Linux进程管理之ps的使用
Posted wang618
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux进程管理之ps的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
主题Linux进程管理之ps工具的使用
一ps工具的介绍
ps: process state 进程状态
ps - report a snapshot of the current processes
Linux系统各进程的相关信息均保存在/proc/PID目录下的各文件中
默认显示的内容很少
[[email protected] ~]# ps PID TTY TIME CMD 2018 pts/0 00:00:00 bash 2656 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
[[email protected] ~]# ps PID TTY TIME CMD 1928 pts/0 00:00:01 bash 101855 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
显示当前终端的进程
[[email protected] ~]# tty /dev/pts/0
[[email protected] ~]# sleep 10 & [1] 2678 [[email protected] ~]# ps PID TTY TIME CMD 2018 pts/0 00:00:00 bash 2678 pts/0 00:00:00 sleep 2679 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
二ps支持的选项
ps [OPTION]...
支持三种选项:
UNIX选项 如-A
BSD选项 如a
GNU选项 如--help
选项:默认显示当前终端中的进程
• a 选项包括所有终端中的进程
• x 选项包括不链接终端的进程
• u 选项显示进程所有者的信息
• f 选项显示进程树,相当于 --forest
• k| --sort 属性 对属性 排序,属性前加- 表示倒序
• o 属性… 选项显示定制的信息 pid、cmd、%cpu、%mem
• L 显示支持的属性列表
(一)BSD风格的选项(最常用)
(1)a显示所有终端中的进程
PID是进程的标识号。
TTY是进程所属的终端控制台。
TIME列是进程所使用的总的CPU时间。
CMD列是正在执行的命令行。
[[email protected] ~]# ps a PID TTY STAT TIME COMMAND 1866 tty1 Ss+ 0:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty1 1868 tty2 Ss+ 0:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty2 1871 tty3 Ss+ 0:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty3 1873 tty4 Ss+ 0:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty4 1875 tty5 Ss+ 0:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty5 1877 tty6 Ss+ 0:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty6 2018 pts/0 Ss 0:00 -bash 2455 pts/1 Ss 0:00 -bash 2496 pts/1 S 0:00 su - wang 2497 pts/1 S+ 0:00 -bash 2752 pts/0 R+ 0:00 ps a
[[email protected] ~]# su - wang [[email protected] ~]$ ls [[email protected] ~]$ vim /etc/fstab [[email protected] ~]$ tty /dev/pts/1
(2)x显示和终端无关的进程
不需要用户账号登录就可以运行,机器启动就运行起来了
[[email protected] ~]# ps ax | head PID TTY STAT TIME COMMAND 1 ? Ss 0:01 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 22 2 ? S 0:00 [kthreadd] 3 ? S 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0] 5 ? S< 0:00 [kworker/0:0H] 7 ? S 0:00 [migration/0] 8 ? S 0:00 [rcu_bh] 9 ? R 0:00 [rcu_sched] 10 ? S< 0:00 [lru-add-drain] 11 ? S 0:00 [watchdog/0] [[email protected] ~]# ps ax | tail 882 ? Ssl 0:00 /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -n 906 ? Ss 0:00 sshd: [email protected]/0 967 ? Ss 0:00 /usr/libexec/postfix/master -w 968 ? S 0:00 pickup -l -t unix -u 969 ? S 0:00 qmgr -l -t unix -u 1142 pts/0 Ss 0:00 -bash 1179 ? S 0:00 [kworker/0:0] 1191 ? S 0:00 [kworker/0:1] 1195 pts/0 R+ 0:00 ps ax 1196 pts/0 D+ 0:00 -bash
(3)显示所有和终端有关的进程用户信息
USER:该进程属于的用户。
PID:该进程的进程号。
%CPU:该进程使用掉的CPU资源百分比,CPU利用率
%MEM:该进程所占用的物理内存百分比,内存利用率
VSZ:该进程使用掉的虚拟内存量(单位为Kbytes)
VSZ虚拟内存占用(操作系统给应用程序的内存大小,包括物理内存和swap内存)
vsz VSZ virtual memory size of the process in KiB (1024-byte units).
进程的虚拟内存大小为KiB(1024字节单位)。
Device mappings are currently excluded; this is subject to change. (alias vsize).
目前不包括设备映射;这一点可能会改变。(别名vsize)。
RSS:Resident Set Size,该进程占用的固定的内存量(单位为Kbytes)。
RSS真正的物理内存
TTY:该进程是在哪个终端机上面运作的,若与终端机无关,则显示“?”,
另外,tty1-tty6是本机上面的登入者进程,若为pts/0等,则表示为由网络连接进主机的进程。
STAT:该进程目前的状态,主要的状态:
R:正在运行,或者是可以运行。
S:正在中断睡眠中,可以由某些信号(signal)唤醒。
D:不可中断睡眠。
T:正在侦测或者是停止了。
Z:已经终止,但是其父进程无法正常终止它,从而变成zombic(僵尸)进程的状态。
+:前台进程。
1:多线程进程。
N:低优先级进程。
<:高优先级进程。
s:进程领导者。
L:已将页面锁定到内存中。
START:该进程被触发启动的时间。
TIME:该进程实际使用CPU运作的时间。也就是TIME时间片的累计值
COMMAND:该进程的实际命令。
[[email protected] ~]# ps au USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 540 0.0 0.0 110088 856 tty1 Ss+ Jul08 0:00 /sbin/agetty --noclear tty1 linux root 1928 0.0 0.2 116092 2944 pts/0 Ss Jul09 0:01 -bash root 5073 0.0 0.1 155324 1868 pts/0 R+ 12:13 0:00 ps au root 103122 0.0 0.2 115832 2464 pts/1 Ss+ 01:00 0:00 -bash
(4)显示所有进程用户信息
组合选项使用最多的,因为显示的信息很详细
[[email protected] ~]# ps axu | tail root 882 0.0 0.8 214424 8664 ? Ssl 16:56 0:00 /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -n root 906 0.0 0.5 154588 5384 ? Ss 16:56 0:00 sshd: [email protected]/0 root 967 0.0 0.2 89620 2080 ? Ss 16:56 0:00 /usr/libexec/postfix/master -w postfix 968 0.0 0.4 89724 4052 ? S 16:56 0:00 pickup -l -t unix -u postfix 969 0.0 0.4 89792 4080 ? S 16:56 0:00 qmgr -l -t unix -u root 1142 0.0 0.2 115968 2692 pts/0 Ss 16:56 0:00 -bash root 1179 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:01 0:00 [kworker/0:0] root 1191 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:06 0:00 [kworker/0:1] root 1197 0.0 0.1 155324 1860 pts/0 R+ 17:08 0:00 ps axu root 1198 0.0 0.0 107984 652 pts/0 R+ 17:08 0:00 tail [[email protected] ~]# ps axu | head USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 1 0.1 0.6 127780 6436 ? Ss 16:55 0:01 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 22 root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 16:55 0:00 [kthreadd] root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 16:55 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0] root 5 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 16:55 0:00 [kworker/0:0H] root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 16:55 0:00 [migration/0] root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 16:55 0:00 [rcu_bh] root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? R 16:55 0:00 [rcu_sched] root 10 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 16:55 0:00 [lru-add-drain] root 11 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 16:55 0:00 [watchdog/0]
(5)f 选项显示进程树,相当于 --forest
[[email protected] ~]# ps auxf | head USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Jul08 0:00 [kthreadd] root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Jul08 0:01 \\_ [ksoftirqd/0] root 5 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< Jul08 0:00 \\_ [kworker/0:0H] root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Jul08 0:00 \\_ [migration/0] root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Jul08 0:00 \\_ [rcu_bh] root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? R Jul08 0:09 \\_ [rcu_sched] root 10 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< Jul08 0:00 \\_ [lru-add-drain] root 11 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Jul08 0:02 \\_ [watchdog/0] root 13 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Jul08 0:00 \\_ [kdevtmpfs]
显示了进程的父子关系
进程必须放到树上的某个分支
[[email protected] ~]# ps auxf | grep apache Warning: bad syntax, perhaps a bogus ‘-‘? See /usr/share/doc/procps-3.2.8/FAQ root 2950 0.0 0.0 103324 836 pts/0 S+ 15:00 0:00 | \\_ grep --color=auto apache apache 2300 0.0 0.5 521880 5344 ? Sl 14:20 0:00 \\_ /usr/sbin/httpd.worker apache 2301 0.0 0.5 521880 5336 ? Sl 14:20 0:00 \\_ /usr/sbin/httpd.worker apache 2303 0.0 0.5 521880 5340 ? Sl 14:20 0:00 \\_ /usr/sbin/httpd.worker
[[email protected] ~]# ps auxf | grep sshd root 862 0.0 0.4 112796 4336 ? Ss Jul08 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D root 1924 0.0 0.5 154872 5756 ? Ss Jul09 0:03 \\_ sshd: [email protected]/0 root 103114 0.0 0.5 154588 5388 ? Ss Jul14 0:00 \\_ sshd: [email protected]/1 root 86615 0.0 0.0 112704 972 pts/1 S+ 16:18 0:00 \\_ grep --color=auto sshd
(6)o自定义输出指定的字段
[[email protected] ~]# ps axo pid,cmd,%cpu k cmd | head PID CMD %CPU 1761 abrt-dump-oops -d /var/spoo 0.0 1751 /usr/sbin/abrtd 0.0 1379 /usr/sbin/acpid 0.0 37 [aio/0] 0.0 14 [async/mgr] 0.0 23 [ata_aux] 0.0 24 [ata_sff/0] 0.0 1808 /usr/sbin/atd 0.0 1203 auditd 0.0
打开另外一个终端
[[email protected] ~]# id wang uid=1000(wang) gid=1000(wang) groups=1000(wang) [[email protected] ~]# su - wang Last login: Thu May 9 16:22:21 CST 2019 on pts/1 [[email protected] ~]$ passwd Changing password for user wang. Changing password for wang. (current) UNIX password:
uid,euid都表示有效用户是root,真正的用户是wang
因为这是因为普通用户具有suid权限
[[email protected] ~]# ps axo pid,cmd,ni,%cpu,uid,euid,ruid | tail 1252 [kworker/0:2] 0 0.0 0 0 0 1269 [kworker/0:0] 0 0.0 0 0 0 1270 [kworker/1:0] 0 0.0 0 0 0 1273 [kworker/1:2] 0 0.0 0 0 0 1276 su - wang 0 0.0 0 0 0 1277 -bash 0 0.0 1000 1000 1000 1300 passwd 0 0.1 0 0 1000 1305 [kworker/0:1] 0 0.0 0 0 0 1308 ps axo pid,cmd,ni,%cpu,uid, 0 0.0 0 0 0 1309 tail 0 0.0 0 0 0
(7)k按照指定字段排序
按照内存排序,在6上不支持
如果使用图形化界面,切换到命令行就会节约很大的内存
[[email protected] ~]# ps axo pid,cmd,%cpu,%mem k %mem | tail 2300 /usr/sbin/httpd.worker 0.0 0.5 2301 /usr/sbin/httpd.worker 0.0 0.5 2303 /usr/sbin/httpd.worker 0.0 0.5 2451 sshd: [email protected]/1 0.0 0.4 2455 -bash 0.0 0.4 2496 su - wang 0.0 0.1 2497 -bash 0.0 0.4 3156 sleep 60 0.0 0.0 3160 ps axo pid,cmd,%cpu,%mem k 0.0 0.1 3161 tail 0.0 0.0
[[email protected] ~]# ps axo pid,cmd,%cpu,%mem k %mem | tail 1507 sshd: [email protected]/0 0.0 0.5 1531 sshd: [email protected]/1 0.0 0.5 766 /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -n 0.0 0.5 526 /usr/bin/VGAuthService -s 0.0 0.6 527 /usr/bin/vmtoolsd 0.0 0.6 372 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-ud 0.0 0.6 1 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd -- 0.0 0.6 539 /usr/sbin/NetworkManager -- 0.0 0.9 541 /usr/lib/polkit-1/polkitd - 0.0 1.1 765 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sb 0.0 1.9
内存的使用情况:
[[email protected] ~]# free -h total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 974M 98M 716M 7.7M 159M 705M Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G
(8)L 显示支持的属性列表
显示线程,可能包含LWP和NLWP列。
[[email protected] ~]# ps L | head %cpu %CPU %mem %MEM _left LLLLLLLL _left2 L2L2L2L2 _right RRRRRRRR _right2 R2R2R2R2 _unlimited U _unlimited2 U2 alarm ALARM args COMMAND [[email protected] ~]# ps L | tail user USER userns USERNS util C utsns UTSNS uunit UUNIT vsize VSZ vsz VSZ wchan WCHAN wname WCHAN zone ZONE
6和7版本的属性数量不一样
[[email protected] ~]# ps L | wc 154 308 3388
[[email protected] ~]# ps L | wc 169 338 3718
(二)UNIX风格的选项
-C cmdlist 指定命令,多个命令用,分隔
-L 显示线程
-e: 显示所有进程,相当于-A
-f: 显示完整格式程序信息
-F: 显示更完整格式的进程信息
-H: 以进程层级格式显示进程相关信息
-u userlist 指定有效的用户ID或名称
-U userlist 指定真正的用户ID或名称
-g gid或groupname 指定有效的gid或组名称
-G gid或groupname 指定真正的gid或组名称
-p pid 显示指pid的进程
--ppid pid 显示属于pid的子进程
-M 显示SELinux信息,相当于Z
(1)-e: 显示所有进程,相当于-A
此选项常用
[[email protected] ~]# ps -e | head PID TTY TIME CMD 1 ? 00:00:01 systemd 2 ? 00:00:00 kthreadd 3 ? 00:00:00 ksoftirqd/0 5 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:0H 7 ? 00:00:00 migration/0 8 ? 00:00:00 rcu_bh 9 ? 00:00:00 rcu_sched 10 ? 00:00:00 lru-add-drain 11 ? 00:00:00 watchdog/0 [[email protected] ~]# ps -e | tail 967 ? 00:00:00 master 968 ? 00:00:00 pickup 969 ? 00:00:00 qmgr 1142 pts/0 00:00:00 bash 1179 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:0 1191 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:1 1206 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:2 1207 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:3 1228 pts/0 00:00:00 ps 1229 pts/0 00:00:00 tail
(2)-f: 显示完整格式程序信息
显示的内容更多
[[email protected] ~]# ps -f UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 1928 1924 0 Jul09 pts/0 00:00:01 -bash root 76668 1928 0 12:54 pts/0 00:00:00 ps -f
(3)-L 显示线程
第4列是线程编号
[[email protected] ~]# ps -L PID LWP TTY TIME CMD 1142 1142 pts/0 00:00:00 bash 1240 1240 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
[[email protected] ~]# ps -Lef | grep sshd root 877 1 877 0 1 16:56 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D root 906 877 906 0 1 16:56 ? 00:00:00 sshd: [email protected]/0 root 1238 1142 1238 0 1 17:21 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto sshd
(4)显示指定用户的进程信息
-u userlist 指定有效的用户ID或名称
[[email protected] ~]# ps -u root | head PID TTY TIME CMD 1 ? 00:00:39 systemd 2 ? 00:00:00 kthreadd 3 ? 00:00:01 ksoftirqd/0 5 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:0H 7 ? 00:00:00 migration/0 8 ? 00:00:00 rcu_bh 9 ? 00:00:09 rcu_sched 10 ? 00:00:00 lru-add-drain 11 ? 00:00:02 watchdog/0 [[email protected] ~]# ps -u root | tail 1928 pts/0 00:00:01 bash 3264 ? 00:00:02 kworker/u256:2 86289 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:0 86830 ? 00:00:00 kworker/u256:0 86866 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:1 87108 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:2 87219 pts/1 00:00:00 ps 87220 pts/1 00:00:00 bash 103114 ? 00:00:00 sshd 103122 pts/1 00:00:00 bash
(5)显示进程的特定属性
默认按PID显示的
[roo[email protected] ~]# ps -o pid,cmd,%cpu | head PID CMD %CPU 1142 -bash 0.0 1248 ps -o pid,cmd,%cpu 0.0 1249 head 0.0
(6)-C cmdlist 指定命令,多个命令用,分隔
[[email protected] ~]# ps -C vim PID TTY TIME CMD 3266 pts/1 00:00:00 vim
注意shebang机制一定要写,否则看不到脚本在运行
查看每个终端的进程
[[email protected] ~]# ll f1.sh -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 23 May 9 15:32 f1.sh [[email protected] ~]# cat f1.sh #!/bin/bash sleep 60 [[email protected] ~]# bash f1.sh
[[email protected] ~]# ps -C f1.sh PID TTY TIME CMD [[email protected] ~]# ps -C bash PID TTY TIME CMD 2018 pts/0 00:00:00 bash 2455 pts/1 00:00:00 bash 3521 pts/1 00:00:00 bash
两个bash,一个是登录bash,一个是执行脚本的bash
[[email protected] ~]# w 15:40:11 up 1:27, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 USER TTY FROM [email protected] IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT root pts/0 192.168.137.1 14:14 0.00s 0.30s 0.00s w root pts/1 192.168.137.1 14:24 44.00s 0.13s 0.00s bash f1.sh
sshd(1632)─┬─sshd(2014)───bash(2018)───pstree(3566)
│ └─sshd(2451)───bash(2455)───bash(3554)───sleep(3555)
注意不同风格的选项可以混用,但是不是全部的,这样就可以关注特定的属性
[[email protected] ~]# ps -C vim,init o pid,cmd,%mem PID CMD %MEM 1 /sbin/init 0.1 3650 vim /etc/fstab 0.4
(7)-F: 显示更完整格式的进程信息
PSR表示进程运行在那颗CPU上
[[email protected] ~]# ps -F UID PID PPID C SZ RSS PSR STIME TTY TIME CMD root 1142 906 0 28992 2692 0 16:56 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash root 1250 1142 0 38831 1844 0 17:42 pts/0 00:00:00 ps -F
目前只有1颗CPU
如果有多颗CPU就会进行切换,因为进程是有时间片的
时间到了就会释放CPU的内存空间
[[email protected] ~]# ps -C vim,init o pid,cmd,%mem,psr PID CMD %MEM PSR 1 /sbin/init 0.1 0 3650 vim /etc/fstab 0.4 0
开启2个CPU,另外开启4个终端
并且执行相同的命令
[[email protected] ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/null
[[email protected] ~]# lscpu Architecture: x86_64 CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit Byte Order: Little Endian CPU(s): 2 On-line CPU(s) list: 0,1 Thread(s) per core: 1 Core(s) per socket: 1 Socket(s): 2 NUMA node(s): 1 Vendor ID: GenuineIntel CPU family: 6 Model: 142 Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7500U CPU @ 2.70GHz Stepping: 9 CPU MHz: 2903.999 BogoMIPS: 5807.99 Hypervisor vendor: VMware Virtualization type: full L1d cache: 32K L1i cache: 32K L2 cache: 256K L3 cache: 4096K NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0,1
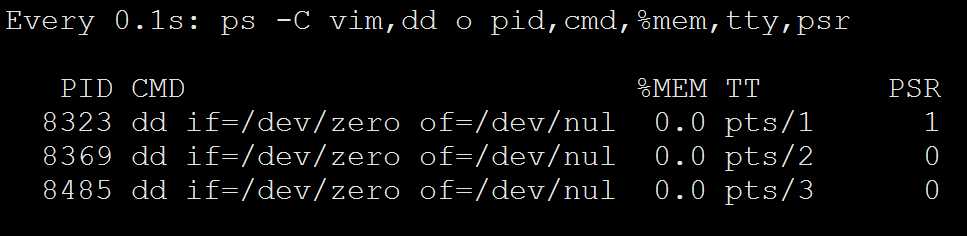
[[email protected] ~]# ps -C vim,dd o pid,cmd,%mem,tty,psr PID CMD %MEM TT PSR 3853 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/1 1 3881 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/2 1 4059 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/3 0 4118 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/4 0
使用watch查看
[[email protected] ~]# watch -n0.1 ps -C vim,dd o pid,cmd,%mem,tty,psr
在6上没有看到变化,在7上看看
开启2个CPU,3个终端
[[email protected] ~]# lscpu Architecture: x86_64 CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit Byte Order: Little Endian CPU(s): 2 On-line CPU(s) list: 0,1 Thread(s) per core: 1 Core(s) per socket: 1 Socket(s): 2 NUMA node(s): 1 Vendor ID: GenuineIntel CPU family: 6 Model: 142 Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7500U CPU @ 2.70GHz Stepping: 9 CPU MHz: 2903.999 BogoMIPS: 5807.99 Hypervisor vendor: VMware Virtualization type: full L1d cache: 32K L1i cache: 32K L2 cache: 256K L3 cache: 4096K NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0,1 Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon nopl xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid rdseed adx smap xsaveopt arat
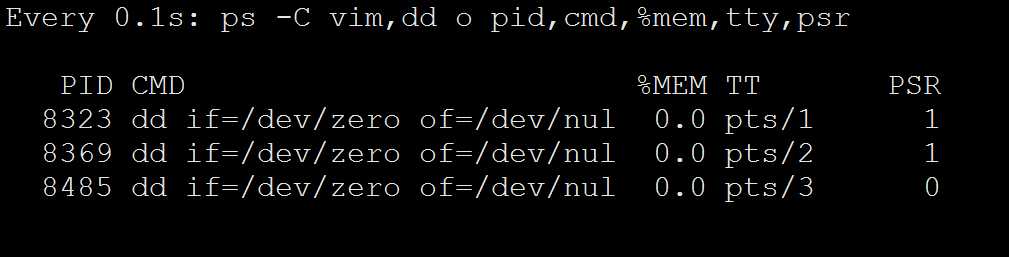
可以很明显的看到变化,说明和版本有关系
7这样可以充分利用CPU资源。避免了一核有难七核围观的尴尬情况
[[email protected] ~]# ps -C vim,dd o pid,cmd,%mem,tty,psr PID CMD %MEM TT PSR 8323 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/1 0 8369 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/2 0 8485 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/3 1 [[email protected] ~]# ps -C vim,dd o pid,cmd,%mem,tty,psr PID CMD %MEM TT PSR 8323 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/1 0 8369 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/2 1 8485 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/nul 0.0 pts/3 1
普通用户wang执行passwd有suid权限,生效的是root
而发起这个进程的用户是wang
[[email protected] ~]# su - wang [[email protected] ~]$ ls [[email protected] ~]$ pwd /home/wang [[email protected] ~]$ passwd Changing password for user wang. Changing password for wang. (current) UNIX password:
[[email protected] ~]# ps -u wang PID TTY TIME CMD 9274 pts/1 00:00:00 bash [[email protected] ~]# ps -U wang PID TTY TIME CMD 9274 pts/1 00:00:00 bash 9390 pts/1 00:00:00 passwd
当普通用户运行具有suid权限的文件时候,身份就变成了这个文件的所有者
[[email protected] ~]# which passwd /usr/bin/passwd [[email protected] ~]# ll /usr/bin/passwd -rwsr-xr-x. 1 root root 27832 Jun 10 2014 /usr/bin/passwd [[email protected] ~]# file /usr/bin/passwd /usr/bin/passwd: setuid ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=1e5735bf7b317e60bcb907f1989951f6abd50e8d, stripped
(8)-p pid 显示指pid对应的进程
[[email protected] ~]# ps -p 1 PID TTY TIME CMD 1 ? 00:00:02 systemd
[[email protected] ~]# ps -p 1 PID TTY TIME CMD 1 ? 00:00:01 init
部分显示进程信息
[[email protected] ~]# ps -p 1 o pid,%mem,cmd PID %MEM CMD 1 0.1 /sbin/init
普通用户执行了passwd
[[email protected] ~]# su - wang [[email protected] ~]$ ls 1.sh [[email protected] ~]$ vim /etc/fstab [[email protected] ~]$ passwd Changing password for user wang. Changing password for wang. (current) UNIX password:
[[email protected] ~]# ps -C passwd o pid,%mem,cmd PID %MEM CMD 5229 0.1 passwd
[[email protected] ~]# su - wang [[email protected] ~]$ ls [[email protected] ~]$ pwd /home/wang [[email protected] ~]$ passwd Changing password for user wang. Changing password for wang. (current) UNIX password:
[[email protected] ~]# ps -C passwd o pid,%mem,cmd PID %MEM CMD 9390 0.1 passwd
常用选项组合ps -ef
C表示CPU的利用率
[[email protected] ~]# ps -ef | head UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 1 0 0 14:12 ? 00:00:01 /sbin/init root 2 0 0 14:12 ? 00:00:00 [kthreadd] root 3 2 0 14:12 ? 00:00:00 [migration/0] root 4 2 0 14:12 ? 00:00:00 [ksoftirqd/0] root 5 2 0 14:12 ? 00:00:00 [stopper/0] root 6 2 0 14:12 ? 00:00:00 [watchdog/0] root 7 2 0 14:12 ? 00:00:01 [events/0] root 8 2 0 14:12 ? 00:00:00 [events/0] root 9 2 0 14:12 ? 00:00:00 [events_long/0]
显示所有进程
[[email protected] ~]# ps -ax | head PID TTY STAT TIME COMMAND 1 ? Ss 0:39 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 22 2 ? S 0:00 [kthreadd] 3 ? S 0:01 [ksoftirqd/0] 5 ? S< 0:00 [kworker/0:0H] 7 ? S 0:00 [migration/0] 8 ? S 0:00 [rcu_bh] 9 ? R 0:09 [rcu_sched] 10 ? S< 0:00 [lru-add-drain] 11 ? S 0:02 [watchdog/0] [[email protected] ~]# ps -ax | tail 3264 ? S 0:02 [kworker/u256:2] 85397 ? S 0:00 pickup -l -t unix -u 86289 ? S 0:00 [kworker/0:0] 86830 ? S 0:00 [kworker/u256:0] 86866 ? S 0:00 [kworker/0:1] 87108 ? S 0:00 [kworker/0:2] 87347 pts/1 R+ 0:00 ps -ax 87348 pts/1 R+ 0:00 tail 103114 ? Ss 0:00 sshd: [email protected]/1 103122 pts/1 Ss 0:00 -bash
[[email protected] ~]# ps -axo pid,cmd,%cpu | head Warning: bad syntax, perhaps a bogus ‘-‘? See /usr/share/doc/procps-3.2.8/FAQ PID CMD %CPU 1 /sbin/init 0.0 2 [kthreadd] 0.0 3 [migration/0] 0.0 4 [ksoftirqd/0] 0.0 5 [stopper/0] 0.0 6 [watchdog/0] 0.0 7 [events/0] 0.0 8 [events/0] 0.0 9 [events_long/0] 0.0
(三)GNU风格的选项
按照命令来排序
[[email protected] ~]# ps -axo pid,cmd,%cpu --sort cmd | head Warning: bad syntax, perhaps a bogus ‘-‘? See /usr/share/doc/procps-3.2.8/FAQ PID CMD %CPU 1761 abrt-dump-oops -d /var/spoo 0.0 1751 /usr/sbin/abrtd 0.0 1379 /usr/sbin/acpid 0.0 37 [aio/0] 0.0 14 [async/mgr] 0.0 23 [ata_aux] 0.0 24 [ata_sff/0] 0.0 1808 /usr/sbin/atd 0.0 1203 auditd 0.0
--ppid pid 显示属于pid的子进程
注意不会显示线程
[[email protected] ~]# pstree -p systemd(1)─┬─NetworkManager(539)─┬─NetworkManager(570) │ └─NetworkManager(572) ├─VGAuthService(526) ├─agetty(552) ├─auditd(501)───auditd(502) ├─crond(545) ├─dbus-daemon(529)───dbus-daemon(538) ├─httpd(2210)─┬─httpd(2212) │ ├─httpd(2213) │ ├─httpd(2214) │ ├─httpd(2215) │ └─httpd(2216) ├─master(849)─┬─pickup(6815) │ └─qmgr(851) ├─polkitd(541)─┬─polkitd(564) │ ├─polkitd(565) │ ├─polkitd(566) │ ├─polkitd(567) │ └─polkitd(568) ├─rsyslogd(766)─┬─rsyslogd(769) │ └─rsyslogd(770) ├─sshd(763)─┬─sshd(1507)───bash(1511) │ ├─sshd(1531)───bash(1535)───pstree(10043) │ ├─sshd(8337)───bash(8345)───dd(8369) │ └─sshd(8457)───bash(8465)───dd(8485) ├─systemd-journal(347) ├─systemd-logind(528) ├─systemd-udevd(372) ├─tuned(765)─┬─tuned(1006) │ ├─tuned(1007) │ ├─tuned(1008) │ └─tuned(1022) └─vmtoolsd(527)───vmtoolsd(553)
[[email protected] ~]# ps --ppid 2210 PID TTY TIME CMD 2212 ? 00:00:00 httpd 2213 ? 00:00:00 httpd 2214 ? 00:00:00 httpd 2215 ? 00:00:00 httpd 2216 ? 00:00:00 httpd
[[email protected] ~]# pstree init─┬─abrt-dump-oops ├─abrtd ├─acpid ├─atd ├─auditd───auditd ├─automount───4*[automount] ├─crond ├─dbus-daemon───dbus-daemon ├─dnsmasq ├─hald─┬─hald-runner─┬─hald-addon-acpi │ │ └─hald-addon-inpu │ └─hald ├─httpd.worker───3*[httpd.worker───26*[httpd.worker]] ├─ksmtuned───sleep ├─libvirtd───10*[libvirtd] ├─master─┬─pickup │ └─qmgr ├─6*[mingetty] ├─rpc.idmapd ├─rpc.mountd ├─rpc.rquotad ├─rpc.statd ├─rpcbind ├─rsyslogd───3*[rsyslogd] ├─sshd─┬─sshd───bash │ └─sshd───bash───pstree ├─udevd───2*[udevd] └─xinetd
[[email protected] ~]# ps --ppid 2298 PID TTY TIME CMD 2300 ? 00:00:00 httpd.worker 2301 ? 00:00:00 httpd.worker 2303 ? 00:00:00 httpd.worker
以上是关于Linux进程管理之ps的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章