结构化程序与自定函数
Posted zuiaimiusi
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了结构化程序与自定函数相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
今天睡了14个小时,真的很舒服,好久没这么爽了,嘿嘿(*?|?∀?|?*~●
结构化程序与自定函数
if else
a=3;
if rem(a,2)==0
disp(‘a is even‘)
else
disp(‘a is odd‘)
end
switch
input_num=1;
switch input_num
case -1
disp(‘negative 1‘);
case 0
disp(‘zero‘);
otherwise
disp(‘other value‘);
end
while
n=1;
while prod(1:n)<1e100
n=n+1;
end
for
for variable=start:increment:end
commands
end
for n=1:2:10
a(n)=2^n;
end
disp(a);
clear all 清除所有的历史数据
close all 关闭所有的数据
clc 清屏
... 换行
ctrl+c 终止程序
edit(which(‘mean.m‘)) 获取内建的函数
>> edit(‘mean.m‘);
自定义函数
function x=freebody(x0,v0,t) x=x0+v0.*t+1/2*9.8*t.*t;
点乘和乘的区别
乘是矩阵的运算,点乘是矩阵中相同位置元素的乘法运算
在自定义函数中使用点乘可以同时算出多组数据
>> freebody([0,9],[2,7],[2,3]) ans = 23.6000 74.1000
建立多个输入和输出的函数
function [a,F]=freebody(v2,v1,t2,t1,m)
a=(v2-v1)./(t2-t1);
F=m.*a;
[a F]=freebody(20,10,5,4,1)
a =
10
F =
10
function handle
基础绘图
line types
solid line -
dashed line --
dash-dotted line -.
dotted line :
hold on x=0:pi/10:2*pi; y1=sin(x); y2=x; plot(x,y1,‘:or‘,x,y2,‘--+g‘); hold off
hold on x=0:0.5:4*pi; y=sin(x); hh=tan(x); h=y./hh; w=1./(1+exp(-x)); g=(1/(2*pi*2)^0.5).*exp((-1.*(x-2*pi).^2)./(2*2^2)); plot(x,y,‘bd-‘,x,h,‘gp:‘,x,w,‘ro-‘,x,g,‘c^-‘); %添加标识 legend(‘sin(x)‘,‘cos(x)‘,‘Sigmoid‘,‘Gauss function‘); %添加标题和坐标 title(‘标题‘); xlabel(‘t=0to2\\pi‘); ylabel(‘value‘); hold off
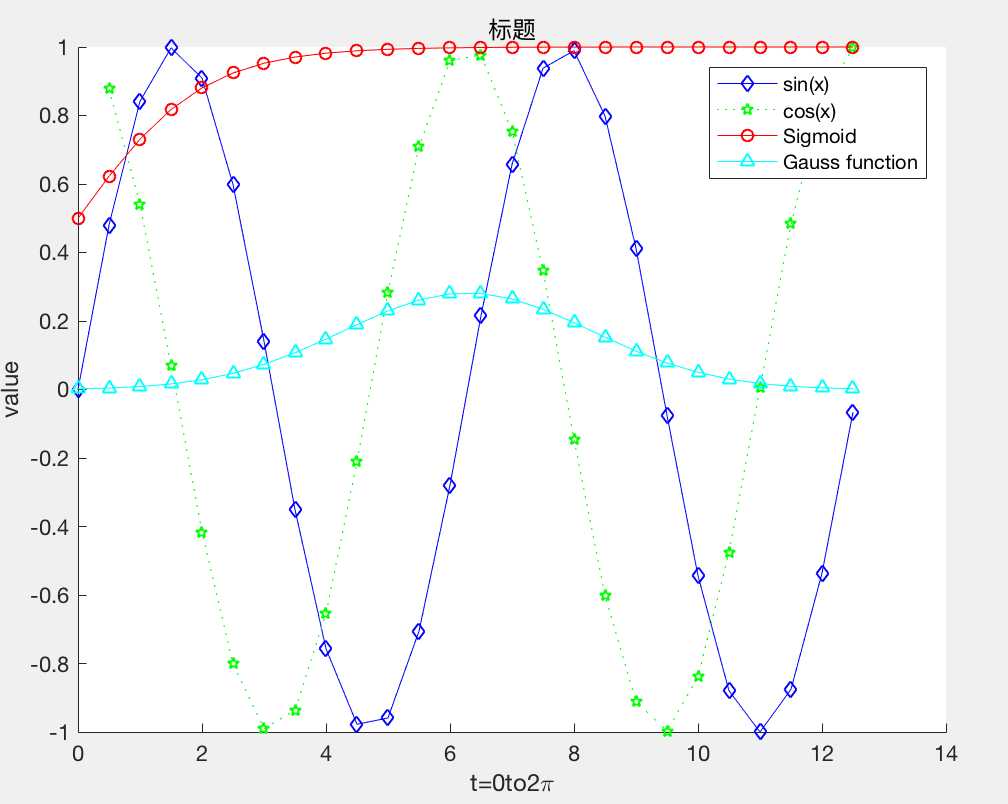
text() 可用该函数在图形中指定的位置上显示字符串。
annotation() 添加注释、箭头、文本框等,默认坐标为0-1的归一化坐标
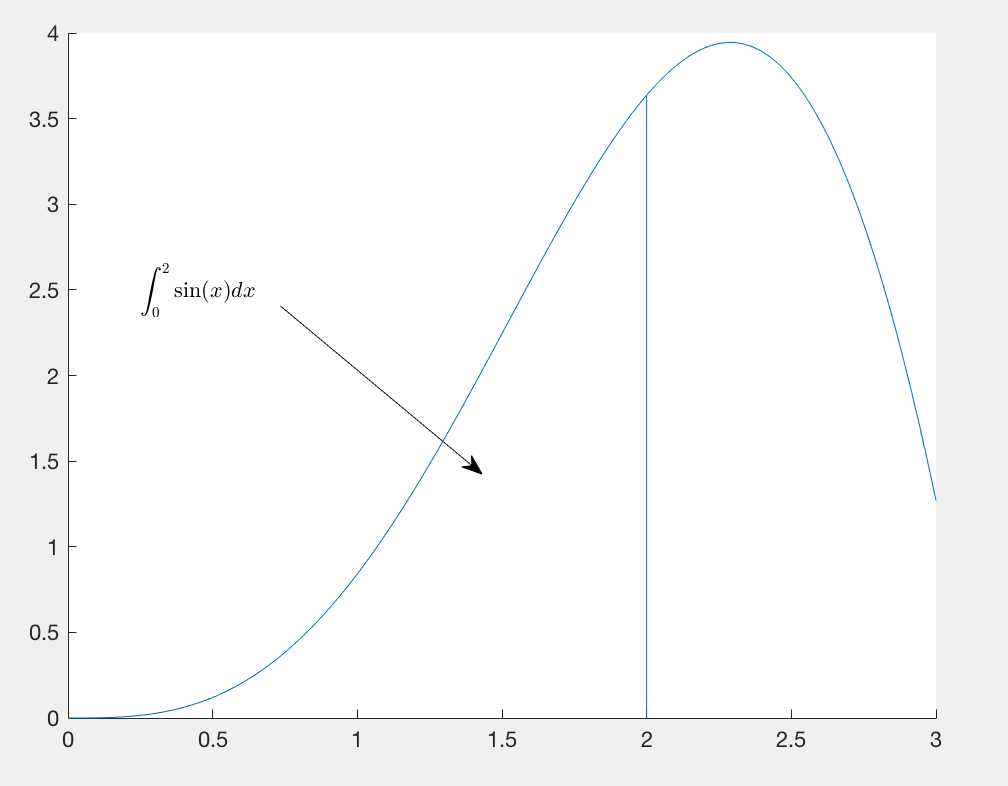
hold on x=linspace(0,3); y=x.^2.*sin(x); plot(x,y); line([2,2],[0,2^2*sin(2)]); %积分符号 \\int 下标_0 上标1 str=‘$$ \\int_0^2\\sin(x) dx $$‘; %以LaTeX表示法表示str,0.25表示x的坐标,2.5表示y的坐标 text(0.25,2.5,str,‘Interpreter‘,‘latex‘); %[0.32,0.5]是代表箭头在x坐标的位置,[0.6,0.4]是代表箭头在y坐标的位置,都要归一化,x乘3,y乘4 annotation(‘arrow‘,‘X‘,[0.32,0.5],‘Y‘,[0.6,0.4]); hold off
get() 获得句柄handle 详情https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/matlab/ref/get.html
gca() return the handle of the "current" axes
gcf() return the handle the "current" figure
hold on x=linspace(0,2*pi,1000); y=sin(x); plot(x,y); h=plot(x,y); get(h); hold off
set(句柄,属性名1,属性值1,属性名2,属性值2,…) 设置句柄handle
set(gca,‘Xlim‘,[0,pi]);
除了上面的方法可以设置handle,下面的方法也可以
xlim([0,2*pi]); ylim([-1.2,1.2]);
%改变坐标的大小 set(gca,‘FontSize‘,25); %tick 设置几个刻度的意思 set(gca,‘XTick‘,0:pi/2:2*pi); set(gca,‘XTickLabel‘,0:90:360); %gca是针对坐标轴的改变 %改变线的样式 set(线的名称;样式;目标值,···); set(h,‘LineStyle‘,‘-.‘,‘LineWidth‘,7.0,‘Color‘,‘g‘);
figure(‘Position‘,[left,bottom,width,height]);
多张图画在一张图上
只有一个figure subplot(row,column,1);
x=-10:0.1:10; y1=x.^2-8; y2=exp(x); %可以表示写position,也可以不写 figure(‘Position‘,[300,100,500,500]),plot(x,y1); figure,plot(x,y2);
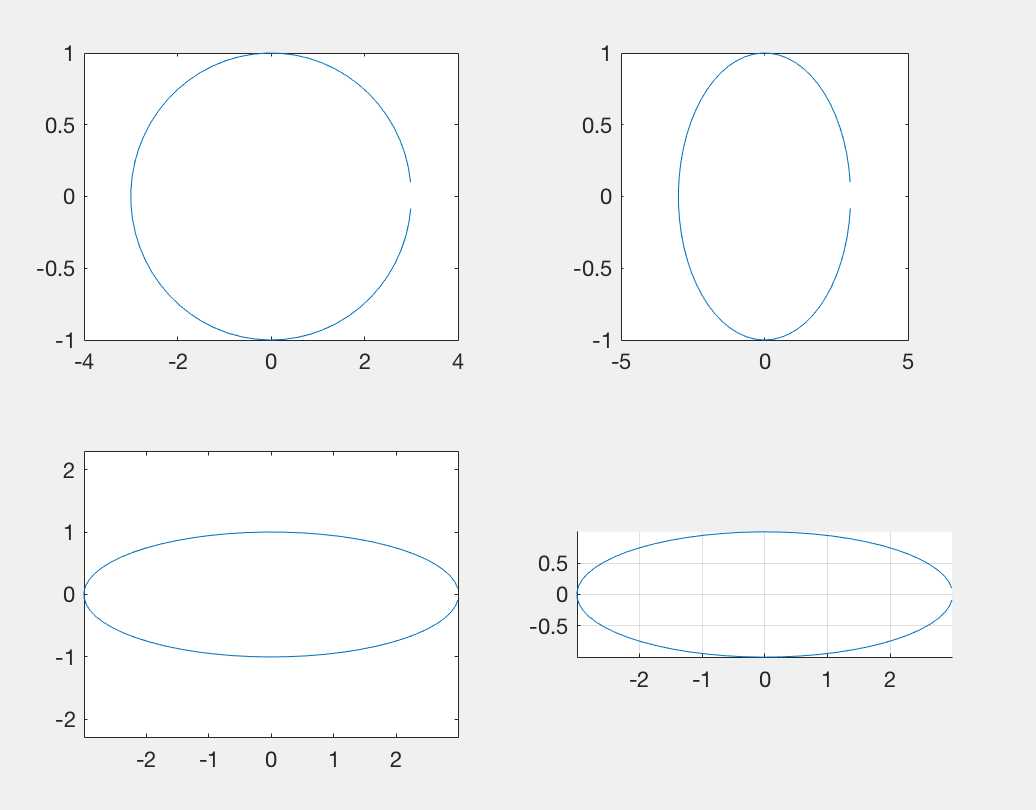
t=0:0.1:2*pi; x=3*sin(t)./tan(t); y=sin(t); subplot(2,2,1);plot(x,y);axis normal; subplot(2,2,2);plot(x,y);axis square; %axis equal x轴上一格距离大小与y轴上一格距离大小一致 subplot(2,2,3);plot(x,y);axis equal; subplot(2,2,4);plot(x,y);axis equal tight;
axis off 关闭最后画的一个图的坐标
axis on 打开最后画的一个图的坐标
box off 关闭最后画的一个图的上边线和右边线
box on 打开最后画的一个图的上边线和右边线
grid off 关闭最后一个画的图的栅格
grid on 打开最后一个画的图的栅格
>>box off >> grid on
进阶绘图
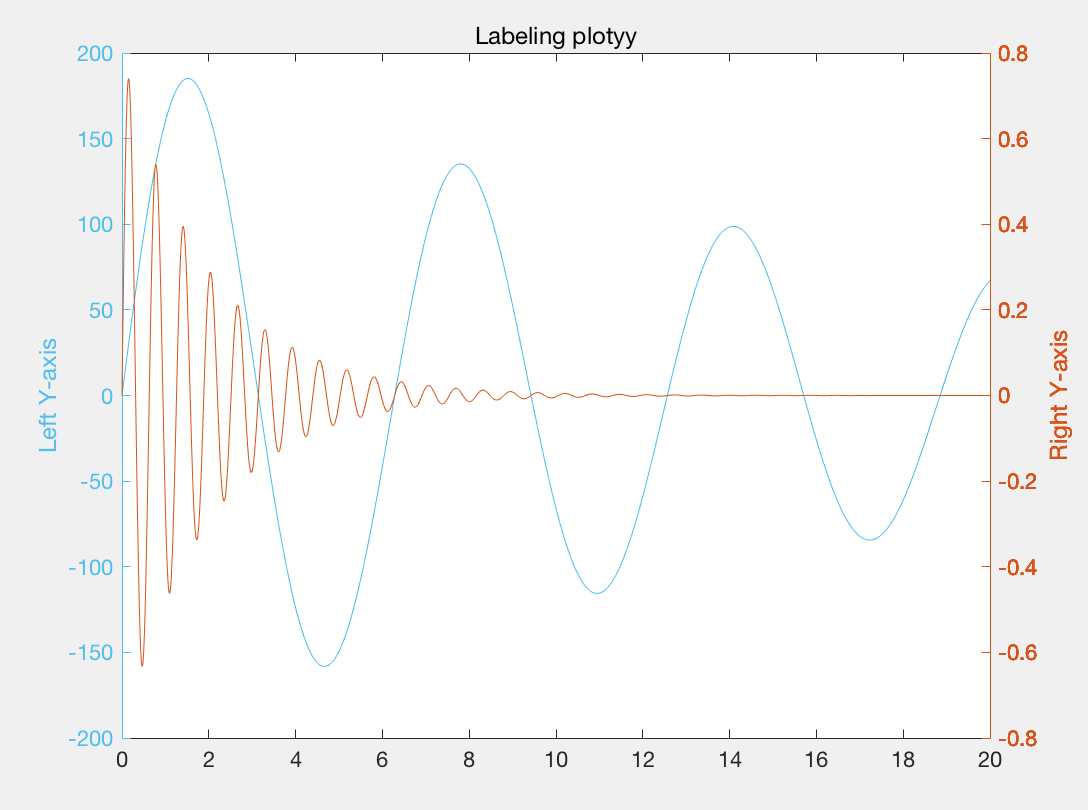
plotyy() 双y轴函数
hold on x=0:0.01:20; y1=200*exp(-0.05*x).*sin(x); y2=0.8*exp(-0.5*x).*sin(10*x); %下面的式子返回三个参数,ax是坐标轴的句柄,ax(1)是左边的纵轴,ax(2)时右边的纵轴 [ax,h1,h2]=plotyy(x,y1,x,y2); set(get(ax(1),‘Ylabel‘),‘String‘,‘Left Y-axis‘); set(get(ax(2),‘Ylabel‘),‘String‘,‘Right Y-axis‘); title(‘Labeling plotyy‘); set(h1,‘LineStyle‘,‘--‘); set(h2,‘LineStyle‘,‘:‘); plotyy(x,y1,x,y2); hold off
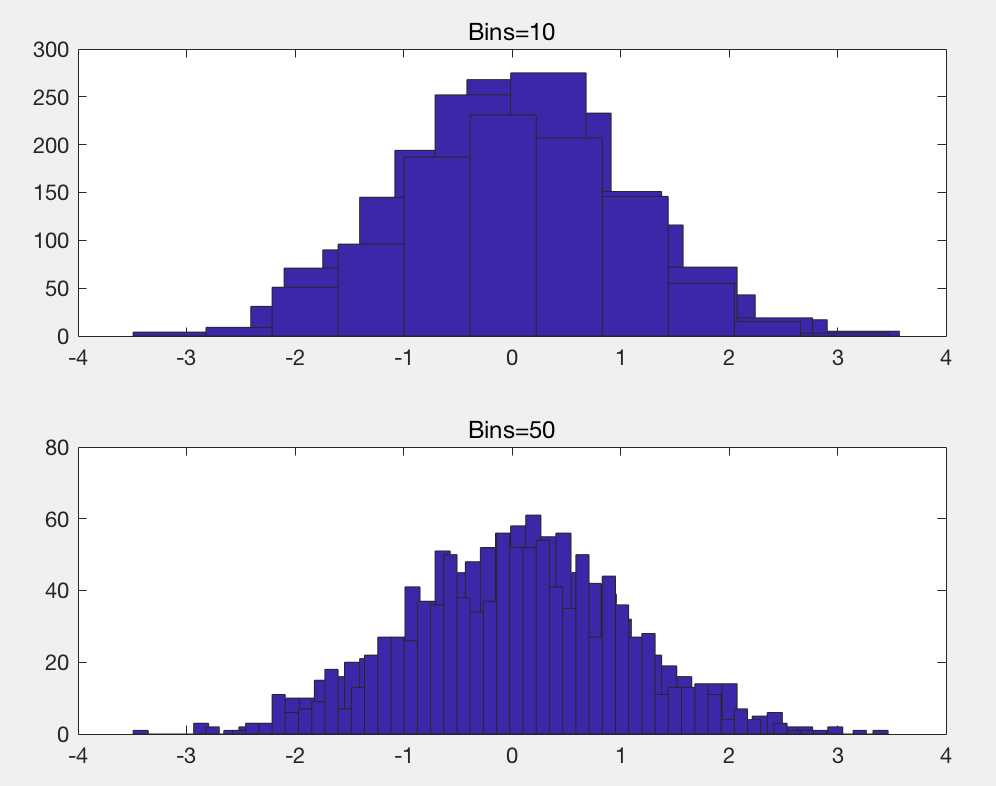
randn()是均值为0方差为1的正态分布
hist(y,m) m是一个标量,表明使用m个箱子
hold on y=randn(1,1000); subplot(2,1,1); hist(y,10); title(‘Bins=10‘); subplot(2,1,2); hist(y,50); title(‘Bins=50‘); hold off
bar
hold on x=[1 2 5 4 8]; y=[x;1:5]; subplot(1,3,1);bar(x);title(‘A bargraph of vector x‘); subplot(1,3,2);bar(y);title(‘A bargraph of vector y‘); subplot(1,3,3);bar3(x);title(‘A 3D bargraph‘); hold off
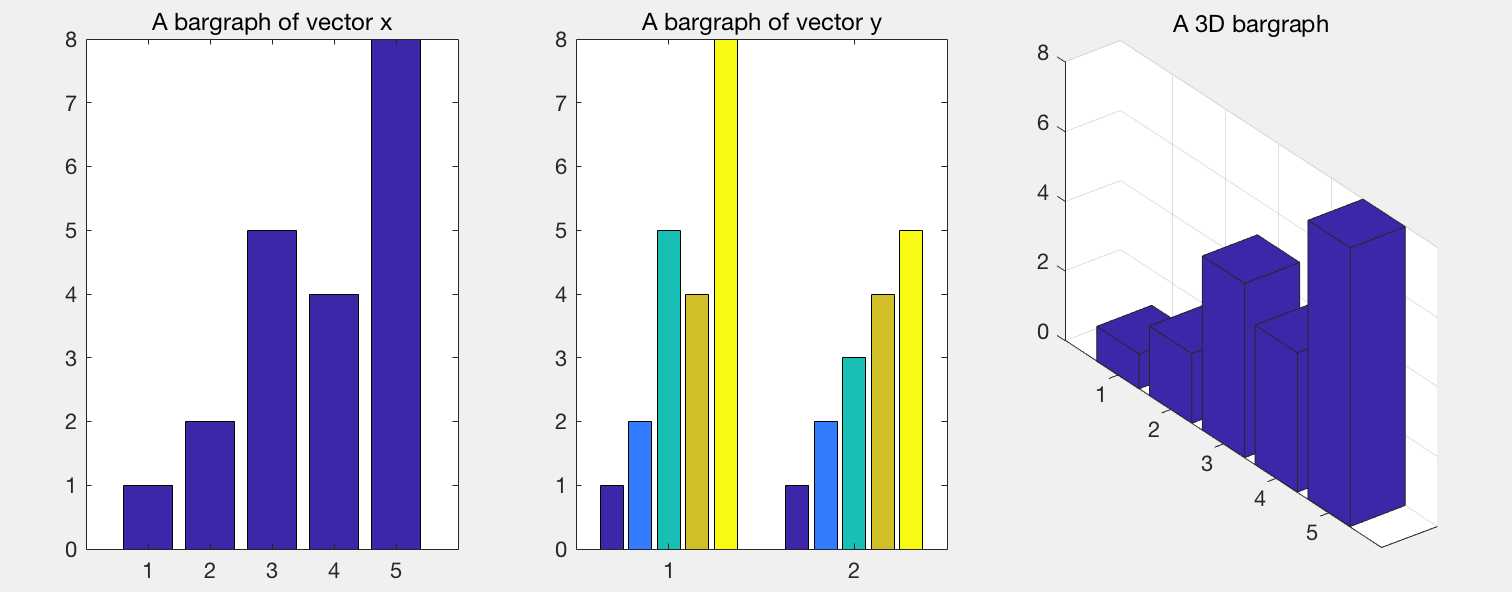
详情https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/barh.html
pie chart
hold on a=[10 5 20 30]; subplot(1,3,1);pie(a); subplot(1,3,2);pie(a,[0,0,0,1]); subplot(1,3,3);pie3(a,[0,0,0,1]); hold off
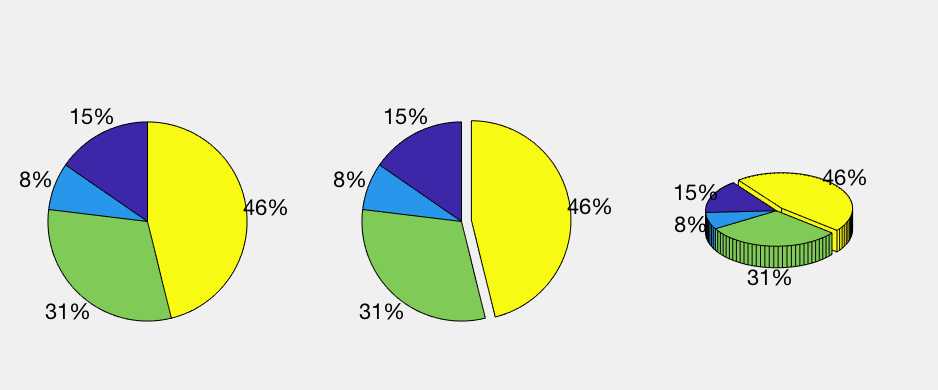
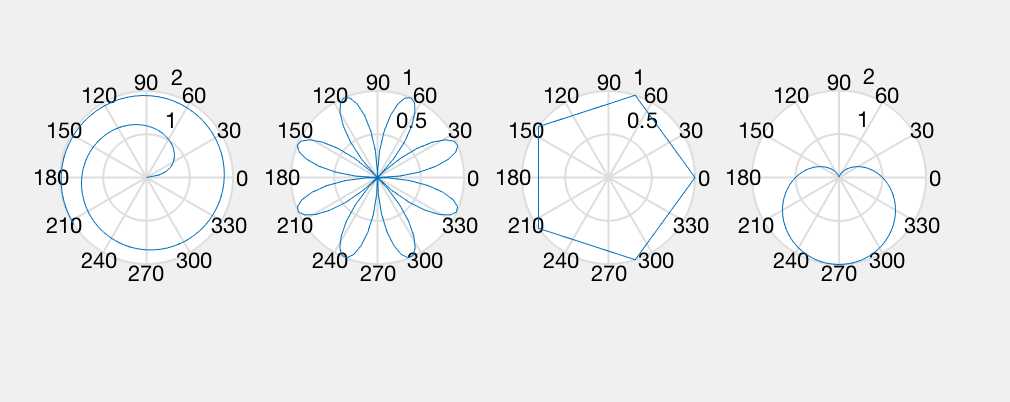
polar chart
hold on x=1:100; theta=x/10;r=log10(x); subplot(1,4,1);polar(theta,r); theta=linspace(0,2*pi);r=sin(4*theta); subplot(1,4,2);polar(theta,r); theta=linspace(0,2*pi,6);r=ones(1,length(theta)); subplot(1,4,3);polar(theta,r); theta=linspace(0,2*pi);r=1-sin(theta); subplot(1,4,4);polar(theta,r); hold off
以上是关于结构化程序与自定函数的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
R语言用户自定义函数的语法结构编写自定义统计值计算函数(使用ifelse结构计算均值和标准差等)编写自定义日期格式化(format)函数(switch函数使用不同分枝格式化日期数据)应用自定函数