MySQL之查询篇(简单查询以及条件)
Posted huiyichanmian
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL之查询篇(简单查询以及条件)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一:查询
1.创建数据库,数据表
-- 创建数据库 create database python_test_1 charset=utf8; -- 使用数据库 use python_test_1; -- students表 create table students( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null, name varchar(20) default ‘‘, age tinyint unsigned default 0, height decimal(5,2), gender enum(‘男‘,‘女‘,‘中性‘,‘保密‘) default ‘保密‘, cls_id int unsigned default 0, is_delete bit default 0 ); -- classes表 create table classes ( id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null, name varchar(30) not null );
2.准备数据
-- 向students表中插入数据 insert into students values (0,‘小明‘,18,180.00,2,1,0), (0,‘小月月‘,18,180.00,2,2,1), (0,‘彭于晏‘,29,185.00,1,1,0), (0,‘刘德华‘,59,175.00,1,2,1), (0,‘黄蓉‘,38,160.00,2,1,0), (0,‘凤姐‘,28,150.00,4,2,1), (0,‘王祖贤‘,18,172.00,2,1,1), (0,‘周杰伦‘,36,NULL,1,1,0), (0,‘程坤‘,27,181.00,1,2,0), (0,‘刘亦菲‘,25,166.00,2,2,0), (0,‘金星‘,33,162.00,3,3,1), (0,‘静香‘,12,180.00,2,4,0), (0,‘郭靖‘,12,170.00,1,4,0), (0,‘周杰‘,34,176.00,2,5,0); -- 向classes表中插入数据 insert into classes values (0, "python_01期"), (0, "python_02期");
3.简单查询
(1)查询所有字段
select * from 表名;
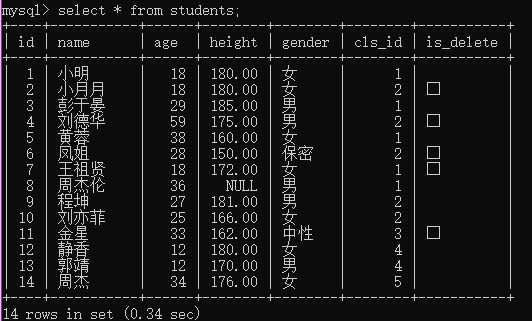
select * from students;
(2)使用as 给字段起别名
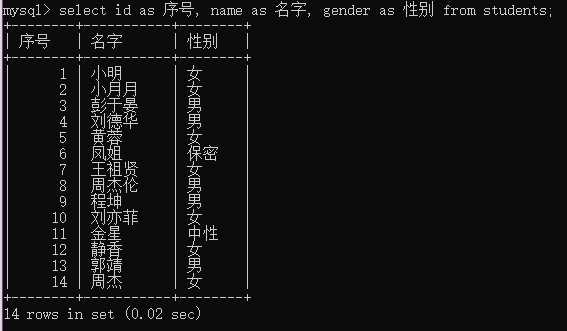
select id as 序号, name as 名字, gender as 性别 from students;
(3)可以通过as 给表起别名
-- 如果是单表查询 可以省略表名 select id, name, gender from students; -- 表名.字段名 select students.id,students.name,students.gender from students; -- 可以通过 as 给表起别名 select s.id,s.name,s.gender from students as s;


(4)消除重复行
在select后面列前使用distinct可以消除重复的行
select distinct 列1,... from 表名;
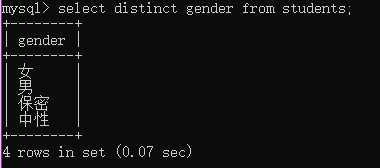
例:select distinct gender from students;
二:条件
使用where子句对表中的数据筛选,结果为true的行会出现在结果集中
1.语法
select * from 表名 where 条件;
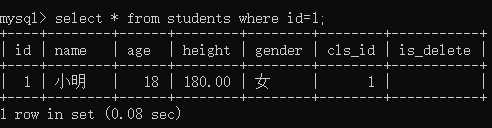
例:select * from students where id=1;
2.where后面支持多种运算符,进行条件的处理
(1)比较运算符
- 等于: =
- 大于: >
- 大于等于: >=
- 小于: <
- 小于等于: <=
- 不等于: != 或 <>
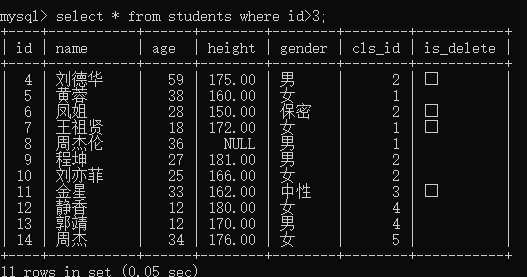
例1:查询编号大于3的学生
select * from students where id>3;
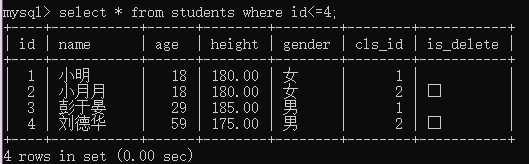
例2:查询编号不大于4的学生
select * from students where id<=4;
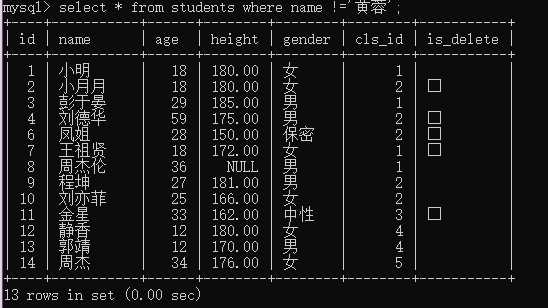
例3:查询姓名不是“黄蓉”的学生
select * from students where name !=‘黄蓉‘;
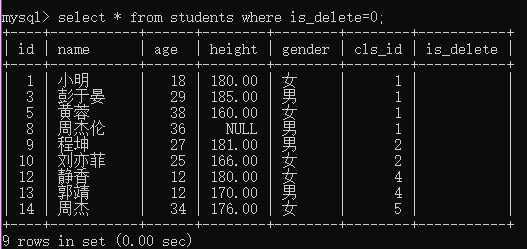
例4:查询没被删除的学生
select * from students where is_delete=0;
(2)逻辑运算符
- and
- or
- not
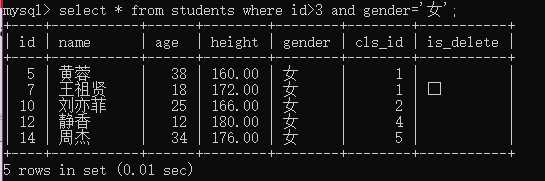
例1:查询编号大于3的女学生
select * from students where id>3 and gender=‘女‘;
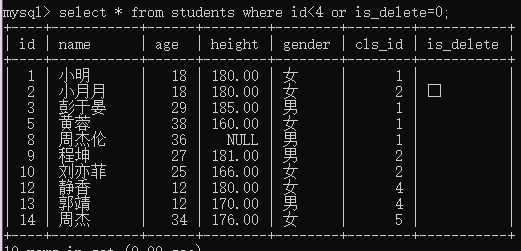
例2:查询编号小于4或没被删除的学生
select * from students where id<4 or is_delete=0;
(3)模糊查询
- like
- %表示任意多个任意字符
- _表示一个任意字符
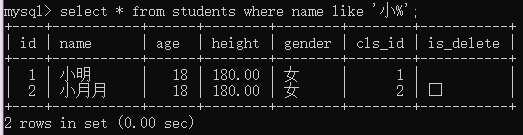
例1:查询姓小的学生;
select * from students where name like ‘小%‘;
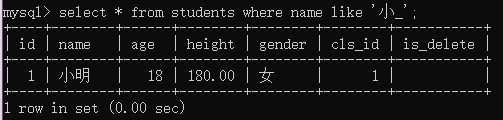
例2:查询姓‘小‘并且“名”是一个字的学生
select * from students where name like ‘小_‘;
例3:查询姓黄或叫靖的学生
select * from students where name like ‘黄%‘ or ‘%靖‘;
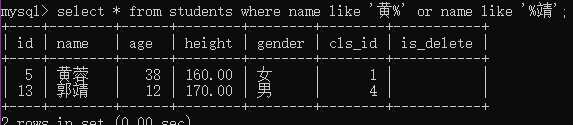
(4)范围查询
- in表示在一个非连续的范围内
- between ... and ...表示在一个连续的范围内
例1:查询编号是1,3或8的学生;
select * from students where id in (1,3,8);
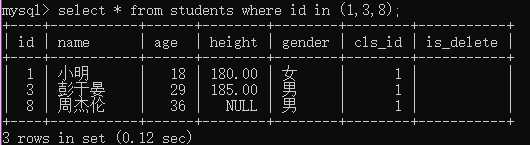
例2:查询编号在3至8之间的学生;
select * from students where id between 3 and 8;
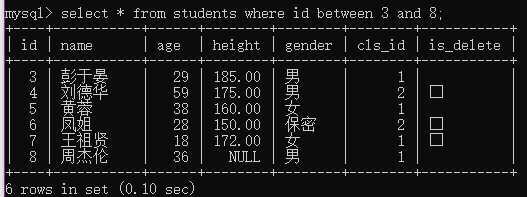
例3:查询编号在3至8之间所有的男生;
select * from students where (id betweent 3 and 8) and gender=1;
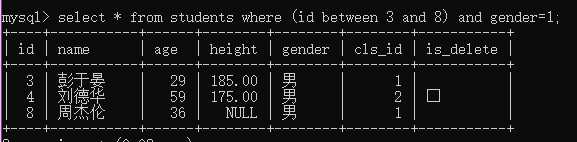
(5)空判断
- 判空is null (注意:null与‘’是不同的)
- 判非空is not null
例1:查询没有填写身高的学生;
select * from students where height is null;

例2:查询填写了身高的学生
select * from students where height is not null;
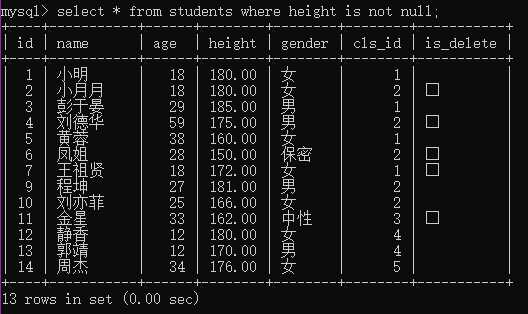
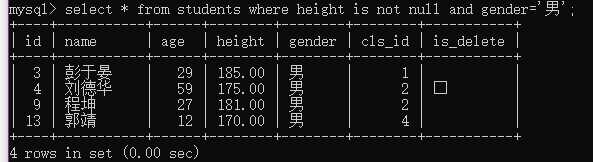
例3:查询填写了身高的男生
select * from students where height is not null and gender=‘男‘;
(6)优先级
- 优先级由高到低的顺序为:小括号,not,比较运算符,逻辑运算符
- and比or先运算,如果同时出现并希望先算or,需要结合()使用
以上是关于MySQL之查询篇(简单查询以及条件)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章