ProxySQL实现读写分离
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ProxySQL实现读写分离相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
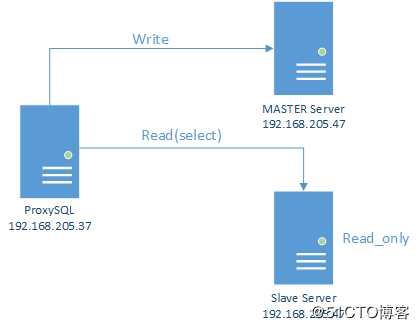
环境:
192.168.205.37: as ProxySQL server
192.168.205.47: as Master server
192.168.205.57: as Slave server版本:
OS: centos 7 1810 with mini install
mariadb-server 5.5.60
proxysql-1.4.15-1-centos7.x86_64.rpm目地:
proxysql可以实现读写分离,它主要读取数据库的read_only变量来判断那些是主从服务器,当创建读写组时它会跟据状态自动将节点划分到相应的组中,如写组10和读组20,并跟据建立好的规则和对应的组名,从而实现读写的分离操作,proxysql是基于一个轻量级的数据库,所有的设置都要在数据库中进行更改,步聚有点繁琐。
步骤:
- 使用如下的脚本安将两个数据库
[root@master data]#cat maridb_yum.sh #!/bin/bash ID=`ip a show dev eth0 | sed -r ‘3!d;s@(.*inet)(.*)(/.*)@\2@‘ | cut -d. -f4` rpm -q mariadb-server ||yum install -y mariadb-server [ -d /data/mysql ] || mkdir -p /data/mysql [ -d /data/logs ] || mkdir -p /data/logs chown mysql:mysql /data/mysql,logs sed -i ‘s@datadir=/var/lib/mysql@datadir=/data/mysql@‘ /etc/my.cnf grep "log-bin" /etc/my.cnf || sed -i ‘/\[mysqld\]/a log-bin=/data/logs/bin‘ /etc/my.cnf grep "innodb_file_per_table" /etc/my.cnf || sed -i ‘/\[mysqld\]/a innodb_file_per_table = on‘ /etc/my.cnf grep "skip_name_resolve" /etc/my.cnf || sed -i ‘/\[mysqld\]/a skip_name_resolve = on‘ /etc/my.cnf grep "server-id" /etc/my.cnf || sed -i "/\[mysqld\]/a server-id=$ID" /etc/my.cnf service mariadb restart - 修改从节点57的数据库为read-only
[root@slave data]#vi /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] read-only - 记录主节点的复制位置并创建复制账号
MariaDB [(none)]> show master logs; +------------+-----------+ | Log_name | File_size | +------------+-----------+ | bin.000001 | 245 | +------------+-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) [root@master data]#mysql -e "grant replication slave on *.* to repluser@‘192.168.205.%‘ identified by ‘centos‘" -
修改slave的change master to,并启动i/o线程
MariaDB [(none)]> CHANGE MASTER TO -> MASTER_HOST=‘192.168.205.47‘, -> MASTER_USER=‘repluser‘, -> MASTER_PASSWORD=‘centos‘, -> MASTER_PORT=3306, -> MASTER_LOG_FILE=‘bin.000001‘, -> MASTER_LOG_POS=245; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> start slave; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show slave status\G *************************** 1. row *************************** Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event Master_Host: 192.168.205.47 Master_User: repluser Master_Port: 3306 Connect_Retry: 60 Master_Log_File: bin.000001 Read_Master_Log_Pos: 401 Relay_Log_File: mariadb-relay-bin.000002 Relay_Log_Pos: 679 Relay_Master_Log_File: bin.000001 Slave_IO_Running: Yes Slave_SQL_Running: Yes - 导入库测试,并在从节点上查看数据库成功
[root@master ~]#mysql < hellodb_innodb.sql MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | hellodb | | mysql | | performance_schema | | test | +--------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)安装ProxySQL
- 创建yum源,通过yum安装proxySQL
cat <<EOF | tee /etc/yum.repos.d/proxysql.repo [proxysql_repo] name= ProxySQL YUM repository #baseurl=https://repo.proxysql.com/ProxySQL/proxysql-2.0.x/centos/\$releasever baseurl=https://repo.proxysql.com/ProxySQL/proxysql-1.4.x/centos/\$releasever gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://repo.proxysql.com/ProxySQL/repo_pub_key EOF [root@Proxy ~]#yum install proxysql - 安装一下mariadb client用来连接ProxySQL使用
[root@Proxy ~]#yum install mariadb - 查看一下装了那些文件呢?好像不多呀
[root@Proxy ~]#rpm -ql proxysql /etc/init.d/proxysql /etc/proxysql.cnf /usr/bin/proxysql /usr/share/proxysql/tools/proxysql_galera_checker.sh /usr/share/proxysql/tools/proxysql_galera_writer.pl - 启用一下服务,他会监听6032用来管理的,6033是用来用户连接的端口
[root@Proxy ~]#service proxysql start Starting ProxySQL: 2019-08-12 17:00:02 [INFO] Using config file /etc/proxysql.cnf DONE! [root@Proxy ~]#ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 *:6032 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:* [root@Proxy ~]# - 改一下我们熟悉的连接端口吧
[root@Proxy ~]#vi /etc/proxysql.cnf interfaces="0.0.0.0:3306" - 发现没有改过来?我们还用SQL命令来改吧
[root@Proxy ~]#service proxysql restart Shutting down ProxySQL: DONE! Starting ProxySQL: 2019-08-12 17:03:54 [INFO] Using config file /etc/proxysql.cnf DONE! [root@Proxy ~]#ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 *:6032 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:6033 *:* - 我们使用默认的帐号来连接proxysqL,可以看到它里面一些系统库文件
[root@Proxy ~]#mysql -uadmin -padmin -P6032 -h127.0.0.1 MySQL [(none)]> show databases; +-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+ | seq | name | file | +-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+ | 0 | main | | | 2 | disk | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql.db | | 3 | stats | | | 4 | monitor | | | 5 | stats_history | /var/lib/proxysql/proxysql_stats.db | +-----+---------------+-------------------------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) - show tables; 默认的是show main库的表与show tables from main;一样
MySQL [(none)]> show tables; +--------------------------------------------+ | tables | +--------------------------------------------+ | global_variables | | mysql_collations | | mysql_group_replication_hostgroups | | mysql_query_rules | | mysql_query_rules_fast_routing | | mysql_replication_hostgroups | | mysql_servers | | mysql_users | | proxysql_servers | | runtime_checksums_values | | runtime_global_variables | | runtime_mysql_group_replication_hostgroups | | runtime_mysql_query_rules | | runtime_mysql_query_rules_fast_routing | | runtime_mysql_replication_hostgroups | | runtime_mysql_servers | | runtime_mysql_users | | runtime_proxysql_servers | | runtime_scheduler | | scheduler | +--------------------------------------------+ 20 rows in set (0.00 sec) - 查看一
MySQL [(none)]> select * from sqlite_master where name=‘mysql_servers‘\G *************************** 1. row *************************** type: table name: mysql_servers tbl_name: mysql_servers rootpage: 2 sql: CREATE TABLE mysql_servers (hostgroup_id INT CHECK (hostgroup_id>=0) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 , hostname VARCHAR NOT NULL , port INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 3306 , status VARCHAR CHECK (UPPER(status) IN (‘ONLINE‘,‘SHUNNED‘,‘OFFLINE_SOFT‘, ‘OFFLINE_HARD‘)) NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘ONLINE‘ , weight INT CHECK (weight >= 0) NOT NULL DEFAULT 1 , compression INT CHECK (compression >=0 AND compression <= 102400) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 , max_connections INT CHECK (max_connections >=0) NOT NULL DEFAULT 1000 , max_replication_lag INT CHECK (max_replication_lag >= 0 AND max_replication_lag <= 126144000) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 , use_ssl INT CHECK (use_ssl IN(0,1)) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 , max_latency_ms INT UNSIGNED CHECK (max_latency_ms>=0) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 , comment VARCHAR NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘‘ , PRIMARY KEY (hostgroup_id, hostname, port) ) 1 row in set (0.00 sec) - 修改主一下记录
MySQL [(none)]> insert into mysql_servers(hostgroup_id,hostname,port) values(10,‘182.168.205.47‘,3306); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MySQL [(none)]> insert into mysql_servers(hostgroup_id,hostname,port) values(10,‘182.168.205.57‘,3306); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec - 可以看一两个节点已经加入
MySQL [(none)]> select * from mysql_servers; +--------------+----------------+------+--------+--------+-------------+-----------------+---------------------+---------+----------------+---------+ | hostgroup_id | hostname | port | status | weight | compression | max_connections | max_replication_lag | use_ssl | max_latency_ms | comment | +--------------+----------------+------+--------+--------+-------------+-----------------+---------------------+---------+----------------+---------+ | 10 | 182.168.205.47 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 | 0 | 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | | 10 | 182.168.205.57 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 | 0 | 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | +--------------+----------------+------+--------+--------+-------------+-----------------+---------------------+---------+----------------+---------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) - 加载配置,使其生效
MySQL [(none)]> load mysql servers to runtime; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) - 保存到磁盘里
MySQL [(none)]> save mysql servers to disk; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) - 由于proxysql是查看主和从的数据的read_only来判读谁是主谁是从的,所以建立一账号用来连接到主和从服务器上,我们要在主节点上建立这个帐号,它会复制到从节点上
MariaDB [(none)]> show variables like ‘read_only‘; +---------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+-------+ | read_only | OFF | +---------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show variables like ‘read_only‘; +---------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+-------+ | read_only | ON | +---------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> grant replication client on *.* to monitor@‘192.168.205.%‘ identified by ‘centos‘; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec - 授权proxy用这个创建的账号连接数据库,设置监控账号和口令
MySQL [(none)]> set mysql-monitor_username=‘monitor‘; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MySQL [(none)]> set mysql-monitor_password=‘centos‘; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) -
存盘并生效
MySQL [(none)]> load mysql variables to runtime; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MySQL [(none)]> save mysql variables to disk; Query OK, 97 rows affected (0.00 sec) -
查看一下相关的日志,以前出错的原因是因为默认没使用monitor密码是monitor进行连接(在proxysql.cnf中可以看到),所以会出错,当你添加完帐号就成功了,
[root@Proxy ~]#vi /etc/proxysql.cnf monitor_username="monitor" monitor_password="monitor" MySQL [(none)]> select * from mysql_server_connect_log; +----------------+------+------------------+-------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | hostname | port | time_start_us | connect_success_time_us | connect_error | +----------------+------+------------------+-------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | 192.168.205.47 | 3306 | 1565603995322153 | 0 | Access denied for user ‘monitor‘@‘192.168.205.37‘ (using password: YES) | | 192.168.205.47 | 3306 | 1565604055779260 | 0 | Access denied for user ‘monitor‘@‘192.168.205.37‘ (using password: YES) | | 192.168.205.57 | 3306 | 1565604159035893 | 3871 | NULL | | 192.168.205.47 | 3306 | 1565604159905593 | 3563 | NULL | +----------------+------+------------------+-------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 22 rows in set (0.00 sec) - 查看ping的结果
MySQL [(none)]> select * from mysql_server_ping_log; +----------------+------+------------------+----------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | hostname | port | time_start_us | ping_success_time_us | ping_error | +----------------+------+------------------+----------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | 192.168.205.57 | 3306 | 1565604094739272 | 0 | Access denied for user ‘monitor‘@‘192.168.205.37‘ (using password: YES) | | 192.168.205.47 | 3306 | 1565604094919486 | 0 | Access denied for user ‘monitor‘@‘192.168.205.37‘ (using password: YES) | | 192.168.205.57 | 3306 | 1565604099107658 | 745 | NULL | | 192.168.205.47 | 3306 | 1565604099295895 | 358 | NULL | +----------------+------+------------------+----------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 122 rows in set (0.00 sec) - 查看read_only的值为空,因为没有分组
MySQL [(none)]> select * from mysql_server_read_only_log; Empty set (0.00 sec) - 查看复制结果为空
MySQL [(none)]> select * from mysql_server_replication_lag_log; Empty set (0.00 sec) - 需要修改的是main库中的mysql_replication_hostgroups表,该表有3个字段:writer_hostgroup, reader_hostgroup,comment, 指定写组的id为10,读组的id为20
MySQL [(none)]> insert into mysql_replication_hostgroups values(10,20,"test"); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) -
保存生效
MySQL [(none)]> load mysql servers to runtime; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MySQL [(none)]> save mysql servers to disk; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) - proxySQL会跟据刚才连接帐号判断read_only并自动的把两个服务器加到这个表中了
MySQL [(none)]> select hostgroup_id,hostname,port,status,weight from mysql_servers; +--------------+----------------+------+--------+--------+ | hostgroup_id | hostname | port | status | weight | +--------------+----------------+------+--------+--------+ | 20 | 192.168.205.57 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 | | 10 | 192.168.205.47 | 3306 | ONLINE | 1 | +--------------+----------------+------+--------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MySQL [(none)]> select * from mysql_server_read_only_log; - 查看read_only的值已经有记录
+----------------+------+------------------+-----------------+-----------+-------+ | hostname | port | time_start_us | success_time_us | read_only | error | +----------------+------+------------------+-----------------+-----------+-------+ | 192.168.205.57 | 3306 | 1565605365323639 | 565 | 1 | NULL | | 192.168.205.47 | 3306 | 1565605365353823 | 1595 | 0 | NULL | | 192.168.205.57 | 3306 | 1565605366824223 | 1275 | 1 | NULL | | 192.168.205.47 | 3306 | 1565605366844952 | 1607 | 0 | NULL | +----------------+------+------------------+-----------------+-----------+-------+ 280 rows in set (0.02 sec) - 此时proxysql还是不知道那些sql语句算读,那些为写,我们要定义好,让它来区别并发送到不同的服务器上。在主节点创建一个可以访问的帐号
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on *.* to sqluser@‘192.168.205.%‘ identified by ‘centos‘; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) - 在proxysql上定义连接时使用这个帐号去写,也就是使用10组,也就是主服务器上写
MySQL [(none)]> insert into mysql_users(username,password,default_hostgroup) values(‘sqluser‘,‘centos‘,10); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) -
保存生效
MySQL [(none)]> load mysql users to runtime; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MySQL [(none)]> save mysql users to disk; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) - 现在我们使用刚才的帐号连接一下数据库(注意现在连接测试的是proxysql),他会默认只会发送到主服务器,因为没有定义从服务器。
[root@Proxy ~]#mysql -usqluser -pcentos -P6033 -h127.0.0.1 -e ‘select @@server_id‘ +-------------+ | @@server_id | +-------------+ | 47 | +-------------+ [root@Proxy ~]#mysql -usqluser -pcentos -P6033 -h127.0.0.1 -e ‘create database testdb‘ [root@Proxy ~]#mysql -usqluser -pcentos testdb -P6033 -h127.0.0.1 -e ‘create table t(id int)‘ - 在主服务器和从服务器上查看一下刚才创建的库和表,同步过去了
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | hellodb | | mysql | | performance_schema | | test | | testdb | +--------------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> select * from testdb.t; Empty set (0.00 sec) -
目前proxysql还是不知道什么是读,什么是写,所以所有的操作都会发送到10组中,也就是主服务器上,那么现在我们来建SQL语句规则
#select.* for updata为写向10组里发,而其它的select开头的向20组里发,也就是读,那么没定义的呢?默认会往10上发, MySQL [(none)]> insert into mysql_query_rules -> (rule_id,active,match_digest,destination_hostgroup,apply)VALUES -> (1,1,‘^SELECT.*FOR UPDATE$‘,10,1),(2,1,‘^SELECT‘,20,1); Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec) #查看一下你添加的规则 MySQL [(none)]> select rule_id,active,match_digest,destination_hostgroup,apply from mysql_query_rules; +---------+--------+----------------------+-----------------------+-------+ | rule_id | active | match_digest | destination_hostgroup | apply | +---------+--------+----------------------+-----------------------+-------+ | 1 | 1 | ^SELECT.*FOR UPDATE$ | 10 | 1 | | 2 | 1 | ^SELECT | 20 | 1 | +---------+--------+----------------------+-----------------------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) -
保存生效
MySQL [(none)]> load mysql query rules to runtime; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MySQL [(none)]> save mysql query rules to disk; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) - 接着再次测试我们上面运行的命令,select语句就会往20上的从服务器57上发了
[root@Proxy ~]#mysql -usqluser -pcentos -P6033 -h127.0.0.1 -e ‘select @@server_id‘ +-------------+ | @@server_id | +-------------+ | 57 | +-------------+ - 如果是以一个事务来执行呢,我们发现会发送到主节点上,因为begin开始的即不是select updata开头也是select开头,所以发送到了默认节点
[root@Proxy ~]#mysql -usqluser -pcentos -P6033 -h127.0.0.1 -e ‘begin;select @@server_id;commit‘ +-------------+ | @@server_id | +-------------+ | 47 | +-------------+ - 如果是从建表操作是发送到主节点上,然后主节点再复制到从节点
[root@Proxy ~]#mysql -usqluser -pcentos testdb -P6033 -h127.0.0.1 -e ‘create table t1(id int)‘ 在主节点上看这个表,发现已经建成 Database changed MariaDB [testdb]> show tables; +------------------+ | Tables_in_testdb | +------------------+ | t | | t1 | +------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) 在从节点上看也复制过去了 MariaDB [testdb]> show tables; +------------------+ | Tables_in_testdb | +------------------+ | t | | t1 | +------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) - 我们可以使用proxsql查看是否调度成功
MySQL [(none)]> select hostgroup hg,sum_time,count_star,digest_text from stats_mysql_query_digest order by sum_time desc; +----+----------+------------+----------------------------------+ | hg | sum_time | count_star | digest_text | +----+----------+------------+----------------------------------+ | 10 | 18692 | 1 | create table t(id int) | | 10 | 5704 | 1 | create table t1(id int) | | 10 | 2002 | 2 | select @@server_id | | 20 | 1546 | 1 | select @@server_id | | 10 | 819 | 1 | begin | | 10 | 717 | 1 | create database testdb | | 10 | 240 | 1 | commit | | 10 | 0 | 2 | select @@version_comment limit ? | | 10 | 0 | 4 | select @@version_comment limit ? | +----+----------+------------+----------------------------------+
以上是关于ProxySQL实现读写分离的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章