排序算法 - 基数排序
Posted windsun
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了排序算法 - 基数排序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基本思想
基数排序是借助“分配”和“收集”两种操作对单逻辑关键字进行排序的一种内部排序方法。
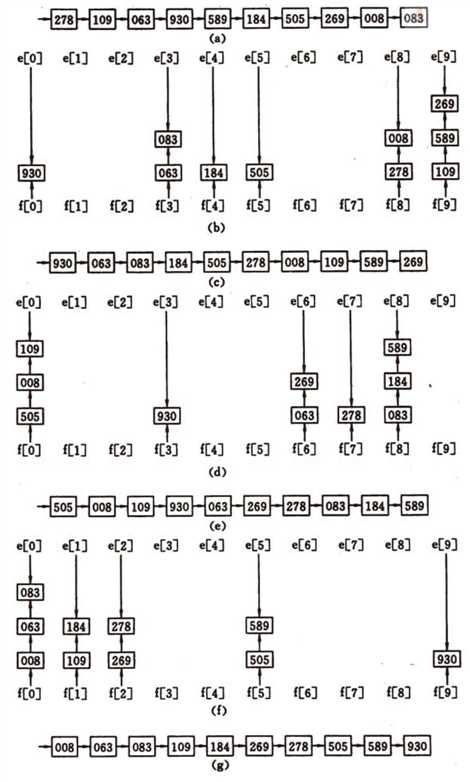
数组下标从0-9,每个数组元素是一个链表
比如对一些三位数以内的树排序,先将个位的数值插入对应的下标的链表中,然后再放回原数组,放回的顺序和插入的顺序一致,将链表清空,再将十位的数字插入对应的下标的链表中,依次操作,最终数组中的数据便以完成排序。
算法代码
1 //基数排序 2 int GetKey(int value, int k) //获取一个数的第k位数字 3 4 int key; 5 while (k > 0) 6 7 key = value % 10; 8 value /= 10; 9 k--; 10 11 return key; 12 13 14 void Distribube(int *arr, int n, int k, list<int> *lists) //分配 15 16 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) 17 18 int index = GetKey(arr[i], k); 19 lists[index].push_back(arr[i]); 20 21 22 23 void Collect(int *arr, list<int> *lists) //收集 24 25 int index = 0; 26 list<int>::iterator it; 27 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) 28 29 it = lists[i].begin(); 30 while (it != lists[i].end()) 31 32 arr[index++] = *it; 33 ++it; 34 35 lists[i].clear(); //收集完成要清空链表 36 37 38 39 void RadixSort(int *arr, int n) 40 41 int k = 3; //对1000以内的数进行排序 42 list<int> lists[10]; //从0-9共10个链表 43 for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i) 44 45 Distribube(arr, n, i, lists); //三位数分发三次,每次都会插入对应的链表中 46 Collect(arr, lists); //每一次将链表中的数据都会被重新放在数组中 47 48
算法分析
基数排序的时间复杂度为O(d(n+r))
其中:分配为O(n)
收集为O(r)(r为“基数”)
d为“分配-收集”的趟数
基数排序的空间复杂度为O(r)
属于稳定的排序算法
以上是关于排序算法 - 基数排序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章