吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:使用ggplot2进行高级绘图
Posted tszr
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:使用ggplot2进行高级绘图相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。





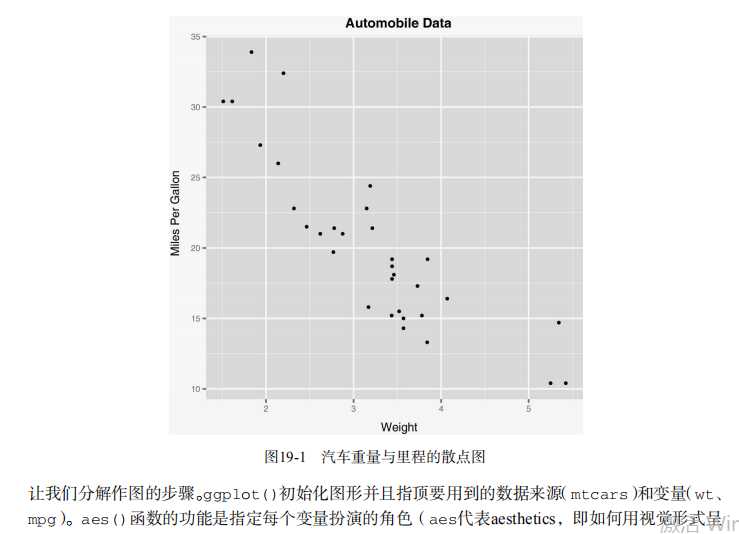

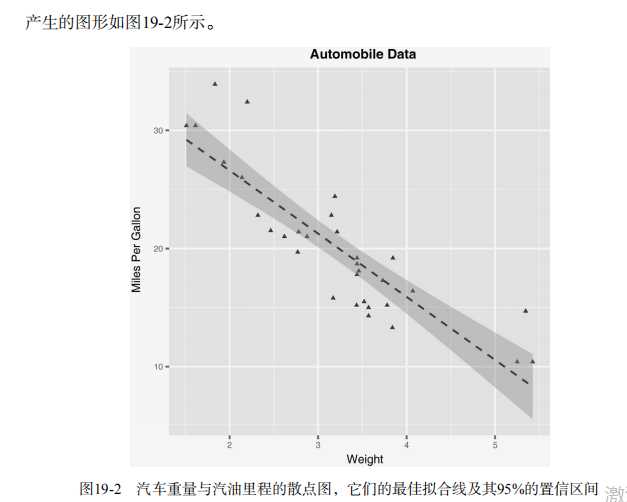


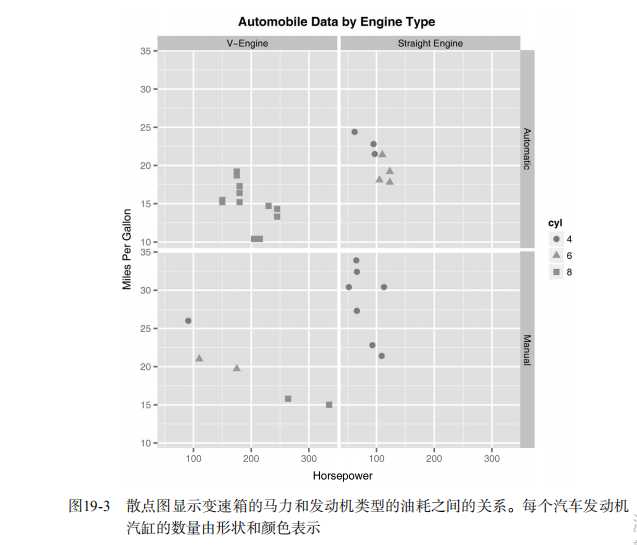


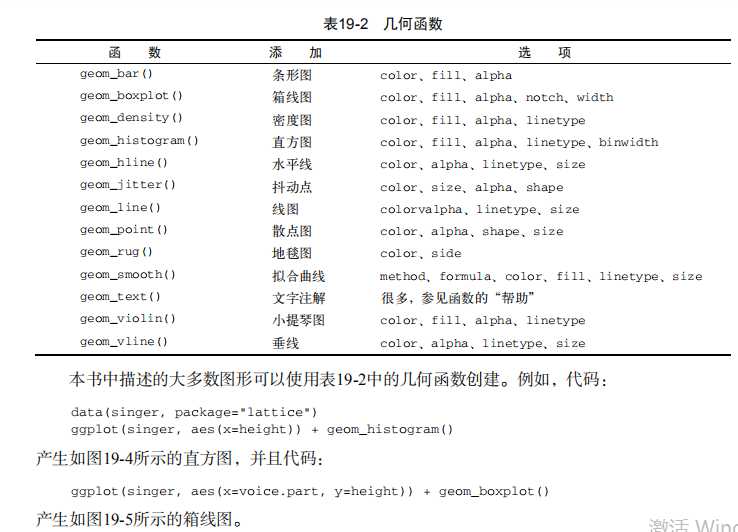

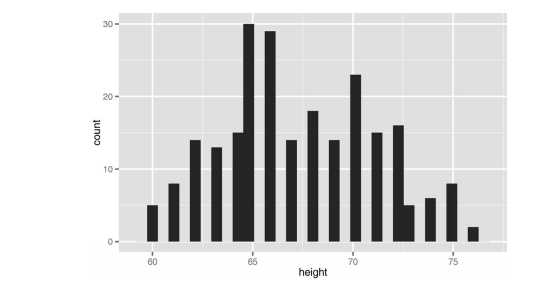
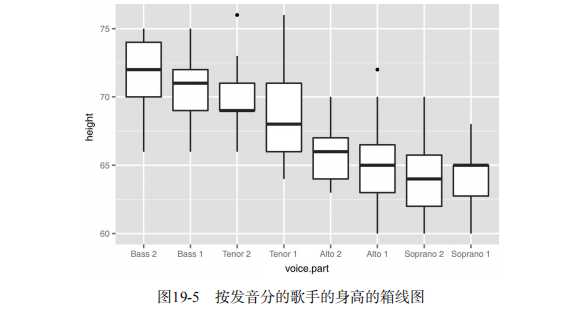
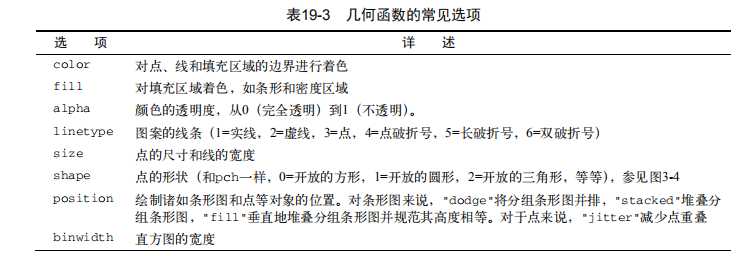

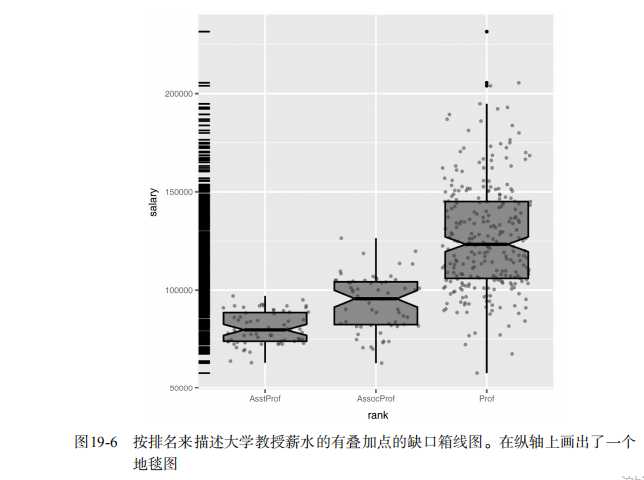


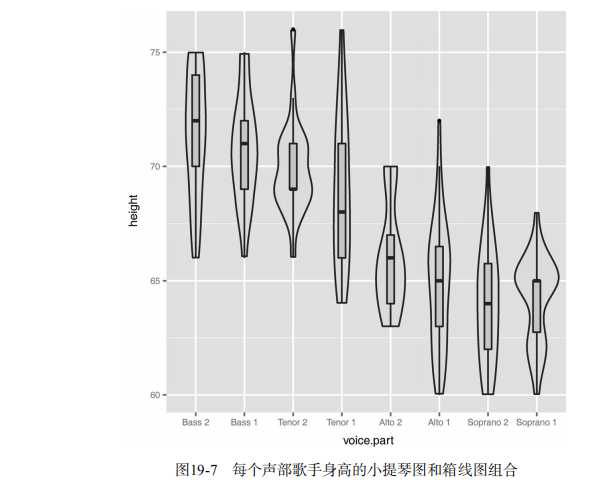

#----------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 19 # # Advanced graphics with ggplot2 # # requires packages ggplot2, RColorBrewer, gridExtra, # # and car (for datasets) # # install.packages(c("ggplot2", "gridExtra", # # "RColorBrewer", "car")) # #----------------------------------------------------------# par(ask=TRUE) # Basic scatterplot library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg)) + geom_point() + labs(title="Automobile Data", x="Weight", y="Miles Per Gallon") # Scatter plot with additional options library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg)) + geom_point(pch=17, color="blue", size=2) + geom_smooth(method="lm", color="red", linetype=2) + labs(title="Automobile Data", x="Weight", y="Miles Per Gallon") # Scatter plot with faceting and grouping data(mtcars) mtcars$am <- factor(mtcars$am, levels=c(0,1), labels=c("Automatic", "Manual")) mtcars$vs <- factor(mtcars$vs, levels=c(0,1), labels=c("V-Engine", "Straight Engine")) mtcars$cyl <- factor(mtcars$cyl) library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=mtcars, aes(x=hp, y=mpg, shape=cyl, color=cyl)) + geom_point(size=3) + facet_grid(am~vs) + labs(title="Automobile Data by Engine Type", x="Horsepower", y="Miles Per Gallon") # Using geoms data(singer, package="lattice") ggplot(singer, aes(x=height)) + geom_histogram() ggplot(singer, aes(x=voice.part, y=height)) + geom_boxplot() data(Salaries, package="car") library(ggplot2) ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=rank, y=salary)) + geom_boxplot(fill="cornflowerblue", color="black", notch=TRUE)+ geom_point(position="jitter", color="blue", alpha=.5)+ geom_rug(side="l", color="black") # Grouping library(ggplot2) data(singer, package="lattice") ggplot(singer, aes(x=voice.part, y=height)) + geom_violin(fill="lightblue") + geom_boxplot(fill="lightgreen", width=.2) data(Salaries, package="car") library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=salary, fill=rank)) + geom_density(alpha=.3) ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=yrs.since.phd, y=salary, color=rank, shape=sex)) + geom_point() ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=rank, fill=sex)) + geom_bar(position="stack") + labs(title=‘position="stack"‘) ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=rank, fill=sex)) + geom_bar(position="dodge") + labs(title=‘position="dodge"‘) ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=rank, fill=sex)) + geom_bar(position="fill") + labs(title=‘position="fill"‘) # Placing options ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=rank, fill=sex))+ geom_bar() ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=rank)) + geom_bar(fill="red") ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=rank, fill="red")) + geom_bar() # Faceting data(singer, package="lattice") library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=singer, aes(x=height)) + geom_histogram() + facet_wrap(~voice.part, nrow=4) library(ggplot2) ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=yrs.since.phd, y=salary, color=rank, shape=rank)) + geom_point() + facet_grid(.~sex) data(singer, package="lattice") library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=singer, aes(x=height, fill=voice.part)) + geom_density() + facet_grid(voice.part~.) # Adding smoothed lines data(Salaries, package="car") library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=yrs.since.phd, y=salary)) + geom_smooth() + geom_point() ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=yrs.since.phd, y=salary, linetype=sex, shape=sex, color=sex)) + geom_smooth(method=lm, formula=y~poly(x,2), se=FALSE, size=1) + geom_point(size=2) # Modifying axes data(Salaries,package="car") library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=rank, y=salary, fill=sex)) + geom_boxplot() + scale_x_discrete(breaks=c("AsstProf", "AssocProf", "Prof"), labels=c("Assistant\\nProfessor", "Associate\\nProfessor", "Full\\nProfessor")) + scale_y_continuous(breaks=c(50000, 100000, 150000, 200000), labels=c("$50K", "$100K", "$150K", "$200K")) + labs(title="Faculty Salary by Rank and Sex", x="", y="") # Legends data(Salaries,package="car") library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=rank, y=salary, fill=sex)) + geom_boxplot() + scale_x_discrete(breaks=c("AsstProf", "AssocProf", "Prof"), labels=c("Assistant\\nProfessor", "Associate\\nProfessor", "Full\\nProfessor")) + scale_y_continuous(breaks=c(50000, 100000, 150000, 200000), labels=c("$50K", "$100K", "$150K", "$200K")) + labs(title="Faculty Salary by Rank and Gender", x="", y="", fill="Gender") + theme(legend.position=c(.1,.8)) # Scales ggplot(mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg, size=disp)) + geom_point(shape=21, color="black", fill="cornsilk") + labs(x="Weight", y="Miles Per Gallon", title="Bubble Chart", size="Engine\\nDisplacement") data(Salaries, package="car") ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=yrs.since.phd, y=salary, color=rank)) + scale_color_manual(values=c("orange", "olivedrab", "navy")) + geom_point(size=2) ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=yrs.since.phd, y=salary, color=rank)) + scale_color_brewer(palette="Set1") + geom_point(size=2) library(RColorBrewer) display.brewer.all() # Themes data(Salaries, package="car") library(ggplot2) mytheme <- theme(plot.title=element_text(face="bold.italic", size="14", color="brown"), axis.title=element_text(face="bold.italic", size=10, color="brown"), axis.text=element_text(face="bold", size=9, color="darkblue"), panel.background=element_rect(fill="white", color="darkblue"), panel.grid.major.y=element_line(color="grey", linetype=1), panel.grid.minor.y=element_line(color="grey", linetype=2), panel.grid.minor.x=element_blank(), legend.position="top") ggplot(Salaries, aes(x=rank, y=salary, fill=sex)) + geom_boxplot() + labs(title="Salary by Rank and Sex", x="Rank", y="Salary") + mytheme # Multiple graphs per page data(Salaries, package="car") library(ggplot2) p1 <- ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=rank)) + geom_bar() p2 <- ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=sex)) + geom_bar() p3 <- ggplot(data=Salaries, aes(x=yrs.since.phd, y=salary)) + geom_point() library(gridExtra) grid.arrange(p1, p2, p3, ncol=3) # Saving graphs ggplot(data=mtcars, aes(x=mpg)) + geom_histogram() ggsave(file="mygraph.pdf")
以上是关于吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:使用ggplot2进行高级绘图的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章