吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:基本图形
Posted tszr
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:基本图形相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。



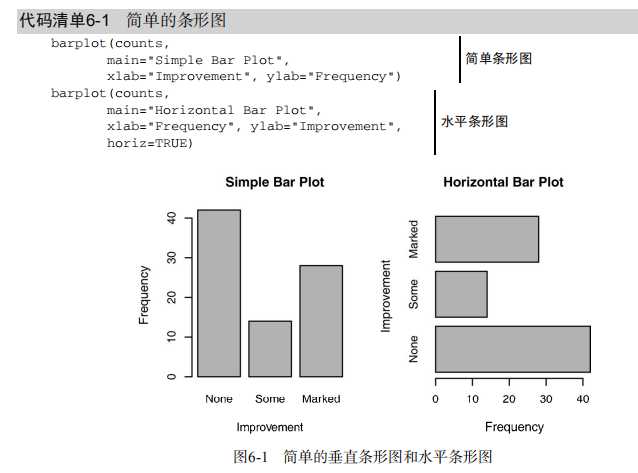


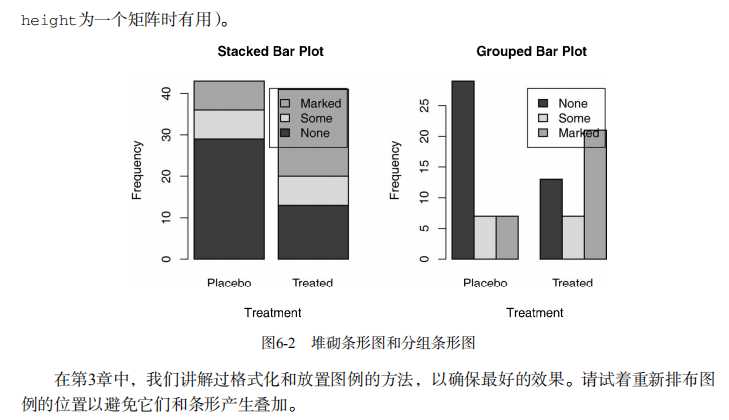

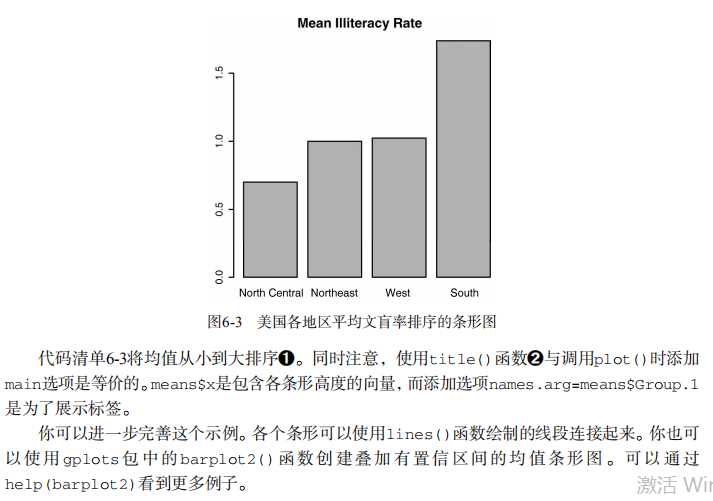

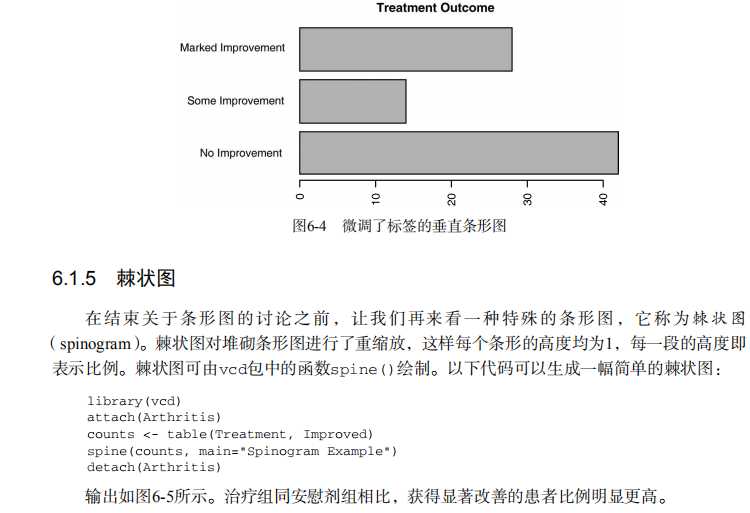
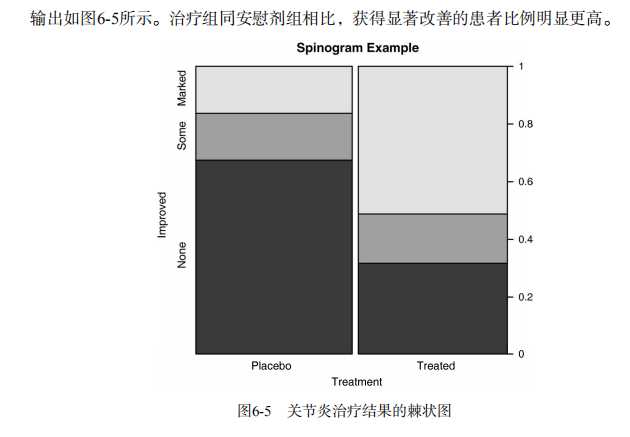

#---------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 6 # # Basic graphs # # requires packages vcd, plotrix, sm, vioplot to be installed # # install.packages(c("vcd", "plotrix", "sm", "vioplot")) # #---------------------------------------------------------------# par(ask=TRUE) opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE) # save original parameter settings library(vcd) counts <- table(Arthritis$Improved) counts # Listing 6.1 - Simple bar plot # vertical barplot barplot(counts, main="Simple Bar Plot", xlab="Improvement", ylab="Frequency") # horizontal bar plot barplot(counts, main="Horizontal Bar Plot", xlab="Frequency", ylab="Improvement", horiz=TRUE) # obtain 2-way frequency table library(vcd) counts <- table(Arthritis$Improved, Arthritis$Treatment) counts # Listing 6.2 - Stacked and grouped bar plots # stacked barplot barplot(counts, main="Stacked Bar Plot", xlab="Treatment", ylab="Frequency", col=c("red", "yellow","green"), legend=rownames(counts)) # grouped barplot barplot(counts, main="Grouped Bar Plot", xlab="Treatment", ylab="Frequency", col=c("red", "yellow", "green"), legend=rownames(counts), beside=TRUE) # Listing 6.3 - Bar plot for sorted mean values states <- data.frame(state.region, state.x77) means <- aggregate(states$Illiteracy, by=list(state.region), FUN=mean) means means <- means[order(means$x),] means barplot(means$x, names.arg=means$Group.1) title("Mean Illiteracy Rate") # Listing 6.4 - Fitting labels in bar plots par(las=2) # set label text perpendicular to the axis par(mar=c(5,8,4,2)) # increase the y-axis margin counts <- table(Arthritis$Improved) # get the data for the bars # produce the graph barplot(counts, main="Treatment Outcome", horiz=TRUE, cex.names=0.8, names.arg=c("No Improvement", "Some Improvement", "Marked Improvement") ) par(opar) # Spinograms library(vcd) attach(Arthritis) counts <- table(Treatment,Improved) spine(counts, main="Spinogram Example") detach(Arthritis) # Listing 6.5 - Pie charts par(mfrow=c(2,2)) slices <- c(10, 12,4, 16, 8) lbls <- c("US", "UK", "Australia", "Germany", "France") pie(slices, labels = lbls, main="Simple Pie Chart") pct <- round(slices/sum(slices)*100) lbls <- paste(lbls, pct) lbls <- paste(lbls,"%",sep="") pie(slices,labels = lbls, col=rainbow(length(lbls)), main="Pie Chart with Percentages") library(plotrix) pie3D(slices, labels=lbls,explode=0.1, main="3D Pie Chart ") mytable <- table(state.region) lbls <- paste(names(mytable), "\\n", mytable, sep="") pie(mytable, labels = lbls, main="Pie Chart from a dataframe\\n (with sample sizes)") par(opar) # Fan plots library(plotrix) slices <- c(10, 12,4, 16, 8) lbls <- c("US", "UK", "Australia", "Germany", "France") fan.plot(slices, labels = lbls, main="Fan Plot") # Listing 6.6 - Histograms # simple histogram 1 hist(mtcars$mpg) # colored histogram with specified number of bins hist(mtcars$mpg, breaks=12, col="red", xlab="Miles Per Gallon", main="Colored histogram with 12 bins") # colored histogram with rug plot, frame, and specified number of bins hist(mtcars$mpg, freq=FALSE, breaks=12, col="red", xlab="Miles Per Gallon", main="Histogram, rug plot, density curve") rug(jitter(mtcars$mpg)) lines(density(mtcars$mpg), col="blue", lwd=2) # histogram with superimposed normal curve (Thanks to Peter Dalgaard) x <- mtcars$mpg h<-hist(x, breaks=12, col="red", xlab="Miles Per Gallon", main="Histogram with normal curve and box") xfit<-seq(min(x),max(x),length=40) yfit<-dnorm(xfit,mean=mean(x),sd=sd(x)) yfit <- yfit*diff(h$mids[1:2])*length(x) lines(xfit, yfit, col="blue", lwd=2) box() # Listing 6.7 - Kernel density plot d <- density(mtcars$mpg) # returns the density data plot(d) # plots the results d <- density(mtcars$mpg) plot(d, main="Kernel Density of Miles Per Gallon") polygon(d, col="red", border="blue") rug(mtcars$mpg, col="brown") # Listing 6.8 - Comparing kernel density plots par(lwd=2) library(sm) attach(mtcars) # create value labels cyl.f <- factor(cyl, levels= c(4, 6, 8), labels = c("4 cylinder", "6 cylinder", "8 cylinder")) # plot densities sm.density.compare(mpg, cyl, xlab="Miles Per Gallon") title(main="MPG Distribution by Car Cylinders") # add legend via mouse click colfill<-c(2:(2+length(levels(cyl.f)))) cat("Use mouse to place legend...","\\n\\n") legend(locator(1), levels(cyl.f), fill=colfill) detach(mtcars) par(lwd=1) # parallel box plots boxplot(mpg~cyl,data=mtcars, main="Car Milage Data", xlab="Number of Cylinders", ylab="Miles Per Gallon") # notched box plots boxplot(mpg~cyl,data=mtcars, notch=TRUE, varwidth=TRUE, col="red", main="Car Mileage Data", xlab="Number of Cylinders", ylab="Miles Per Gallon") # Listing 6.9 - Box plots for two crossed factors # create a factor for number of cylinders mtcars$cyl.f <- factor(mtcars$cyl, levels=c(4,6,8), labels=c("4","6","8")) # create a factor for transmission type mtcars$am.f <- factor(mtcars$am, levels=c(0,1), labels=c("auto","standard")) # generate boxplot boxplot(mpg ~ am.f *cyl.f, data=mtcars, varwidth=TRUE, col=c("gold", "darkgreen"), main="MPG Distribution by Auto Type", xlab="Auto Type") # Listing 6.10 - Violin plots library(vioplot) x1 <- mtcars$mpg[mtcars$cyl==4] x2 <- mtcars$mpg[mtcars$cyl==6] x3 <- mtcars$mpg[mtcars$cyl==8] vioplot(x1, x2, x3, names=c("4 cyl", "6 cyl", "8 cyl"), col="gold") title("Violin Plots of Miles Per Gallon") # dot chart dotchart(mtcars$mpg,labels=row.names(mtcars),cex=.7, main="Gas Mileage for Car Models", xlab="Miles Per Gallon") # Listing 6.11 - Dot plot grouped, sorted, and colored x <- mtcars[order(mtcars$mpg),] x$cyl <- factor(x$cyl) x$color[x$cyl==4] <- "red" x$color[x$cyl==6] <- "blue" x$color[x$cyl==8] <- "darkgreen" dotchart(x$mpg, labels = row.names(x), cex=.7, pch=19, groups = x$cyl, gcolor = "black", color = x$color, main = "Gas Mileage for Car Models\\ngrouped by cylinder", xlab = "Miles Per Gallon")
以上是关于吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:基本图形的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章