Java基础教程——线程状态
Posted tigerlion
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java基础教程——线程状态相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
线程状态
JAVA定义了6种线程状态:
Thread.State
public enum State
NEW, RUNNABLE, BLOCKED, WAITING, TIMED_WAITING, TERMINATED;
分别是:
- 新建状态·NEW
- 运行状态·RUNNABLE
- 阻塞状态·BLOCKED
- 无限等待状态·WAITING
- 休眠状态·TIMED_WAITING
- 死亡状态·TERMINATED
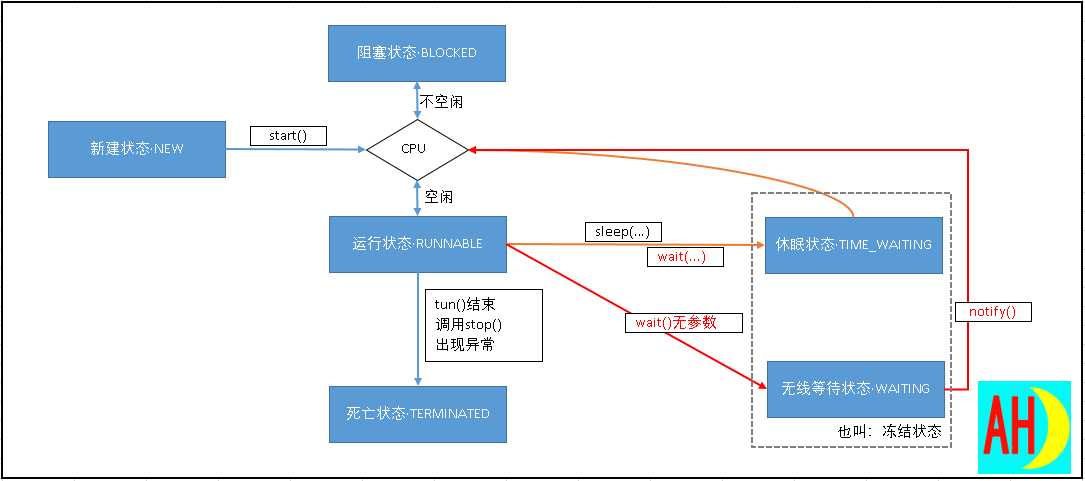
线程不可能一直运行,除非瞬间执行结束。
为了给其他线程执行的机会,正在执行的线程会被中断。线程调度的细节取决于操作系统:
|--现代桌面操作系统和服务器操作系统采用抢占式调度策略,给每个线程一个时间段,时间到了就换其他线程执行,在选择下一线程时会考虑优先级。
|--手机等小型设备可能采用协作式调度策略,需要线程主动放弃占用的资源。
sleep
【运行】→sleep()→【休眠】
public class TestSleep
public static void main(String[] args)
// 获得当前运行的线程
Thread tMain = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("当前运行的线程是:" + tMain.toString());
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
System.out.println(i);
try
// 使当前线程休眠1秒
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("END");
示例:显示时间
一个时间每秒更新,一个时间三秒更新(使用到了GUI)
这个示例用到了JAVA的图形界面编程,必须要继承JLabel类,因此无法继承Thread类,这也体现了Runnable接口的优点。
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class 每秒更新
public static void main(String[] args)
JFrame form1 = new JFrame();
form1.setBounds(300, 300, 350, 100);
form1.setVisible(true);
Container cp = form1.getContentPane();
cp.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1));
cp.add(new ShowDateLabel(1000));
cp.add(new ShowDateLabel(3000));
class ShowDateLabel extends JLabel implements Runnable
private int sleepTime; // 休眠时间
public ShowDateLabel(int sleepTime)
this.sleepTime = sleepTime;
// 启动线程
new Thread(this).start();
public void run()
try
while (true)
// 显示当前时间
this.setText(new Date().toString());
Thread.sleep(sleepTime);
catch (InterruptedException ie)
ie.printStackTrace();
interrupt
中断线程,属于异常,尽量不用
import java.util.Date;
public class SleepInterrupt
public static void main(String[] args)
SleepThread thread = new SleepThread();
thread.start();
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
thread.interrupt();
class SleepThread extends Thread
boolean flag = true;
public void run()
while (flag)
System.out.println("===" + new Date() + "===");
try
sleep(10000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
System.out.println("===Sleep被吵醒===");
return;
yield(礼不下庶人)
yield:屈服,退让
暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程。
有机会被执行的是优先级相同或更高的线程,被yield的线程有可能被重新执行。
public class TestYield
public static void main(String[] args)
ThreadTestYield t1 = new ThreadTestYield("t1");
ThreadTestYield t2 = new ThreadTestYield(" t2");
// 如果t2优先级较低:yield时t1不让t2;sleep(100)时会让
// t2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t1.start();
t2.start();
class ThreadTestYield extends Thread
ThreadTestYield(String s)
super(s);
public void run()
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
try
Thread.sleep(100);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
if (i % 10 == 0)
System.out.println(getName() + ": " + i + ": yield");
yield();
else
System.out.println(getName() + ": " + i);
join(等你做完)
join方法用于“等待线程终止”。
package ahjava.p06thread;
public class _31TestJoin
public static void main(String[] args)
MyThread2 t1 = new MyThread2("abcde");
t1.start();
try
t1.join();// 等子线程先运行
catch (InterruptedException e)
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
System.out.println("i am main thread");
class MyThread2 extends Thread
MyThread2(String s)
super(s);
public void run()
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
System.out.println("i am " + getName());
try
sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
return;
后台线程
线程分为前台线程、后台线程。
前台线程也叫用户线程
后台线程也叫守护线程
JVM的垃圾回收线程就是后台线程。
通过设置thread.setDaemon(true)可以把线程设为后台线程。但是需要在线程启动之前设置。
deamon本是守护神的意思。
前台线程在主线程结束后也要执行完才结束;
后台线程会在前台线程都结束之后自动结束,不会等自己执行完毕。
默认情况下,由前台线程创建的线程仍是前台线程,由后台线程创建的线程仍是后台线程。
public class TestDaemonThread extends Thread
public void run()
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
System.out.println(getName() + " " + i);
System.out.println("-----子线程结束-----");
public static void main(String[] args)
TestDaemonThread t = new TestDaemonThread();
// 设为后台线程,不会看到“子线程结束”语句的输出
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
System.out.println("=====main线程结束=====");
以上是关于Java基础教程——线程状态的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章