2019年8月14日星期三(系统编程)
Posted zjlbk
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2019年8月14日星期三(系统编程)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
2019年8月14日星期三
一.线程属性 -> 分离属性
1. 什么是分离属性?
分离: 说明主线程不需要接合子线程 -> 不需要pthread_join子线程 -> 当主线程退出时,子线程还是会退出。
非分离: 说明主线程需要接合子线程 -> 需要pthread_join子线程
默认pthread_create()创建出来的线程都是非分离属性。
2. 如何创建出分离属性的线程呢?
思路: 添加分离属性到一个属性变量中,然后使用该属性变量去创建一个新的线程,那么这个线程就是一个分离的线程。
1)定义一个属性变量 (数据类型: pthread_attr_t)
pthread_attr_t attr;
2)初始化属性变量。 -> pthread_attr_init() -> man 3 pthread_attr_init
功能: initialize thread attributes object
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_attr_init(pthread_attr_t *attr);
attr:需要初始化的属性变量
返回值:
成功:0
失败:非0错误码
3)设置分离属性到属性变量中 -> pthread_attr_setdetachstate() -> man 3 pthread_attr_setdetachstate
功能:set detach state attribute in thread attributes object
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_attr_setdetachstate(pthread_attr_t *attr, int detachstate);
attr:已初始化的属性变量的地址
detachstate:PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED -> 分离属性
PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE -> 非分离属性
返回值:
成功:0
失败:非0错误码
4)利用线程属性变量去创建一个分离属性的线程。
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,...);
5)销毁属性变量 -> pthread_attr_destroy() -> man 3 pthread_attr_destroy
功能:destroy thread attributes object
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_attr_destroy(pthread_attr_t *attr);
attr: 已初始化的属性变量
返回值:
成功:0
失败:非0错误码
练习1:验证一个分离属性线程,在主线程比自己提前退出时,该分离的线程会不会继续运行? -> 不会继续运行。
#include "head.h"
void *routine(void *arg)
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
printf("child %d\\n",i);
sleep(1);
int main()
//1. 设置分离属性
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
//2. 创建线程
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid,&attr,routine,NULL);
//3. 主线程
int i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
printf("parent %d\\n",i);
sleep(1);
return 0;
3. 设置线程本身的属性为分离属性。 -> pthread_detach() -> man 3 pthread_detach
功能: detach a thread
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
thread:需要分离的线程的ID号
返回值:
成功:0
失败:非0错误码
4. 获取线程自己的TID号。 -> pthread_self() -> man 3 pthread_self
功能:obtain ID of the calling thread
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_t pthread_self(void);
参数:无
返回值: 线程的TID号
例子:
void *routine(void *arg)
pthread_detach(pthread_self()); -> 线程就会变成分离属性。
int main()
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,routine,NULL);
pause();
二. 线程的取消?
1. 一般而言,都是主线程去控制子线程的状态。例如:主线程发送取消请求给子线程。
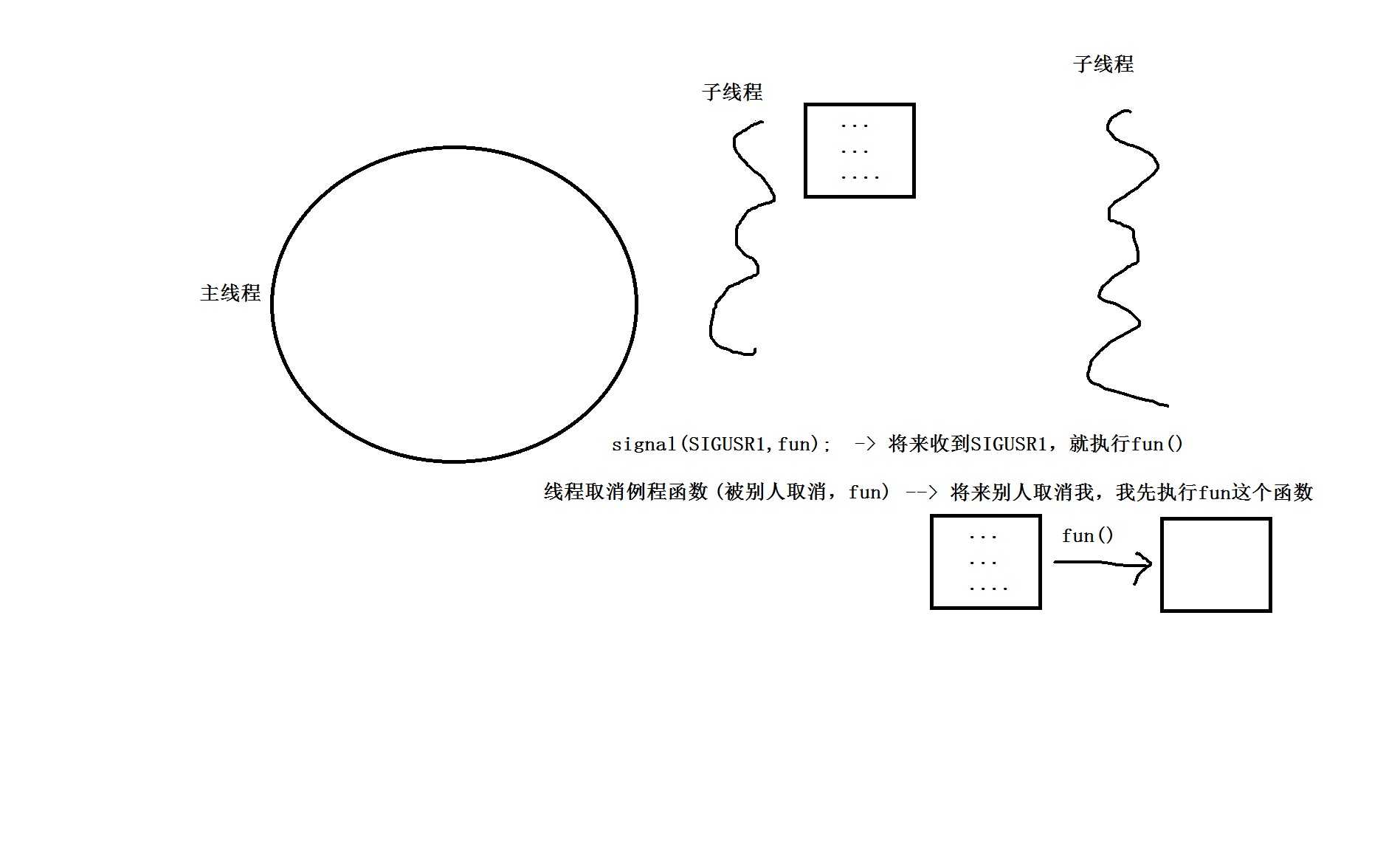
函数: pthread_cancel() -> man 3 pthread_cancel
功能: send a cancellation request to a thread -> 发送取消请求给线程。
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
thread:需要取消的线程的TID号。
返回值:
成功:0
失败:错误码
注意:
收到取消请求就等价于是提前调用pthread_exit(),如果因为取消而退出,则不能把退出状态返回给主线程,但是线程主动退出pthread_exit()可以返回。
#include "head.h"
void *routine(void *arg)
int i;
for(i=10;i>0;i--)
printf("%d\\n",i);
sleep(1);
pthread_exit(NULL);
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,routine,NULL); -> 普通线程默认是可以响应的!
sleep(5);
pthread_cancel(tid);
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
return 0;
2. 设置线程的取消响应的状态。 -> pthread_setcancelstate() -> man 3 pthread_setcancelstate
功能: set cancelability state
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_setcancelstate(int state, int *oldstate);
state:
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE -> 可以响应
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE -> 不可以响应
oldstate:原来的取消状态的值,不关心原来的状态,则填NULL。
结论:
If a cancellation request is received, it is blocked until cancelability is enabled.
假设当前是不能响应取消请求的状态,但是这时收到一个取消请求,那么这个请求会一直阻塞等待,直到线程能响应取消请求为止才会被执行。
练习2:验证结论。
#include "head.h"
void *routine(void *arg)
int i;
pthread_setcancelstate(PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE,NULL);
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
sleep(1);
printf("disable %d\\n",i);
pthread_setcancelstate(PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE,NULL);
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
sleep(1);
printf("enable %d\\n",i);
pthread_exit(NULL);
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,routine,NULL);
sleep(2);
pthread_cancel(tid);
printf("I send cancel to thread!\\n");
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
return 0;
3. 设置线程取消响应的类型 -> pthread_setcanceltype() -> man 3 pthread_setcanceltype
功能:set cancelability type
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_setcanceltype(int type, int *oldtype);
type:
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DEFERRED -> 延迟取消
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS -> 立即取消 -> 默认创建的线程都是立即取消。
oldtype:
原来的取消类型的值,不关心原来的状态,则填NULL。
取消点函数有哪些? -> man 7 pthreads
Cancellation Points
fgetc()
fgets()
fopen()
fprintf()
fputc()
例子:
#include "head.h"
void *routine(void *arg)
pthread_setcanceltype(PTHREAD_CANCEL_DEFERRED,NULL);
//for循环不属于取消点函数
long i,j;
for(i=0;i<100000;i++)
for(j=0;j<100000;j++)
while(1)
fputc(‘a‘,stderr); //执行完这次取消点函数之后,再响应取消。
printf("helloworld!\\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,routine,NULL);
pthread_cancel(tid);
printf("I send cancel to thread!\\n");
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
return 0;
三. 线程的取消例程函数。
1. 什么是线程取消例程函数?
当线程收到取消请求时,先不要马上响应取消请求,而是要执行一个线程的例程函数,执行完这个函数之后再响应取消。
一般而言,线程例程函数里面写一些释放公共资源的内容,例如:互斥锁,条件变量..
2. 为什么要使用线程取消例程函数?
为了防止线程带着一些系统公共资源一起被取消掉,如果带着资源而退出,则其他的线程就无法再次使用该资源。
3. 如何实现?
1)只需要在线程内部调用压栈函数。 -> pthread_cleanup_push() -> man 3 pthread_cleanup_push
功能: push thread cancellation clean-up handlers
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
void pthread_cleanup_push(void (*routine)(void *),void *arg);
routine:线程取消例程函数 -> 以后收到取消请求,就会先执行该函数!
arg:传递给线程取消例程函数的参数
返回值:无
回顾学习过的例程函数:
信号处理函数: void fun(int sig)
线程例程函数: void *fun(void *arg)
线程取消例程函数: void fun(void *arg)
2)将取消的例程函数弹栈
功能: pop thread cancellation clean-up handlers
使用格式:
#include <pthread.h>
void pthread_cleanup_pop(int execute);
execute: 0 -> 在删除时,不执行该函数,直接删除。
非0 -> 在删除时,先执行一次该函数,再删除。
返回值:无
例子:
pthread_cleanup_push(fun);
...
.. <- 取消请求 执行fun
. <- pthread_exit() 执行fun
... <- return 不执行fun
pthread_cleanup_pop(非0); -> 执行fun
例题:子线程收到主线程的取消时,不要马上取消,而是先打印"I recv cancel!",再取消。
#include "head.h"
void myfun(void *arg)
printf("I recv cancel!\\n");
void *routine(void *arg)
pthread_cleanup_push(myfun,NULL); //只要将来我收到取消的请求,就会先执行myfun。
/* 线程持续10秒,在此期间,必定会收到取消请求。 */
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++) //在10秒收到取消请求,会执行fun()
printf("thread i = %d\\n",i);
sleep(1);
//pthread_exit(NULL); // -> 还没有来得及删除例程就因为pthread_exit而退出,则执行例程函数。
//return; -> 还没有来得及删除例程就因为return而退出,则不会执行例程函数
//sleep(3);
printf("helloworld!\\n");
pthread_cleanup_pop(1); //非0 -> 会执行
//0 -> 不会执行
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,routine,NULL);
//sleep(3);
//pthread_cancel(tid);
//printf("I send cancel to thread!\\n");
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
return 0;
四. 线程同步互斥的方式。
1. 什么是同步互斥?为什么要处理同步互斥?
同步互斥就是使得线程处理任务时有先后顺序,为了解决线程抢占资源问题。
2. 处理同步互斥方式有哪些?
信号量 -> 进程
有名信号量 -> 进程
无名信号量 -> 线程
3. 有名信号量
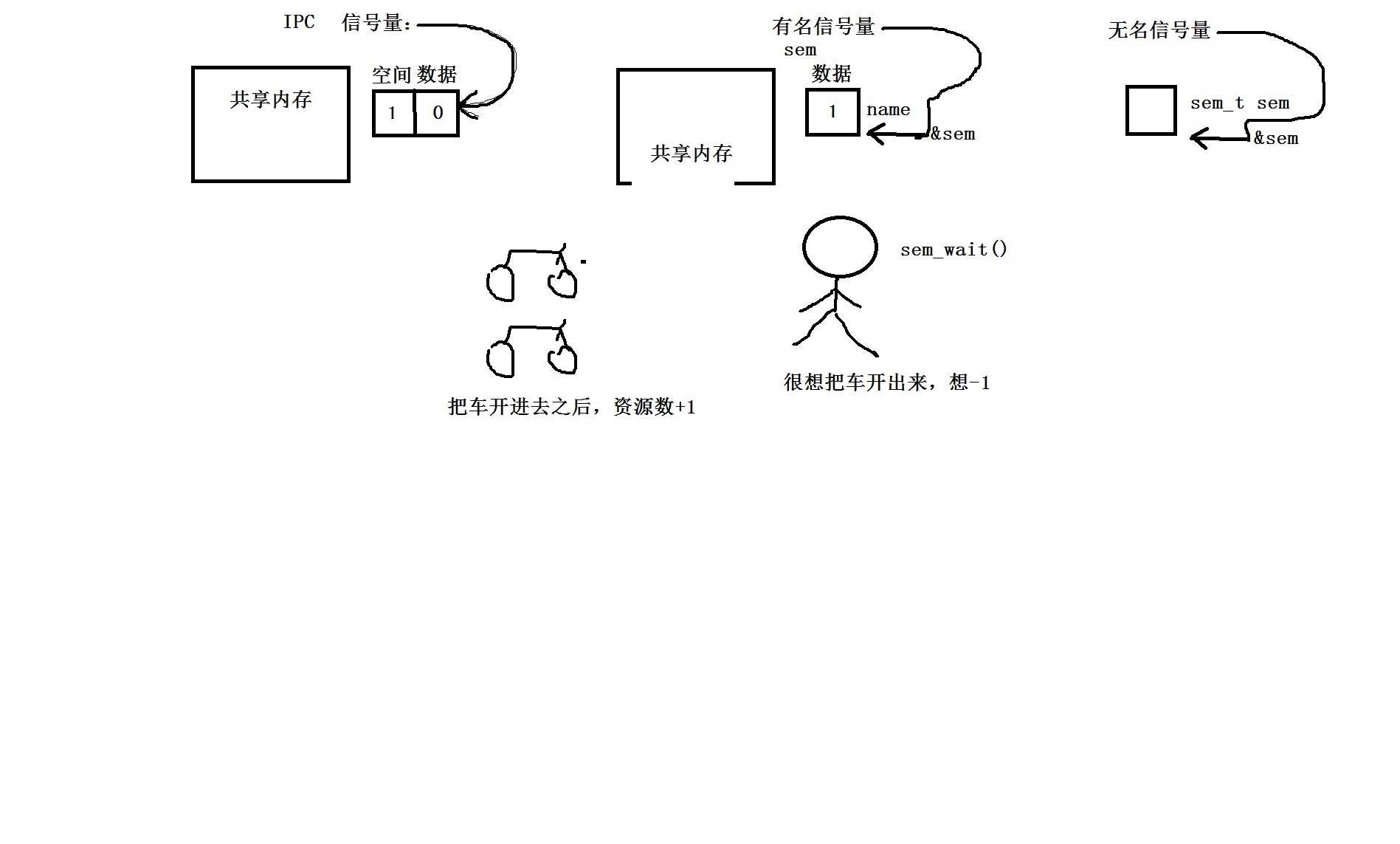
1)创建并打开一个有名信号量? -> sem_open() -> man 3 sem_open
功能: initialize and open a named semaphore
使用格式:
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
sem_t *sem_open(const char *name, int oflag, mode_t mode, unsigned int value);
name:有名信号量的名字,要求必须以"/"开头,例如: /sem_test
oflag:O_CREAT -> 不存在则创建
O_EXCL -> 存在则报错
mode:有名信号量的八进制权限,例如: 0777
value:有名信号量的起始值
返回值:
成功:有名信号量的地址
失败:SEM_FAILED -1
2)有名信号量P/V操作
P操作: sem_wait() 资源数-1操作 -> man 3 sem_wait
使用格式:
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
sem:有名信号量的地址
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
V操作: sem_post() 资源数+1操作 -> man 3 sem_post
使用格式:
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
sem:有名信号量的地址
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
3)关闭有名信号量。 -> sem_close() -> man 3 sem_close
功能:close a named semaphore
使用格式:
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_close(sem_t *sem);
sem:有名信号量的地址
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
4)删除有名信号量。 -> sem_unlink() -> man 3 sem_unlink
功能:remove a named semaphore
使用格式:
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_unlink(const char *name);
name:有名信号量的名字
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
练习3:实现Jack进程与Rose进程使用共享内存来通信,要求使用有名信号量来处理同步互斥!
Jack进程:
#include "head.h"
int main()
//1. 申请key值
key_t key = ftok(".",10);
//2. 根据key值申请共享内存ID号
int shmid = shmget(key,2048,IPC_CREAT|0666);
//3. 根据ID号申请共享内存的起始地址
char *p = (char *)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);
//4. 往共享内存中写入数据
bzero(p,2048);
//5. 创建并打开一个有名信号量
sem_t *sem = NULL;
sem = sem_open("/sem_test",O_CREAT,0777,0); //说明当前有名信号量的资源数为0
while(1)
//想开车进去
fgets(p,2048,stdin);
//资源数+1
sem_post(sem);
if(strncmp(p,"quit",4) == 0)
break;
return 0;
Rose进程:
#include "head.h"
int main()
//1. 申请key值
key_t key = ftok(".",10);
//2. 根据key值申请共享内存ID号
int shmid = shmget(key,2048,IPC_CREAT|0666);
//3. 根据ID号申请共享内存的起始地址
char *p = (char *)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);
//4. 创建并打开一个有名信号量
sem_t *sem = NULL;
sem = sem_open("/sem_test",O_CREAT,0777,0); //说明当前有名信号量的资源数为0
//5. 不断读取共享内存的数据
while(1)
//当前资源数能-1不?
//能 -> 返回 不能 -> 阻塞
sem_wait(sem);
//想开车走
printf("from shm:%s",p);
if(strncmp(p,"quit",4) == 0)
break;
sem_close(sem);
sem_unlink("/sem_test");
shmdt(p);
shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,NULL);
return 0;
4. 无名信号量 -> 既可以作用于进程,也可以作用于线程!
1)由于无名信号量没有名字的,所以说不能打开,只能初始化。 -> sem_init() -> man 3 sem_init
功能: initialize an unnamed semaphore -> 初始化未命名的信号量
使用格式:
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
sem: 无名信号量的地址
pshared: 0 -> 作用于线程之间 -> 一般都是这个!
非0 -> 作用于进程之间
value:无名信号量的起始值
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
2)无名信号量P/V操作
P操作: sem_wait() 资源数-1操作 -> man 3 sem_wait
使用格式:
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
sem:无名信号量的地址
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
V操作: sem_post() 资源数+1操作 -> man 3 sem_post
使用格式:
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
sem:无名信号量的地址
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
3)销毁无名信号量 -> sem_destroy() -> man 3 sem_destroy
功能:destroy an unnamed semaphore
使用格式:
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
sem:无名信号量的地址
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
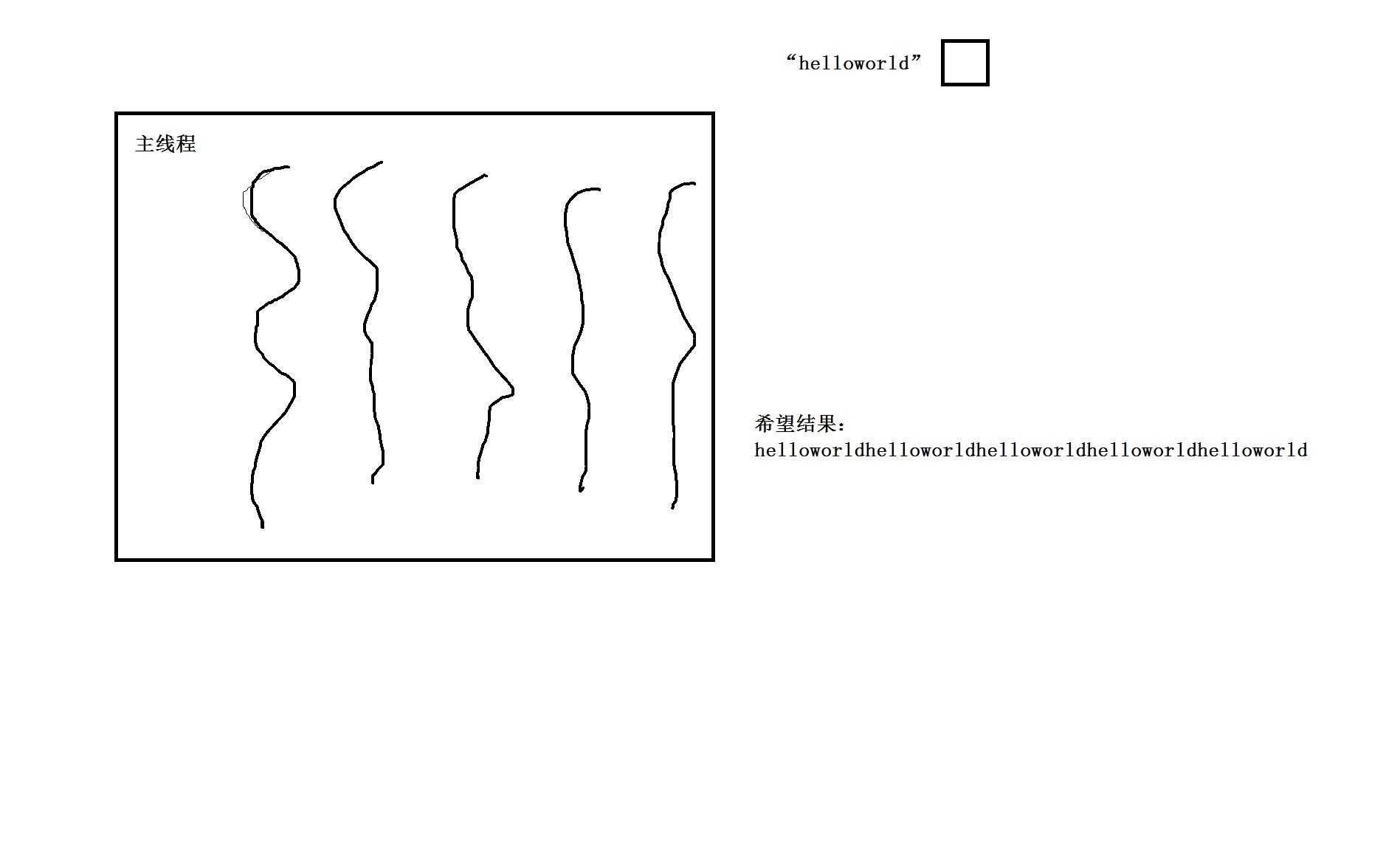
练习4:创建5个线程,每一个线程任务都是一样。
任务:将“helloworld”字符串每隔1S就打印一个字符 -> 完成任务:10秒
要求5个子线程依次打印helloworld,不要同时打印。
正确: helloworldhelloworldhelloworldhelloworldhelloworld
错误: hhhhheeeeellllllllllooooowwwwwooooorrrrrlllllddddd
作业1: 练习4。
作业2: 昨晚的第三题。
作业3: 整理所有学习过的函数。
以上是关于2019年8月14日星期三(系统编程)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章