SpringBoot 2.0.3 源码解析
Posted yueguanguanyun
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringBoot 2.0.3 源码解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
用SpringBoot也有很长一段时间了,一直是底层使用者,没有研究过其到底是怎么运行的,借此机会今天试着将源码读一下,在此记录。。。我这里使用的SpringBoot 版本是 2.0.3.RELEASE
源码解析
SpringApplication 的初始化
1.首先一个完整的SpringBoot项目一定会有个启动类,这里就是我们整个程序的入口;
@SpringBootApplication public class TeachercommunitystudioApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer public static void main(String[] args) SpringApplication.run(TeachercommunitystudioApplication.class, args);
2.只有一行代码,调用了 SpringApplication的静态 run()方法,
//调用重载run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) return run(new Class[]primarySource, args);
//参数为Class<?>数组 1.+版本这里是Object public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) return (new SpringApplication(primarySources)).run(args);
3.在run()方法中调用构造函数创建SrpingApplicatin的对象,入参其实就是启动类的class对象,并调用该对象的run方法。
//resourceLoader这里传入的是null, primarySources就是有启动类的class对象
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources)
//为成员变量sources复制,sources是set<String> 类型
this.sources = new LinkedHashSet(); this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE; this.logStartupInfo = true; this.addCommandLineProperties = true; this.headless = true; this.registerShutdownHook = true; this.additionalProfiles = new HashSet(); this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//primarySources就是启动类class对象 this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
/*① 程序类型 通过一个枚举类判断web程序类型,WebApplicationType枚举类中的字段
包括 响应式程序,none, servlet程序*/ this.webApplicationType = this.deduceWebApplicationType();
//② 初始化classPath下的所有可用的应用初始化器 ApplicationContextInitalizer this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//④ 初始化监听器 this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//⑤ 获取main方法的类名 this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
① SpringBoot 2.0以后引入WebApplicationType新特性,该类是个枚举类,deduceWebApplicationType()方法推断使用哪中web程序,默认servlet程序
private WebApplicationType deduceWebApplicationType() if (ClassUtils.isPresent("org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler", (ClassLoader)null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet", (ClassLoader)null)) return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE; else String[] var1 = WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES; int var2 = var1.length; for(int var3 = 0; var3 < var2; ++var3) String className = var1[var3]; if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, (ClassLoader)null)) return WebApplicationType.NONE; //默认servlet return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
//枚举类,web应用程序种类
public enum WebApplicationType NONE, SERVLET, //servlet程序 REACTIVE; //响应式程序 private WebApplicationType()
② 给SpringApplication的成员变量 List<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers 赋值, initializers--初始化器集合
调用 setInitializers(Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) ...方法。代码如下
public void setInitializers(Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) this.initializers = new ArrayList(); this.initializers.addAll(initializers);
在构造方法中调用 setInitializers(Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>>) 入参为方法 getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) 获取Srping工厂初始化器 的返回值
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) return this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class[0]); private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); //获取所有BeanFactory的名字 ③ Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); //创建工厂实例 List<T> instances = this.createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);//排序 return instances; private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) List<T> instances = new ArrayList(names.size()); Iterator var7 = names.iterator(); while(var7.hasNext()) String name = (String)var7.next(); try
//实例数容器中的BeanFactory(这里指ApplicationContextInitializer) Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader); Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
//反射机制获取到构造方法对象,执行实例化 Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes); T instance = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args); instances.add(instance); catch (Throwable var12) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, var12); return instances;
③ SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader) 方法,从META/Spring.factories的资源文件中,读取key为ApplicationContextInitialiner对应的值
从下面的代码我们可以看到,根据从构造方法中 ApplicationContextInitializer.class对象获取到ApplicationContextInitializer的类名路径,然后根据该类名路径
从 META/Spring.factoryes 文件中 获取对应的值,如下图
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader)
//获取到类的全路径名称 String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList()); private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) return result; else try Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories"); LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); while(urls.hasMoreElements())
...
...
...
META-INF/spring.factories文件的内容,及ApplicationContextInitializer所对应的值
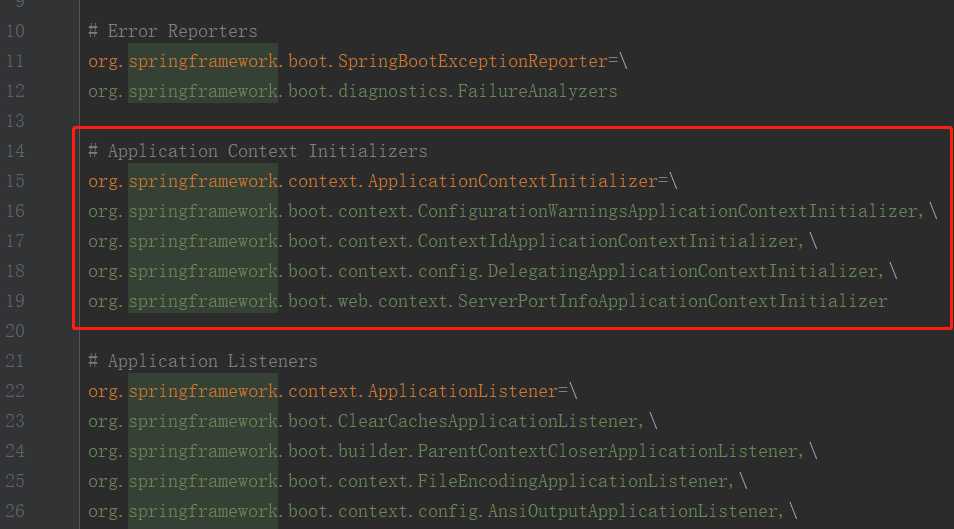
可以看到,这里得到的值有四个类 ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer、ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer、DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer、ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
所以 List<T> instances = this.createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);这一步得到的List<T>的值就是他们四个的实例
public void setInitializers(Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) this.initializers = new ArrayList(); this.initializers.addAll(initializers);
所以成员变量 initializers 的初始化变量值其实就是以上四个类的对象组成的List
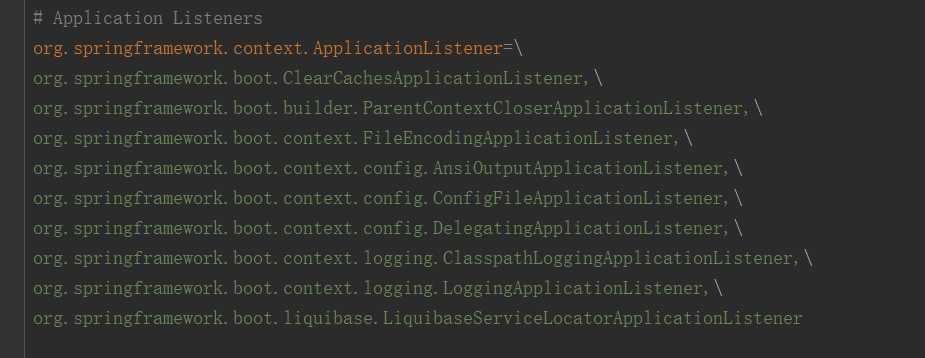
④ 初始化监听器方法 this.setListeners()
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
整体流程和初始化应用初始化器类似,只不过从 META-INF/spring.factories 中获取的key为 ApplicationListener 的值,然后实例化几个对象后,封装为集合赋值给 this.setListeners()
⑤ this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass(); 获取main方法的类名
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() try StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = (new RuntimeException()).getStackTrace(); StackTraceElement[] var2 = stackTrace; int var3 = stackTrace.length;
//遍历堆栈跟踪元素,获取到调用当前类的方法判断是否为("main"),是的话返回main所在的类名 for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4)
StackTraceElement stackTraceElement = var2[var4];
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName()); catch (ClassNotFoundException var6) return null;
2.run方法的执行流程
上面的流程执行完毕后,SpringApplication类就初始化完毕了,我们得到一个SpringApplication对象,然后掉用该对象的run()方法。run方法返回值为ConfigurableApplicationContext ---继承自---> ApplicationContext
run()方法内都做了什么事情呢,简单来说就是:
1)准备Spring的环境,
2)打印banner
3)通过spring环境准备上下文 ApplicationContext
4)刷新上下文,即真正去准备项目的Spring环境
下面我们根据代码来分析一下。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) // 声明一个秒表。计算并打印出程序耗时
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 程序异常报告 Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
// ①设置系统为Headless模式 this.configureHeadlessProperty();
// ② 初始化SrpingApplicationRunListeners监听器 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(); Collection exceptionReporters; try
// 初始化应用参数,参数为main方法中传入的args ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// ③ 根据listeners和 applicationArguments 应用参数 来配置SpringBoot的应用环境 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 根据环境配置去除要忽略的 bean信息
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// Banner打印,这里就不再多说了 Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
/* ④ 根据 webApplicationType 应用类型来确定该 SpringBoot 项目应该创建什么类型的应用上下文 ApplicationContext
如果没有明确的设置应用程序上下文会返回合适的默认值, */ context = this.createApplicationContext();
/* 和上面说的getSpringFactoriesInstances是一个套路,从META-INF/springfactories中获取键为SpringBootExceptionReporter的value
然后将这些值使用反射,进行实例化返回一个集合 */
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]ConfigurableApplicationContext.class, context);
// ⑤ 完成整个容器的创建于启动以及 bean的注入功能
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// ⑥ 刷新上下文 this.refreshContext(context); this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) (new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); listeners.started(context); this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments); catch (Throwable var10) this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(var10); try listeners.running(context); return context; catch (Throwable var9) this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null); throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
① 设置系统为Headless模式
Headess模式是系统的一种配置模式,在系统缺少显示设备,鼠标键盘等外设时可以使用该模式。一般是在程序开始激活headless模式,告诉程序,现在你要工作在Headless mode下,就不要指望硬件帮忙了,你得自力更生,依靠系统的计算能力模拟出这些特性来。
private boolean headless;
//构造函数中
this.headless = true;
private void configureHeadlessProperty() System.setProperty("java.awt.headless", System.getProperty("java.awt.headless", Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
② 初始化SrpingApplicationRunListeners监听器
这里依然调用 getSpringFactoriesInstances()方法,和上面基本是一样的套路,从 META-INF/spring.factories 中获取键 SpringApplicationRunListener 的 value.
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting();
try ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment); context = this.createApplicationContext(); exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]ConfigurableApplicationContext.class, context); this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); this.refreshContext(context); this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) (new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); listeners.started(context); this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
try
listeners.running(context);
return context;
// getSpringFactoriesInstances()方法和构造函数中的应用程序初始化类的初始化过程是同一个方法,基本流程就是从META-INF/spring.factories 配置文件里根据键取值
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) Class<?>[] types = new Class[]SpringApplication.class, String[].class; return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
③ 根据listeners和 applicationArguments 应用参数 来配置SpringBoot的应用环境
// environment成员变量, 在构造函数中未赋值 private ConfigurableEnvironment environment; private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 配置环境 this.configureEnvironment((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs()); listeners.environmentPrepared((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment); this.bindToSpringApplication((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment); if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.NONE) environment = (new EnvironmentConverter(this.getClassLoader())).convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment); ConfigurationPropertySources.attach((Environment)environment); return (ConfigurableEnvironment)environment; // environment不为null直接返回,为null则新建 private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() if (this.environment != null) return this.environment; else return (ConfigurableEnvironment)(this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.SERVLET ? new StandardServletEnvironment() : new StandardEnvironment());
// 配置环境
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args)
this.configurePropertySources(environment, args); //配置要使用的属性源 PropertySources
this.configureProfiles(environment, args); //配置要使用的Profiles
// 将环境绑定到 SpringApplication
protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment)
try
Binder.get(environment).bind("spring.main", Bindable.ofInstance(this));
catch (Exception var3)
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", var3);
④ 根据 webApplicationType 应用类型创建不同类型的ApplicationContext,未指定的话返回默认的ApplicationContext
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass; if (contextClass == null) try switch(this.webApplicationType) case SERVLET: contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext"); break; case REACTIVE: contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext"); break; default: contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext"); catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", var3); return (ConfigurableApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
⑤ 完成整个容器的创建、启动以及 bean 的注入功能
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) // 将上面获取到的 environment(配置环境类) 设置给创建好的Application
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// a. 该方法对 context 进行了预设置,设置了 ResourceLoader 和 ClassLoader,并向 bean 工厂中添加了一个beanNameGenerator this.postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// b. 在刷新前将 ApplicationContextInitializer 应用于上下文 this.applyInitializers(context); listeners.contextPrepared(context); if (this.logStartupInfo) // 启动日志 this.logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); this.logStartupProfileInfo(context); context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments); if (printedBanner != null) context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner); Set<Object> sources = this.getAllSources(); Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty"); this.load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); listeners.contextLoaded(context);
a. postProcessApplicationContext(context); 对context 进行了预设值,设置了 ResourceLoader 和 ClassLoader, 并向bean工厂中添加了一个BeanNameGenerator。
protected void postProcessApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) // 给ApplicationContext设置BeanNameGenerator;
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator", this.beanNameGenerator); if (this.resourceLoader != null) // 设置ResourceLoader 设置资源加载器
if (context instanceof GenericApplicationContext) ((GenericApplicationContext)context).setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader); // 给ApplicationContext 设置 ClassLoader类加载器 if (context instanceof DefaultResourceLoader) ((DefaultResourceLoader)context).setClassLoader(this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
b. 刷新前将所有ApplicationContextInitializer 应用于上下文
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) Iterator var2 = this.getInitializers().iterator(); while(var2.hasNext()) ApplicationContextInitializer initializer = (ApplicationContextInitializer)var2.next(); Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(), ApplicationContextInitializer.class); Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer."); initializer.initialize(context);
c. 主要是加载各种beans 到Application对象中,sources和primarySources,primarySources就是构造函数的入参,启动类的class对象
// 获取所有资源列表
public Set<Object> getAllSources() Set<Object> allSources = new LinkedHashSet(); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.primarySources)) allSources.addAll(this.primarySources); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.sources)) allSources.addAll(this.sources); return Collections.unmodifiableSet(allSources);
// 加载各种bean到ApplicationContext对象中 protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) logger.debug("Loading source " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(sources)); BeanDefinitionLoader loader = this.createBeanDefinitionLoader( // (2)
this.getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources); // (1) if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator); if (this.resourceLoader != null) loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader); if (this.environment != null) loader.setEnvironment(this.environment); loader.load(); // (3)
(1) getBeanDefinitionRegistry(ApplicationContext context) 获取bean定义注册表
private BeanDefinitionRegistry getBeanDefinitionRegistry(ApplicationContext context) if (context instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) return (BeanDefinitionRegistry)context; else if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) return (BeanDefinitionRegistry)((AbstractApplicationContext)context).getBeanFactory(); else throw new IllegalStateException("Could not locate BeanDefinitionRegistry");
(2) createBeanDefinitionLoader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object[] sources)
通过BeanDefinitionLoader的构造方法把参数(注册表、资源)传进去,然后创建BeanDefinitionLoader。
protected BeanDefinitionLoader createBeanDefinitionLoader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object[] sources) return new BeanDefinitionLoader(registry, sources);
(3) load() 调用BeanDefinitionLoader 对象的方法 load();把资源全部加载
// 遍历所有资源
public int load() int count = 0; Object[] var2 = this.sources; int var3 = var2.length; for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) Object source = var2[var4]; count += this.load(source); return count;
// 根据资源的类型,调用不同的重载方法进行加载 private int load(Object source) Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null"); if (source instanceof Class) return this.load((Class)source); else if (source instanceof Resource) return this.load((Resource)source); else if (source instanceof Package) return this.load((Package)source); else if (source instanceof CharSequence) return this.load((CharSequence)source); else throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass());
⑥ 刷新上下文
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) this.refresh(context); // a. 刷新底层的 ApplicationContext if (this.registerShutdownHook) try
/* registerShutdownHook 是一个公共方法,它可以创建线程并将其注册到 Java 虚拟机,
以便在关机时运行,以关闭 ApplicationContext */
context.registerShutdownHook(); catch (AccessControlException var3)
a. refresh ( ApplicationContext context ) 刷新底层的ApplicationContext
refresh()调用了 ApplicationContext 的一个子接口的实现类AvstractApplicationContext (抽象类) 中的 refresh() 方法
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext); ((AbstractApplicationContext)applicationContext).refresh();
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor)
// 准备刷新上下文 this.prepareRefresh();
// 通知子类刷新内部Bean工厂 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 准备Bean工厂, 在上下文中使用 this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try
// 允许在上下文子类中对Bean工厂进行后处理 this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 调用上下文中注册为Bean 的工厂处理器 this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册拦截Bean创建的bean处理器 this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册上下文中的消息源 this.initMessageSource();
// 初始化事件广播机制 this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 在特定上下文子类中初始化其他特殊Bean this.onRefresh();
// 检查注册监听器Bean this.registerListeners();
// 实例化所有剩余单例(非惰性)完成BeanFactory的初始化 this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 发布相应的事件 this.finishRefresh(); catch (BeansException var9) if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9); // 销毁已创建的单例,避免资源的浪费 this.destroyBeans();
// 重置活动的标志 this.cancelRefresh(var9); throw var9; finally
// 重置Spring中的常见内省缓存 this.resetCommonCaches();
通过以上代码可以看到,这里在做各种初始化工作, 后面有个 finishBeanFactoryInitialization() 方法完成BeanFactory的初始化,我们重点看下这个;该方法进行了非懒加载beans的初始化工作。进去看一下。
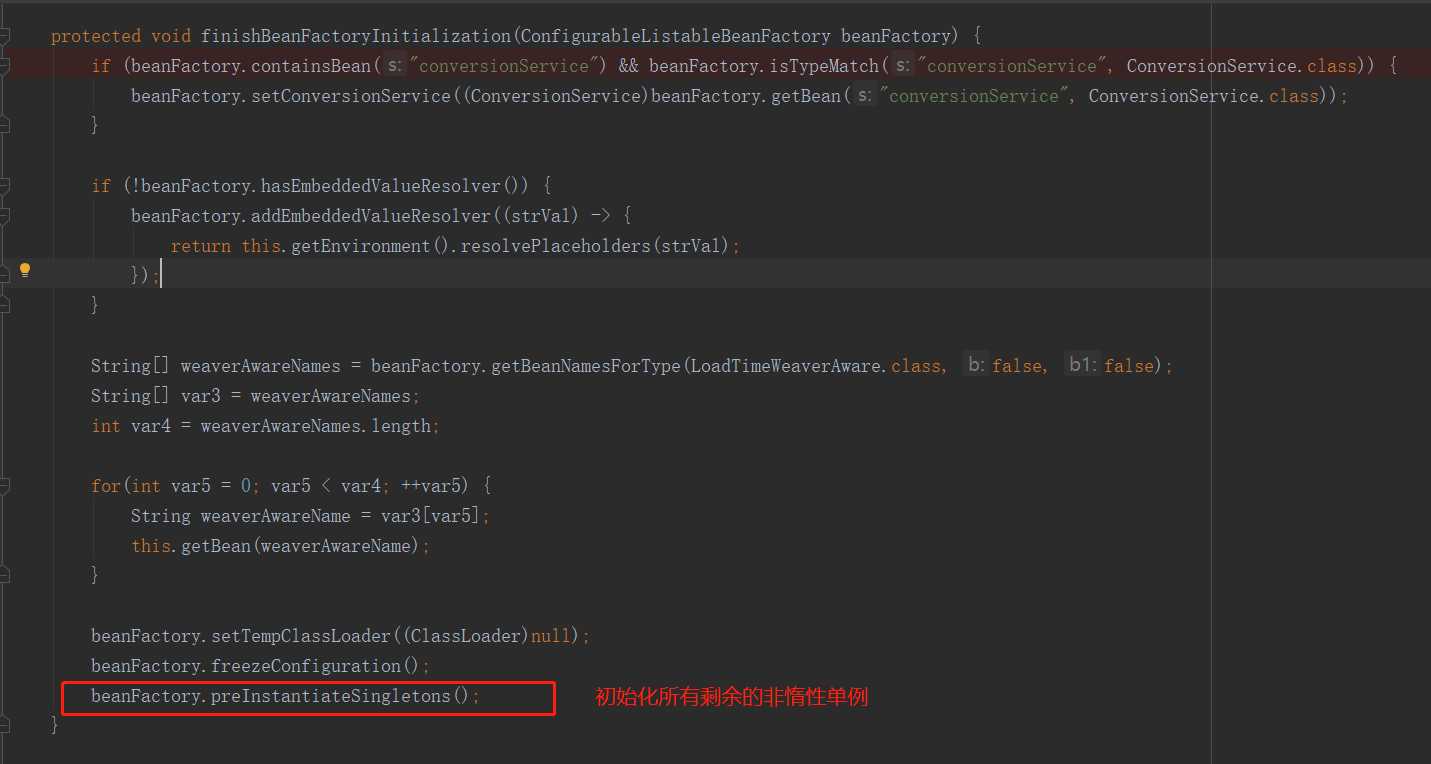
我们看到,最后调用了 beanFactory的 preInstantiateSingletons();再进去看一下,beanFactory - -ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 只有一个实现类 DefaultListableBeanFactory 实现了 该方法,进去看看具体如何实现的。
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this); List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList(this.beanDefinitionNames); Iterator var2 = beanNames.iterator(); while(true) String beanName; Object bean; do while(true) RootBeanDefinition bd; do do do if (!var2.hasNext()) var2 = beanNames.iterator(); while(var2.hasNext()) beanName = (String)var2.next(); Object singletonInstance = this.getSingleton(beanName); if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton)singletonInstance; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) AccessController.doPrivileged(() -> smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); return null; , this.getAccessControlContext()); else smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); return; beanName = (String)var2.next(); bd = this.getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); while(bd.isAbstract()); while(!bd.isSingleton()); while(bd.isLazyInit()); if (this.isFactoryBean(beanName)) bean = this.getBean("&" + beanName); break; this.getBean(beanName); while(!(bean instanceof FactoryBean)); FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean)bean; boolean isEagerInit; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) SmartFactoryBean var10000 = (SmartFactoryBean)factory; ((SmartFactoryBean)factory).getClass(); isEagerInit = (Boolean)AccessController.doPrivileged(var10000::isEagerInit, this.getAccessControlContext()); else isEagerInit = factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && ((SmartFactoryBean)factory).isEagerInit(); if (isEagerInit) this.getBean(beanName);
猛地一看有点多顿时不知从何下手,但仔细看看,好像整段代码都围绕着 getBean()来写的,由此推测getBean才是重头戏,找到重点那就跟踪看一下,发现进入了AbstractBeanFactory类,(好像有点熟悉,先不管继续向下看),在getBean中最终调用了AbstractBeanFactory中的doGetBean()方法()。
protected <T> T doGetBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException String beanName = this.transformedBeanName(name); Object sharedInstance = this.getSingleton(beanName); Object bean; if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) if (this.isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) this.logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean ‘" + beanName + "‘ that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); else this.logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean ‘" + beanName + "‘"); bean = this.getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, (RootBeanDefinition)null); else if (this.isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = this.getParentBeanFactory(); if (parentBeanFactory != null && !this.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) String nameToLookup = this.originalBeanName(name); if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) return ((AbstractBeanFactory)parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly); if (args != null) return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); if (!typeCheckOnly) this.markBeanAsCreated(beanName); try RootBeanDefinition mbd = this.getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); this.checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); String[] var11; if (dependsOn != null) var11 = dependsOn; int var12 = dependsOn.length; for(int var13 = 0; var13 < var12; ++var13) String dep = var11[var13]; if (this.isDependent(beanName, dep)) throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Circular depends-on relationship between ‘" + beanName + "‘ and ‘" + dep + "‘"); this.registerDependentBean(dep, beanName); try this.getBean(dep); catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException var24) throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "‘" + beanName + "‘ depends on missing bean ‘" + dep + "‘", var24); if (mbd.isSingleton()) sharedInstance = this.getSingleton(beanName, () -> try return this.createBean(beanName, mbd, args); catch (BeansException var5) this.destroySingleton(beanName); throw var5; ); bean = this.getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); else if (mbd.isPrototype()) var11 = null; Object prototypeInstance; try this.beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); prototypeInstance = this.createBean(beanName, mbd, args); finally this.afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); bean = this.getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); else String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); Scope scope = (Scope)this.scopes.get(scopeName); if (scope == null) throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name ‘" + scopeName + "‘"); try Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> this.beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); Object var4; try var4 = this.createBean(beanName, mbd, args); finally this.afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); return var4; ); bean = this.getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); catch (IllegalStateException var23) throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Scope ‘" + scopeName + "‘ is not active for the current thread; consider defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", var23); catch (BeansException var26) this.cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); throw var26; if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) try T convertedBean = this.getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType); if (convertedBean == null) throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); else return convertedBean; catch (TypeMismatchException var25) if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) this.logger.debug("Failed to convert bean ‘" + name + "‘ to required type ‘" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "‘", var25); throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); else return bean;
在doGetBean()方法中看到createBean(); 该方法在这里并没有实现;由AbstractBeanFactory的实现类 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 实现了该方法;该类时一个抽象类。
public Object createBean(Class<?> beanClass, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck) throws BeansException RootBeanDefinition bd = new RootBeanDefinition(beanClass, autowireMode, dependencyCheck); bd.setScope("prototype"); return this.createBean(beanClass.getName(), bd, (Object[])null); protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) this.logger.debug("Creating instance of bean ‘" + beanName + "‘"); RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd; Class<?> resolvedClass = this.resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName, new Class[0]); if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd); mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass); try mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides(); catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException var9) throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", var9); Object beanInstance; try beanInstance = this.resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse); if (beanInstance != null) return beanInstance; catch (Throwable var10) throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", var10); try beanInstance = this.doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) this.logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean ‘" + beanName + "‘"); return beanInstance; catch (ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException | BeanCreationException var7) throw var7; catch (Throwable var8) throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", var8);
这里就可以看出来,这里是创建bean的核心方法了,头铁着又向下跟了一段,最终了了的发现其底层是cglib和jdk的aop切面来实现的。差点迷失在Spring庞大的代码里出不来。到这里run方法的流程就差不多执行完毕了。还有最后一步。
结语
最后再来总结一下,springboot大体的执行流程
1. prepareRefresh:预处理,包括属性验证等。
2. prepareBeanFactory:主要对beanFactory设置了相关属性,并注册了3个Bean:environment,systemProperties和systemEnvironment供程序中注入使用。
3. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:执行所以BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法。
4. registerBeanPostProcessors:注册BeanFactoryPostProcessors到BeanFactory。
5. initMessageSource:初始化MessageSource。
6. initApplicationEventMulticaster:初始化事件广播器ApplicationEventMulticaster。
7. registerListeners:事件广播器添加监听器,并广播早期事件。
8. finishBeanFactoryInitialization:结束BeanFactory的实例化,也就是在这真正去创建单例Bean。
9. finishRefresh:刷新的收尾工作。清理缓存,初始化生命周期处理器等等。
10. destroyBeans:销毁创建的bean。
11. cancelRefresh:取消刷新。
12. resetCommonCaches:清理缓存。
以上是关于SpringBoot 2.0.3 源码解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章