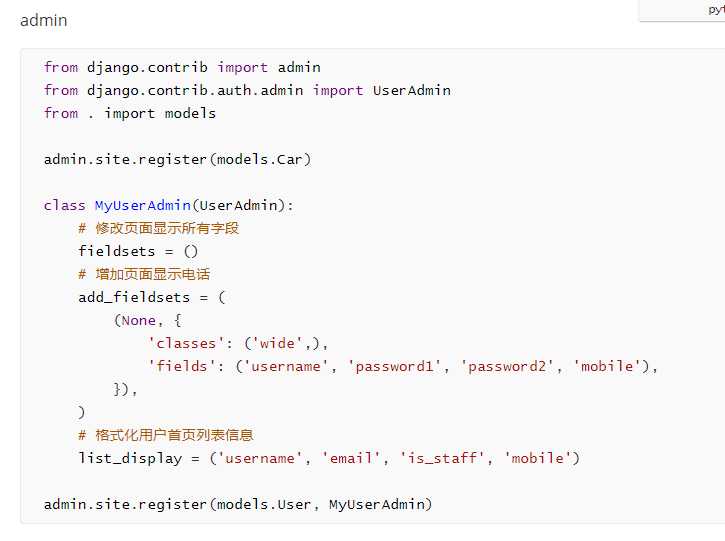
7.频率校验
系统: 1)AnonRateThrottle:对同一IP游客的限制 2)UserRateThrottle:对同一IP登录用户的限制 必须在settings.py中 ‘DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES‘: ‘user‘: ‘10/min‘, # 登录的用户一分钟可以访问10次 ‘anon‘: ‘3/min‘, # 游客一分钟可以访问3次 在视图类中: class TempAPIView(APIView): ... throttle_classes = [AnonRateThrottle, UserRateThrottle] 自定义:基于auth的Group与Permission表 1)自定义频率类,继承SimpleRateThrottle,重写get_cache_key,明确scope SimpleRateThrottle已经帮我们实现了 allow_request、wait 2)scope与settings.py的DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES配合使用 3)get_cache_key中完成 拿到限制信息 ident <= request中获取 没有限制信息 返回None => 不限制 有限制信息 返回限制信息字符串 => 有限制
视图类中校验频率:
def check_throttles(self, request): """ Check if request should be throttled. Raises an appropriate exception if the request is throttled. """ throttle_durations = [] for throttle in self.get_throttles(): if not throttle.allow_request(request, self): throttle_durations.append(throttle.wait()) if throttle_durations: self.throttled(request, max(throttle_durations))
SimpleRateThrottle类
throttle调方法前要初始化:
allow_request方法:
def allow_request(self, request, view): """ Implement the check to see if the request should be throttled. On success calls `throttle_success`. On failure calls `throttle_failure`. """ if self.rate is None: return True self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view) if self.key is None: return True self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, []) self.now = self.timer() # Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the # throttle duration while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration: self.history.pop() if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests: return self.throttle_failure() return self.throttle_success()
以上是关于DRF的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章