逻辑回归-3.决策边界
Posted shuai-long
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了逻辑回归-3.决策边界相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
决策边界
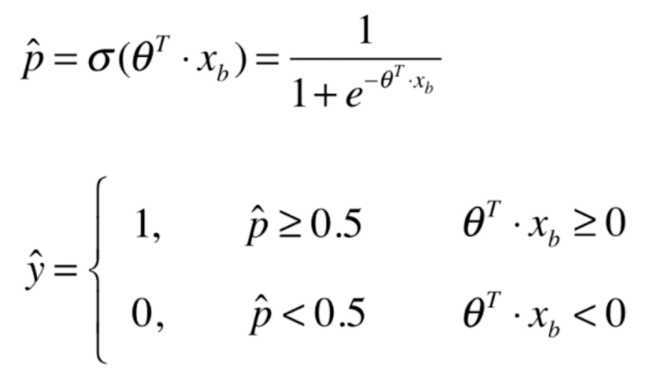
我们可以看出 决定y取不同值的边界为:\\[ \\theta^T \\cdot x_b = 0 \\]
上式表达式是一条直线,为决策边界,如果新来一个样本,和训练后得到的$ \\theta $相乘,根据是否大于0,决定到底属于哪一类
画出决策边界
如果样本有两个特征\\(x1,x2\\),则决策边界有:\\(\\theta_0 + \\theta_1 \\cdot x1 +\\theta_2 \\cdot x2 = 0\\) ,求得\\(x2 = \\frac-\\theta_0 - \\theta_1 \\cdot x1\\theta_2\\)
# 定义x2和x1的关系表达式
def x2(x1):
return (-logic_reg.interception_ - logic_reg.coef_[0] * x1)/logic_reg.coef_[1]
x1_plot = numpy.linspace(4,8,1000)
x2_plot = x2(x1_plot)
pyplot.scatter(X[y==0,0],X[y==0,1],color='red')
pyplot.scatter(X[y==1,0],X[y==1,1],color='blue')
pyplot.plot(x1_plot,x2_plot)
pyplot.show()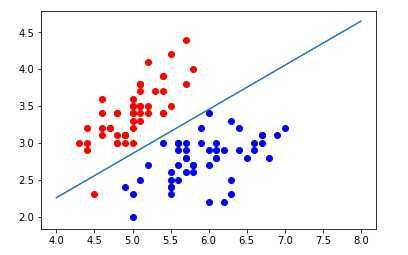
不规则决策边界的绘制
特征域(为了可视化,特征值取2,即矩形区域)中可视化区域中所有的点,查看不规则决策边界
定义绘制特征域中所有点的函数:
def plot_decision_boundary(model,axis):
x0,x1 = numpy.meshgrid(
numpy.linspace(axis[0],axis[1],int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)),
numpy.linspace(axis[2],axis[3],int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100))
)
x_new = numpy.c_[x0.ravel(),x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(x_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9'])
pyplot.contourf(x0,x1,zz,cmap=custom_cmap)绘制逻辑回归的决策边界:
plot_decision_boundary(logic_reg,axis=[4,7.5,1.5,4.5])
pyplot.scatter(X[y==0,0],X[y==0,1],color='blue')
pyplot.scatter(X[y==1,0],X[y==1,1],color='red')
pyplot.show()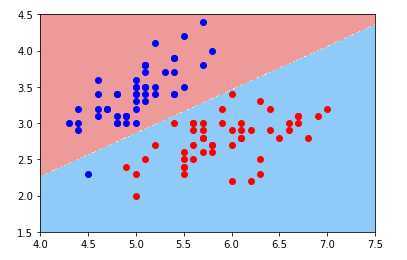
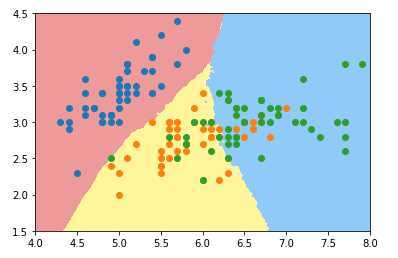
绘制K近邻算法的决策边界:
from mylib import KNN
knn_clf_all = KNN.KNNClassifier(k=3)
knn_clf_all.fit(iris.data[:,:2],iris.target)
plot_decision_boundary(knn_clf_all,axis=[4,8,1.5,4.5])
pyplot.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==0,0],iris.data[iris.target==0,1])
pyplot.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==1,0],iris.data[iris.target==1,1])
pyplot.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==2,0],iris.data[iris.target==2,1])
pyplot.show()k近邻多分类(种类为3)下的决策边界
k取3时:
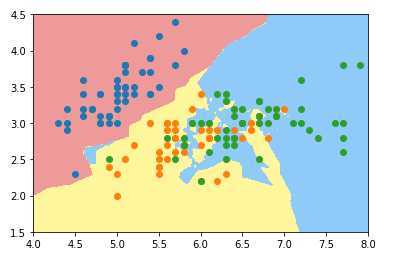
k取50时:
参考:慕课笔记
以上是关于逻辑回归-3.决策边界的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章