输入输出流的应用
Posted zhai1997
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了输入输出流的应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、文件复制
用FileInputStream和FileOutPutStream实现文件的复制,此方法不能复制文件夹。
package pers.zhh.copy; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class CopyDemo public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("M:\\\\数据库.zip"); FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("M:\\\\数据库1.zip"); int num = 0; long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); while ((num = fi.read()) != -1) fo.write(num); fo.close(); fi.close(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("执行此程序用了" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒。");
(2)缓冲数组:
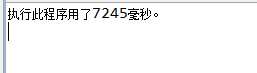
package pers.zzz.copy; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class CopyDemo1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("M:\\\\网页设计.zip"); FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("M:\\\\网页设计3.zip"); byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); while ((len = fi.read(buf)) != -1) fo.write(buf, 0, len); // 将数组中的指定长度的数据写入到输出流中。 fo.close(); fi.close(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("执行此程序用了" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒。");

在第一个方法中,一次只能读取一个数据字节,复制只有几M的数据花了7s时间,效率极低。而第二种采用缓冲数组的方式,复制接近1G的文件只花费了4s的时间,效率大大提升。
2、IO流的异常处理
package pers.zzz.copy; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class CopyDemo1 public static void main(String[] args) FileOutputStream fo = null; FileInputStream fi = null; long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try fi = new FileInputStream("M:\\\\网页设1计.zip"); fo = new FileOutputStream("M:\\\\网页设计11.zip"); byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = fi.read(buf)) != -1) fo.write(buf, 0, len); // 将数组中的指定长度的数据写入到输出流中。 catch (IOException e) System.out.println(e.toString()); finally if (fo != null) try fo.close(); catch (IOException e) System.out.println(e.toString()); throw new RuntimeException(); if (fi != null) try fi.close(); catch (IOException e) System.out.println(e.toString()); throw new RuntimeException(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("执行此程序用了" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒。");
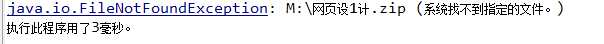
以上是关于输入输出流的应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章