二叉树 + 递归 + 分治法总结
Posted bella2017
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了二叉树 + 递归 + 分治法总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
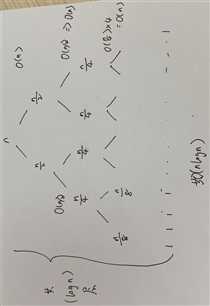
二叉树递归相关题目的时间复杂度基本上都是O(n) = 一共有n个点 + 每个点的时间复杂度(1)
而二叉树分治法最坏的时间复杂度为O(n^2)
时间复杂度:T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(1) = O(n)
Merge Sort, Quick Sort: T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(n) = O(nlogn)
前序遍历:
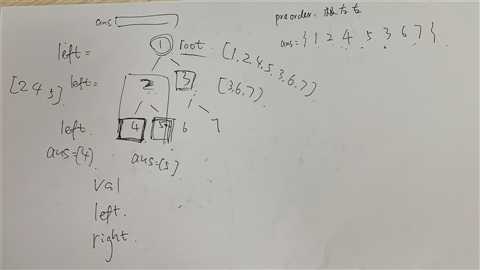
解法一:递归,通常是设置一个全局变量来保存结果。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) vector<int> result; traverse(root, result); return result; void traverse(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res) //递归终止条件 if(root == NULL) return; res.push_back(root->val); traverse(root->left, res); traverse(root->right, res); ;
解法二:Divide & Conquer
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) vector<int> res; if(root == NULL) return res; //divide vector<int> left = preorderTraversal(root->left); vector<int> right = preorderTraversal(root->right); //conquer res.push_back(root->val); for(auto i : left) res.push_back(i); for(auto i : right) res.push_back(i); return res; ;
解法三:非递归版本C++
采用堆栈实现。
- 根节点先入栈
- 判断栈是否为空,飞空则出栈并加入结果队列
- 先把右子树入栈再把左子树入栈,这样出栈的时候是先左后右,(中间根已经在上一步输出)
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) vector<int> res; if(root == NULL) return res; stack<TreeNode*> st; st.push(root); while(!st.empty()) TreeNode* node = st.top(); st.pop(); res.push_back(node->val); if(node->right) st.push(node->right); if(node->left) st.push(node->left); return res; ;
中序遍历:
一. 递归
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) vector<int> res; if(root == NULL) return res; stack<TreeNode*> st; st.push(root); while(!st.empty()) TreeNode* node = st.top(); st.pop(); res.push_back(node->val); if(node->right) st.push(node->right); if(node->left) st.push(node->left); return res; ;
二. Divide and Quaqer
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) vector<int> res; if(root == NULL) return res; vector<int> left = inorderTraversal(root->left); vector<int> right = inorderTraversal(root->right); for(int i : left) res.push_back(i); res.push_back(root->val); for(int i: right) res.push_back(i); return res; ;
三. 非递归,用栈来实现。
栈或者当前结点不为空时:
1)把当前结点压入栈中,然后继续压入它的左结点,直到左结点为空;
2)将栈顶元素的值保存在res中,并弹出;
3)转到右结点。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) vector<int> res; stack<TreeNode* > st; TreeNode* cur = root; while(cur || !st.empty()) while(cur) st.push(cur); cur = cur->left; cur = st.top(); st.pop(); res.push_back(cur->val); cur = cur->right; return res; ;
后序遍历:
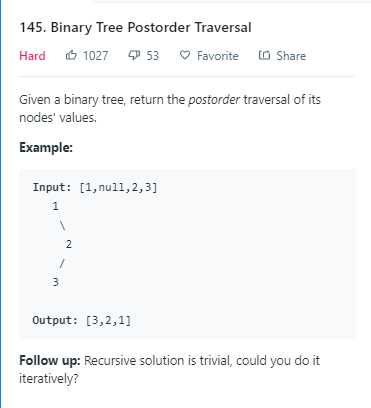
一.
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) vector<int> res; traverse(root, res); return res; void traverse(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res) if(root == NULL) return; traverse(root->left, res); traverse(root->right, res); res.push_back(root->val); ;
二.
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) vector<int> res; if(root == NULL) return res; vector<int> left = postorderTraversal(root->left); vector<int> right = postorderTraversal(root->right); for(int i: left) res.push_back(i); for(int i: right) res.push_back(i); res.push_back(root->val); return res; ;
三.
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) vector<int> res; stack<TreeNode* > st; if(root == NULL) return res; st.push(root); while(!st.empty()) TreeNode* tmp = st.top(); st.pop(); res.insert(res.begin(), tmp->val); //在前端插入 if(tmp->left) st.push(tmp->left); if(tmp->right) st.push(tmp->right); return res; ;

一.
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution private: int dep_max; //全局变量 public: int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) dep_max = 0; helper(root, 1); //1为当前根结点 return dep_max; void helper(TreeNode* root, int depth) if(root==NULL) return; dep_max = max(dep_max, depth); helper(root->left, depth+1); helper(root->right, depth+1); ;
二.
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) if(root==NULL) return 0; //左右子树的深度 int left = maxDepth(root->left); int right = maxDepth(root->right); return max(left, right)+1; ;
平衡二叉树:左右子树高度相差不超过1

/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) if(root==NULL) return true; if(abs(getDepth(root->left) - getDepth(root->right)) > 1) return false; return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right); int getDepth(TreeNode* root) if(!root) return 0; return max(getDepth(root->left), getDepth(root->right)) + 1; ;
上面的方法使得每个结点都会被上面的点计算深度时访问一次,优化一下:若发现某个结点的子树不平衡,则不计算它的深度,直接返回-1
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) if(depth(root) == -1) return false; return true; int depth(TreeNode* root) if(!root) return 0; int left = depth(root->left); if(left==-1) return -1; int right = depth(root->right); if(right == -1) return -1; int dif = abs(left - right); if(dif>1) return -1; else return max(left, right)+1; ;
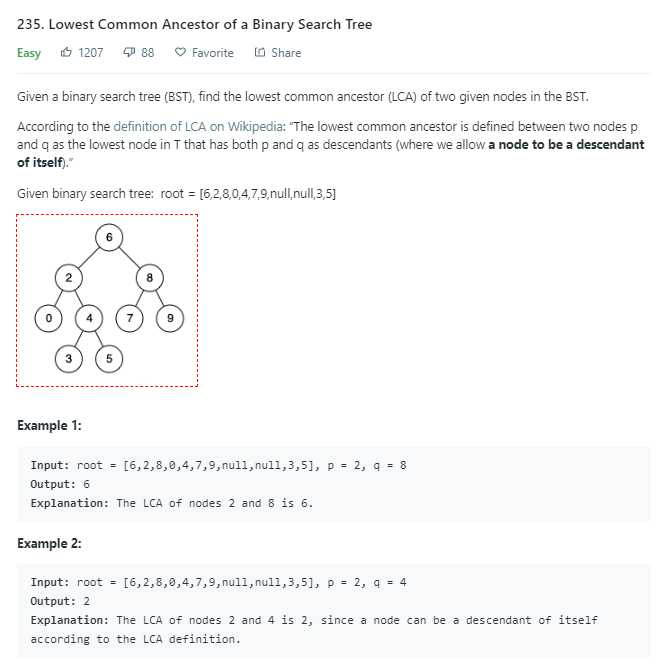
二叉搜索树的性质是:左子树的值 < 根节点 < 右子树的值
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) if(p->val > q->val) swap(p,q); // ensure p < q while(root) if(root->val < p->val) root = root->right; else if(root->val > q->val) root = root->left; else return root; return NULL; ;
已知A和B的父亲结点:



思路:把A和A的父结点保存在set中,若在B及B的父结点中找到一个和set中相同的结点,就返回这个公共祖先。
/** * Definition of ParentTreeNode: * class ParentTreeNode * public: * int val; * ParentTreeNode *parent, *left, *right; * */ class Solution public: /* * @param root: The root of the tree * @param A: node in the tree * @param B: node in the tree * @return: The lowest common ancestor of A and B */ ParentTreeNode * lowestCommonAncestorII(ParentTreeNode * root, ParentTreeNode * A, ParentTreeNode * B) // write your code here if(root == NULL) return NULL; unordered_set<ParentTreeNode*> s; //保存A向上的路径 while(A!=NULL) s.insert(A); A = A->parent; while(B) if(s.find(B) == s.end()) //s中找不到相同的结点 B = B->parent; else return B; ;
未知p,q的父亲结点:
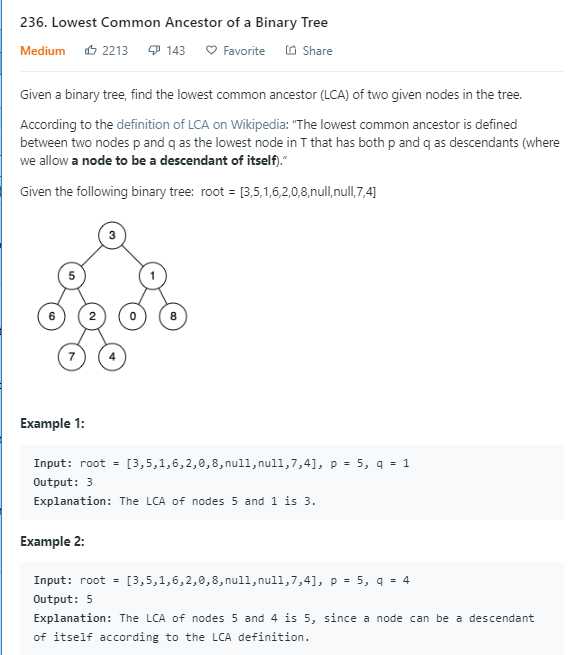
分治法:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ //若找到了LCA,就返回LCA,即 p和q出现在一左一右,返回它的根结点 //若只找到n1, 就返回n1 //若只找到了n2, 就返回n2 //若都不存在,返回NULL class Solution public: TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) if(root == NULL) return NULL; if(root == p || root == q) return root; //divide TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q); TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q); //Conquer if(left != NULL && right != NULL) return root; if(left != NULL) return left; if(right != NULL) return right; return NULL; ;
/** * Definition of TreeNode: * class TreeNode * public: * int val; * TreeNode *left, *right; * TreeNode(int val) * this->val = val; * this->left = this->right = NULL; * * */ //一颗二叉树,求从根结点到叶子结点的路径的最大值;求从根结点到任一结点的路径的最大值 class Solution public: /** * @param root: The root of binary tree. * @return: An integer */ int maxPathSum(TreeNode * root) // write your code here if (root == NULL) return 0; int left = maxPathSum(root->left); int right = maxPathSum(root->right); //root -> leaf //return max(left, right) + root->val; //root-> anynode return max(0, max(left, right)) + root->val; ;
从任一结点到任一结点路径的最大值:
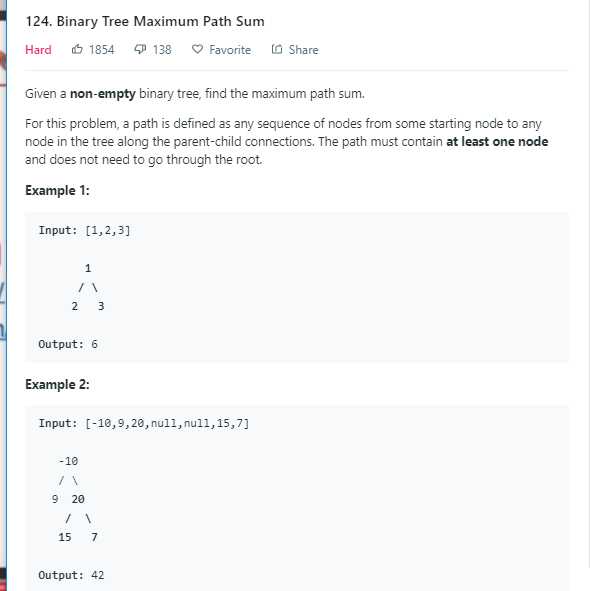
参考链接:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/find-maximum-path-sum-in-a-binary-tree/
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ //any to any node: 最长路径的位置:完全在左边;完全在右边;跨过根结点 //O(n) class Solution public: int findMax(TreeNode* root, int &res) if(root == NULL) return 0; int l = findMax(root->left, res); int r = findMax(root->right, res); int max_single = max(max(l, r)+root->val, root->val); int max_round = max(max_single, l+r+root->val); res = max(res, max_round); //store the maximum result return max_single; int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) int res = INT_MIN; findMax(root, res); return res; ;
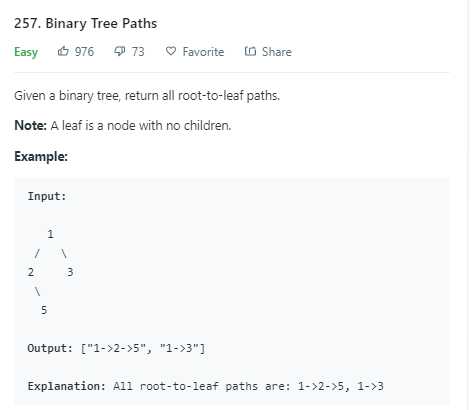
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) * ; */ class Solution public: vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) vector<string> res; if(root == NULL) return res; //返回空vector res if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL) res.push_back(to_string(root->val)); //divide vector<string> left = binaryTreePaths(root->left); vector<string> right = binaryTreePaths(root->right); //conquer for(string s : left) res.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + s); for(string s : right) res.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + s); return res; ;
以上是关于二叉树 + 递归 + 分治法总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章