输入输出流和顶级父类
Posted gookiki
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了输入输出流和顶级父类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
输入输出流分为:字符流 和 字节流
字节流: InputStream OutputStream (一切都是字节流)
字符流:Reader Writer(主要是强调功能,用来读取字符流的继承自Object)
OutputtStream -----是一个超类,和抽象类
FileOutputStream -- 字节输出流
public class CopyDemo
// 字节流的演示 public static void main(String[] args) try // 创建输入输出--这都是字节流,但是中文需要字符流 FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("src\\\\main\\\\java\\\\com\\\\nowcoder\\\\Gday09\\\\test.jpg"); FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("src\\\\main\\\\java\\\\com\\\\nowcoder\\\\Gday09\\\\test0.jpg"); // 设定每次读取的字节数1024个字节 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int length = 0; while ((length = inputStream.read(bytes))!= -1) // 从0开始读取,读取的 // 从指定的字节数组写入 bytes个字节,从偏移 off开始输出到输出流 outputStream.write(bytes,0,length); System.out.println("复制成功!"); // 先创建的流,可以后关闭,后创建的后关闭 // 防止可能被使用的流,先关闭 inputStream.close(); outputStream.close(); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
用FileReader 的方法读取字符流,可以用来读中文
public class ReaderDemo public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("src\\\\main\\\\java\\\\com\\\\nowcoder\\\\Gday09\\\\a.txt"); int a ; /* 因为read返回的值是int * 把返回的int值赋值给a, * 判断a 是否等于-1 * 如果等于-1,就表示已经读到了文件的末尾 * */ while ((a=fileReader.read())!=-1) // System.out.print(a); System.out.print((char)(a)); // 针对中文的字节输入流 // System.out.println(a);
// 还是需要关闭流
fileReader.close();
字符输入流
读取一组的字符,只能操作一系列的文本文件,单纯操作文本的时候用这个,在操作其他的时候用字节流
每次自定义一个读取的字符长度,但是读到文件末尾的时候,不一定会读满定义的长度,所以再定义一个变量
用来读取每次读到的有效长度。
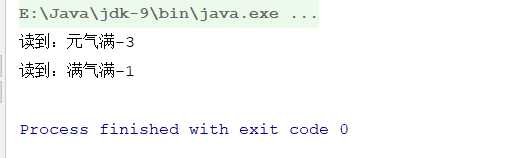
public class ChineseDemo public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException FileReader reader = new FileReader("src\\\\main\\\\java\\\\com\\\\nowcoder\\\\Gday09\\\\a.txt"); int a ; // 表示到底新读了几个。 // 这里来规定到底要读取几个文字 char[] data = new char[3]; while ((a=reader.read(data))!=-1) System.out.println("读到:"+( new String(data))+"-"+a); reader.close();
public class ChineseDemo public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException FileReader reader = new FileReader("src\\\\main\\\\java\\\\com\\\\nowcoder\\\\Gday09\\\\a.txt"); int a ; // 表示到底新读了几个。 // 这里来规定到底要读取几个文字 char[] data = new char[3]; while ((a=reader.read(data))!=-1) // System.out.println("读到:"+( new String(data))+"-"+a); // data 是需要读取的文件,0是读取文件的起始位置,a是最后一次读的数字 System.out.println(new String(data,0,a)); reader.close();

IO流的异常处理
用IDEA的自动提示的功能,免去添加finally和流关闭的过程
surround with try-with-resour block
public class ExceptionDemo public static void main(String[] args) try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("a.txt"); FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("a1.txt")) catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
另一种清爽的写法

1 public class ExceptionDemo 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException 3 // 这种情况下是不需要close的,拿到外部去的方式。也是一种简写,在这种情况下,就可以直接抛出异常throws IOException 4 FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("a.txt"); 5 FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("a1.txt"); 6 // 有多个流的情况,直接在小括号中添加分号 7 try ( fileReader;fileWriter) 8 9 catch (IOException e) 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 12 13 14
以上是关于输入输出流和顶级父类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
