练习题
Posted banmei-brandy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了练习题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
做一下倒数两题,都是在队列模拟的程序基础上做点修改测试。
5.找出平均等候时间为1分钟时,每小时到达的客户数为多少(试验时间不少于100小时)。
指定队伍最大长度10人,模拟100小时。粗略估计答案在10到20之间,所以我在开始输入的时候为其生成10到20之间的随机数,通过循环不断去试,直到模拟完的平均等待时间等于1分钟为止。
//Bank.cpp -- Using Class #include "Queue.h" #include <iostream> #include <ctime> //for time() const int MIN_PER_HR = 60; bool newcustomer(double x); int main() using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::ios_base; std::srand(std::time(0)); //生成随机数时间种子 int flag = 1; //用于保持循环 cout<<"Case Study: Bank of Heather Automatic Teller\\n"; cout<<"Enter maximum size of queue: "; int qs; cin>>qs; //指定排队的最大人数,不指定默认为10 Queue line(qs); //初始化Queue类对象line cout<<"Enter the number of simulation hours: "; int hours; cin>>hours; //指定想要模拟的小时数 long cyclelimit = MIN_PER_HR * hours; //将小时转化为分钟,因为后面每分钟为一个循环周期 while(flag) cout<<"Enter the average number of customers per hour: "; double perhour; cout<<"(Generated)"; perhour = rand()%20 + 10; //在10到20之间随机试 //cin>>perhour; //指定一小时平均有多少顾客 double min_per_cust; min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / perhour; //换算平均下来每多少分钟到达一位顾客 Item temp; //一个临时顾客对象,用于代表每个循坏周期服务的顾客 long turnaways = 0; long customers = 0; long served = 0; long sum_line = 0; int wait_time = 0; long line_wait = 0; //开始模拟 for(int cycle = 0;cycle < cyclelimit;cycle++) if(newcustomer(min_per_cust)) if(line.isfull()) turnaways ++; //因为队伍已满而离去的人+1 else customers ++; //到达的顾客数+1 temp.set(cycle); //为这位顾客生成随机的服务时间(1-3分钟),并记录其到达的时间 line.enqueue(temp); //顾客入队,更新内部所有指针 /* wait_time是每位顾客服务时间的计数器,可以这么想象:*/ /* 每有一位顾客到达了队首,就开始掐表倒计时(1-3分钟随机)*/ /* 时间一到0,表示服务完毕,下一个人补上,重新倒计时,如此重复 */ if(wait_time <=0 && !line.isempty()) //上一位服务完毕且队伍里还有人 line.dequeue(temp); //下一位出队,开始服务 wait_time = temp.ptime(); //置计数器为该位顾客的服务时间 line_wait += cycle - temp.when(); //用现在的时间减去该顾客的到达时间,所有结果累加(即总等待时间) served ++; //已服务的人数+1 if(wait_time>0) wait_time--; //上一位服务未完毕,保持当前状态,时间-1 sum_line += line.queuecount(); //数一下现在队伍有多少人,把每一分钟的结果都累加起来 //报告结果 if(customers > 0) cout<<"customers accepted: "<<customers<<endl; //总到来的顾客数 cout<<" customers served: "<<served<<endl; //总服务的顾客数 cout<<" turnaways: "<<turnaways<<endl; //总离去的顾客数(到来却因队伍满了而离去) cout<<"average queue size: "; cout.precision(2); //设定输出的有效数字为两位 cout.setf(ios_base::fixed,ios_base::floatfield); //输出浮点数为定点模式,结合上句的效果就是输出到小数点后两位 cout<<(double)sum_line/cyclelimit<<endl; //平均每分钟的排队人数 cout<<" average wait time: "<<(double)line_wait/served<<" minutes\\n"; //平均每个人的等待时间 else cout<<"No customers!\\n"; cout<<"Done!\\n"; if((double)line_wait/served == 1) flag = 0; cout<<"the average number of customers per hour: "<<perhour<<endl; //cout<<"Enter 1 to simulate again,0 to quit: "; //cin>>flag; //输入0以终止循环 return 0; /* 判断顾客是否到达的函数 */ /* RAND_MAX是能够生成的最大随机数,rand()会生成[0,RAND_MAX)之间的随机数 */ /* 因此rand()/RAND_MAX会生成[0,1)之间的随机数,再乘以x就是[0,x)之间的随机数 */ /* 加上小于1的判断,生成的数会有1/x的概率小于1,而小于1就表示这一分钟内有顾客到了 */ bool newcustomer(double x) return (std::rand() * x/RAND_MAX < 1);
此种情况下,最后计算的结果为18人。
6.再开一台ATM,新来的顾客会根据人数拍队,模拟新的情况,再次找出平均等待时间为1分钟,每小时到达的客户数应为多少。
设定每队最大能容纳5人,模拟200小时。平均每小时到达人数从50开始一个个试。
如果某一队人比另一队少的话,新来的顾客就会去那一队。如果两队人一样多,就随便选一个(随机数)。
//Bank.cpp -- Using Class #include "Queue.h" #include <iostream> #include <ctime> //for time() const int MIN_PER_HR = 60; bool newcustomer(double x); int main() using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::ios_base; std::srand(std::time(0)); //生成随机数时间种子 int flag = 1; //用于保持循环 cout<<"Case Study: Bank of Heather Automatic Teller\\n"; cout<<"Enter maximum size of queue: "; int qs; cin>>qs; //指定排队的最大人数,不指定默认为10 Queue line(qs); //初始化Queue类对象line Queue line2(qs); cout<<"Enter the number of simulation hours: "; int hours; cin>>hours; //指定想要模拟的小时数 long cyclelimit = MIN_PER_HR * hours; //将小时转化为分钟,因为后面每分钟为一个循环周期 Item temp1; //一个临时顾客对象,用于代表每个循坏周期服务的顾客 Item temp2; while(flag) cout<<"Enter the average number of customers per hour: "; double perhour; cin>>perhour; //指定一小时平均有多少顾客 double min_per_cust; min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / perhour; //换算平均下来每多少分钟到达一位顾客 long turnaways = 0; long customers = 0; long served = 0; long sum_line_1 = 0; long sum_line_2 = 0; int wait_time_1 = 0; int wait_time_2 = 0; long line_wait_1 = 0; long line_wait_2 = 0; //开始模拟 for(int cycle = 0;cycle < cyclelimit;cycle++) if(newcustomer(min_per_cust)) if(line.isfull()&&line2.isfull()) turnaways ++; //因为队伍已满而离去的人+1 else customers ++; //到达的顾客数+1 if(line.queuecount() < line2.queuecount()) temp1.set(cycle); //为这位顾客生成随机的服务时间(1-3分钟),并记录其到达的时间 line.enqueue(temp1); else if(line.queuecount() > line2.queuecount()) temp2.set(cycle); //为这位顾客生成随机的服务时间(1-3分钟),并记录其到达的时间 line2.enqueue(temp2); else int choice = rand()%2; if(choice<1) temp1.set(cycle); line.enqueue(temp1); else temp2.set(cycle); line2.enqueue(temp2); /* wait_time是每位顾客服务时间的计数器,可以这么想象:*/ /* 每有一位顾客到达了队首,就开始掐表倒计时(1-3分钟随机)*/ /* 时间一到0,表示服务完毕,下一个人补上,重新倒计时,如此重复 */ if(wait_time_1 <=0 && !line.isempty()) //上一位服务完毕且队伍里还有人 line.dequeue(temp1); //下一位出队,开始服务 wait_time_1 = temp1.ptime(); //置计数器为该位顾客的服务时间 line_wait_1 += cycle - temp1.when(); //用现在的时间减去该顾客的到达时间,所有结果累加(即总等待时间) served ++; //已服务的人数+1 if(wait_time_2 <=0 && !line2.isempty()) line2.dequeue(temp2); //下一位出队,开始服务 wait_time_2 = temp2.ptime(); //置计数器为该位顾客的服务时间 line_wait_2 += cycle - temp2.when(); //用现在的时间减去该顾客的到达时间,所有结果累加(即总等待时间) served ++; //已服务的人数+1 if(wait_time_1>0) wait_time_1--; //上一位服务未完毕,保持当前状态,时间-1 if(wait_time_2>0) wait_time_2--; sum_line_1 += line.queuecount(); //数一下现在队伍有多少人,把每一分钟的结果都累加起来 sum_line_2 += line2.queuecount(); //报告结果 if(customers > 0) cout<<"customers accepted: "<<customers<<endl; //总到来的顾客数 cout<<" customers served: "<<served<<endl; //总服务的顾客数 cout<<" turnaways: "<<turnaways<<endl; //总离去的顾客数(到来却因队伍满了而离去) cout<<"average queue size:(1) "; cout.precision(2); //设定输出的有效数字为两位 cout.setf(ios_base::fixed,ios_base::floatfield); //输出浮点数为定点模式,结合上句的效果就是输出到小数点后两位 cout<<(double)sum_line_1/cyclelimit<<endl; //1平均每分钟的排队人数 cout<<"average queue size:(2) "; cout<<(double)sum_line_2/cyclelimit<<endl; //2平均每分钟的排队人数 cout<<" average wait time: "<<(double)(line_wait_1+line_wait_2)/served<<" minutes\\n"; //平均每个人的等待时间 else cout<<"No customers!\\n"; cout<<"Done!\\n"; cout<<"Enter 1 to simulate again,0 to quit: "; cin>>flag; //输入0以终止循环 return 0; /* 判断顾客是否到达的函数 */ /* RAND_MAX是能够生成的最大随机数,rand()会生成[0,RAND_MAX)之间的随机数 */ /* 因此rand()/RAND_MAX会生成[0,1)之间的随机数,再乘以x就是[0,x)之间的随机数 */ /* 加上小于1的判断,生成的数会有1/x的概率小于1,而小于1就表示这一分钟内有顾客到了 */ bool newcustomer(double x) return (std::rand() * x/RAND_MAX < 1);
模拟结果:
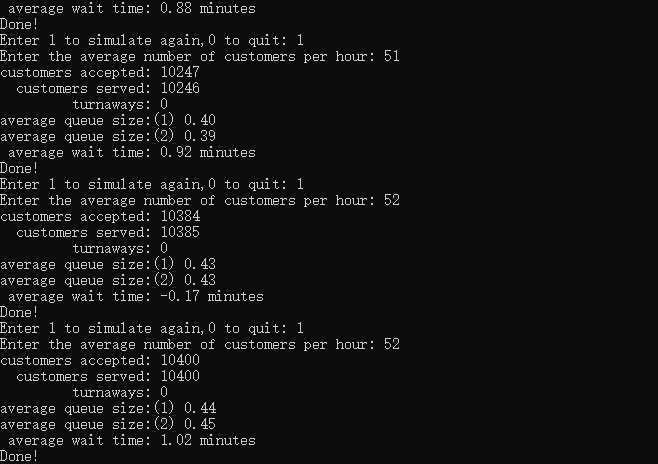
可以看出大约平均每小时到达51或52个顾客,等待时间会保持在1分钟。但是,我翻来覆去地看代码,也不知道为什么平均等待时间会算出负数来,总觉得哪里有问题。
以上是关于练习题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章