Centos7安装Mysql(Mariadb)
Posted quantum-world
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Centos7安装Mysql(Mariadb)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一:安装方式
yum安装(配置yum源)
1- centos官方的yum源
#不同的yum源,软件包的名字也可能不一样,区分大小写 !!!!
2- 阿里云的yum源(下载速度快,但是版本较低)
安装命令如下:
(由于网速问题,我选择用阿里云的精简版)
yum install mariadb-server mariadb
3- mysql官方的yum源 (版本你自由去选择,下载较慢,文件完整性最好)
配置如下方式
1.找到yum仓库目录,创建repo文件
touch /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo
[[email protected] ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d
[[email protected] yum.repos.d]# ls
CentOS-Base.repo epel.repo repobak
[[email protected] yum.repos.d]# touch mariadb.repo
2.添加repo仓库配置 :写入如下内容,指定mysql官方的yum源
[[email protected] yum.repos.d]# vim mariadb.repo
[mariadb]
name = MariaDB
baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.1/centos7-amd64
gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgcheck=1
3.此时yum会自动的加载这个repo文件,读取内容
4.下载mariadb数据库,服务端和客户端
yum install MariaDB-server MariaDB-client
# 或者
yum install MariaDB-server MariaDB-client -y
yum源就是配置在/etc/yum.repos.d/底下的*.repo文件而已二:启动mariadb数据库
#启动MariaDB
systemctl start mariadb
# 启动以后 查看有没有mysql进程
ps -ef | grep mysql
# 查看mysql的网络信息
netstat -tunlp | grep 3306
[[email protected] yum.repos.d]# netstat -tunlp | grep 3306
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 86177/mysqld
mysql -uroot -p
通过客户端连接数据库
mysql有哪些种类的客户端?
mysql -uroot -p
pymysql
navicat(可视化工具)
启动mariadb相关命令
mariadb数据库的相关命令是:
systemctl start mariadb #启动MariaDB
systemctl stop mariadb #停止MariaDB
systemctl restart mariadb #重启MariaDB
systemctl enable mariadb #设置开机启动
三:初始化mysql
3.1:详解
在确认 MariaDB 数据库软件程序安装完毕并成功启动后请不要立即使用。为了确保数据 库的安全性和正常运转,需要先对数据库程序进行初始化操作。这个初始化操作涉及下面 5 个 步骤。
? 设置 root 管理员在数据库中的密码值(注意,该密码并非 root 管理员在系统中的密 码,这里的密码值默认应该为空,可直接按回车键)。
? 设置 root 管理员在数据库中的专有密码。
? 随后删除匿名账户,并使用 root 管理员从远程登录数据库,以确保数据库上运行的业
务的安全性。
? 删除默认的测试数据库,取消测试数据库的一系列访问权限。
? 刷新授权列表,让初始化的设定立即生效。
确保mariadb服务器启动后,执行命令初始化
mysql_secure_installation
3.2:配置信息
# 默认回车
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
# 设置密码 123
Set root password? [Y/n] y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
#移出匿名用户 yes
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
# 允许远程连接
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n
... skipping.
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
# 删除测试数据库
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
# 立即刷新权限表
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
3.3:配置信息图片




四:配置mysql
4.1:中文编码设置
1.中文编码设置,编辑mysql配置文件/etc/my.cnf,下入以下内容
[mysqld]
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_general_ci
log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
[client]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysql]
default-character-set=utf8
修改mariadb数据库的的中文支持
# 一定要在创建数据信息 提前设置这一步 ,要不然会显示拉丁文,在修改会有一些麻烦
\\s 查看数据库编码
# \\s 查看的详细信息内容
"""
MariaDB [(none)]> \\s
--------------
mysql Ver 15.1 Distrib 5.5.60-MariaDB, for Linux (x86_64) using readline 5.1
Connection id: 11
Current database:
Current user: [email protected]
SSL: Not in use
Current pager: stdout
Using outfile: ''
Using delimiter: ;
Server: MariaDB
Server version: 5.5.60-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Protocol version: 10
Connection: Localhost via UNIX socket
Server characterset: latin1 # 为拉丁文
Db characterset: latin1 # 为拉丁文
Client characterset: utf8
Conn. characterset: utf8
UNIX socket: /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
Uptime: 10 min 7 sec
Threads: 1 Questions: 29 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 1 Flush tables: 2 Open tables: 27 Queries per second avg: 0.047
--------------
"""
修改mysql的配置文件,让它支持中文
通过yum安装的配置文件在/etc/my.cnf
vim /etc/my.cnf
配置内容如下:
#服务端的编码添加如下内容
[mysqld]
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_general_ci
# datadir=/var/lib/mysql
# socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
# 自带的这两行不删除
#客户端的编码如下
[client]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysql]
default-character-set=utf8
#重启mariadb生效编码
systemctl restart mariadb
# [[email protected] yum.repos.d]# mysql -uroot -p
# Enter password:
# MariaDB [(none)]> \\s
# 查看编码变为utf8
"""
Server characterset: utf8
Db characterset: utf8
Client characterset: utf8
Conn. characterset: utf8
"""
# 备注
# 如果在创建的时候没有换编码 写入的数据都是拉丁文的、
# 修改为拉丁文的数据库的编码
alter database 数据库名字 default character set 'utf8'
# 修改为拉丁文的表的编码
alte table 表名字 default character set 'utf8'
# 发现 表里的数据还是拉丁文 因为表字段的类型还是拉丁文
# 修改字段的编码
alter table 表名 modify name varchar(30) character set 'ut-8'
# 发现以前表里为拉丁文的数据 还是拉丁文
# 但是此时 新建的数据都是 正常的 utf8 了
4.2:数据库权限设置
mysql使用grant命令对账户进行授权,grant命令常见格式如下
grant 权限 on 数据库.表名 to 账户@主机名 对特定数据库中的特定表授权
grant 权限 on 数据库.* to 账户@主机名 对特定数据库中的所有表给与授权
grant 权限1,权限2,权限3 on *.* to 账户@主机名 对所有库中的所有表给与多个授权
grant all privileges on *.* to 账户@主机名 对所有库和所有表授权所有权限退出数据库,使用root登录,开始权限设置
[[email protected] ~]# mysql -uroot -p
MariaDB [(none)]> use mysql;
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on *.* to [email protected];
MariaDB [mysql]> show grants for [email protected];移除权限
MariaDB [(none)]> revoke all privileges on *.* from [email protected];配置mysql
远程连接设置哦设置所有库,所有表的所有权限,赋值权限给所有ip地址的root用户
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on *.* to [email protected]'%' identified by 'password';
grant all privileges on *.* to [email protected]'%' identified by '123';
[[email protected] yum.repos.d]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password: 123
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on *.* to [email protected]'%' identified by '123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
#创建用户
MariaDB [(none)]> create user 'username'@'%' identified by 'password';
#刷新权限
flush privileges;
五:mysql基本命令
#修改mysql密码
MariaDB [(none)]> set password = PASSWORD('redhat123');生产环境里不会死磕root用户,为了数据库的安全以及和其他用户协同管理数据库,就需要创建其他数据库账户,然后分配权限,满足工作需求。
MariaDB [(none)]> create user [email protected]'127.0.0.1' identified by 'redhat123';
MariaDB [(none)]> use mysql;
MariaDB [mysql]> select host,user,password from user where user='ivan';切换普通用户yuchao,查看数据库信息,发现无法看到完整的数据库列表
[[email protected] ~]# mysql -uivan -p -h 127.0.0.1
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;# 准备数据 先创建一个库 一个表格
# 创建库
MariaDB [(none)]> create databases t1
-> ;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MariaDB server version for the right syntax to use near 'databases t1' at line 1
MariaDB [(none)]> create database t1;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| t1 |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 创建一个表
MariaDB [(none)]> use t1
Database changed
MariaDB [t1]> create table student(id int,name varchar(50));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
# 插入数据
MariaDB [t1]> insert into student values(1,'ivan');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [t1]> select * from student;
+------+------+
| id | name |
+------+------+
| 1 | ivan |
+------+------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)六:数据库备份与恢复
6.1:备份数据库数据
# mysqldump命令用于备份数据库数据
mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases > /tmp/db.dump
导出db1、db2两个数据库的所有数据
mysqldump -uroot -proot --databases db1 db2 >/tmp/user.sql
# 备份命令:
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases > /opt/alldb.sql
[[email protected] ]# mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases > /opt/alldb.sqlEnter password:
[[email protected] ]# cd /opt/
[[email protected] opt]# ls
! luffy_boy Python-3.6.2
07-luffy_project_01 luffy_boy.zip Python-3.6.2.tgz
07-luffy_project_01.zip __MACOSX s20static
alldb.sql node-v8.6.0-linux-x64 tengine-2.3.1
allenv node-v8.6.0-linux-x64.tar.gz tengine-2.3.1.tar.gz
crm python36
6.2:先删除数据库
此为测试,所以先删除一个
进入mariadb数据库,删除一个db
[[email protected] ]# mysql -uroot -p
MariaDB [(none)]> drop database t1
-> ;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> source /opt/alldb.sql
MariaDB [t1]> show databases ;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| t1 |
+--------------------+6.3:数据恢复
方式1:
进入数据库后,用source命令读取sql文件
[mysql] > source /opt/alldb.sql
方式2:
用登录命令导入数据 把刚才重定向备份的数据库文件导入到mysql中
mysql -uroot -p < /opt/alldb.sql
[[email protected] opt]# mysql -uroot -p < /opt/alldb.sql
Enter password:
方式3:
当数据量特别大的时候,以上方式不推荐,使用第三方工具进行导入七:MYSQL主从复制
7.1:详解
MySQL数据库的主从复制方案,是其自带的功能,并且主从复制并不是复制磁盘上的数据库文件,而是通过binlog日志复制到需要同步的从服务器上。
MySQL数据库支持单向、双向、链式级联,等不同业务场景的复制。在复制的过程中,一台服务器充当主服务器(Master),接收来自用户的内容更新,而一个或多个其他的服务器充当从服务器(slave),接收来自Master上binlog文件的日志内容,解析出SQL,重新更新到Slave,使得主从服务器数据达到一致。
主从复制的逻辑有以下几种
一主一从,单向主从同步模式,只能在Master端写入数据
一主多从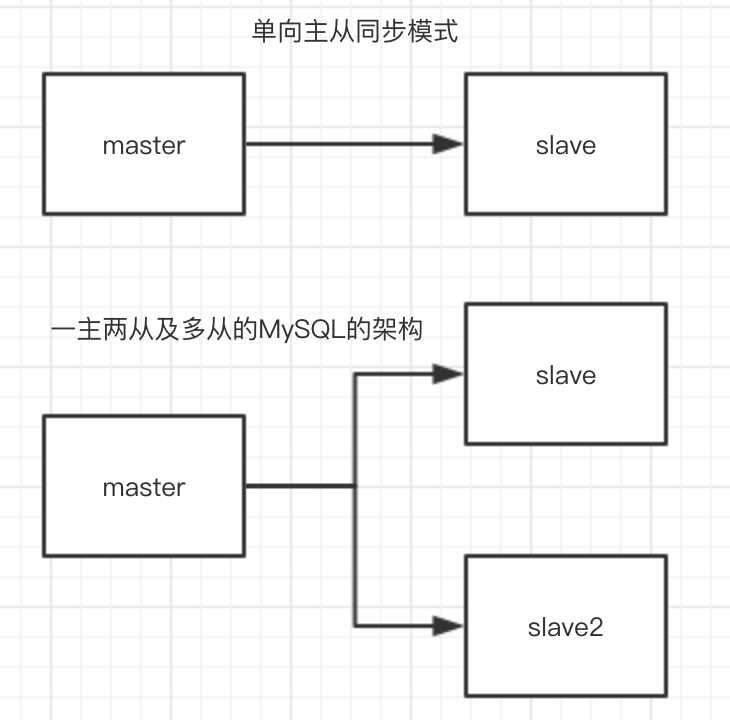
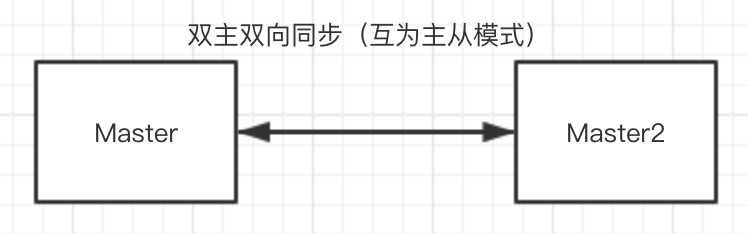
双主主复制逻辑架构,此架构可以在Master1或Master2进行数据写入,或者两端同事写入(特殊设置)
在生产环境中,MySQL主从复制都是异步的复制方式,即不是严格的实时复制,但是给用户的体验都是实时的。
MySQL主从复制集群功能使得MySQL数据库支持大规模高并发读写成为可能,且有效的保护了服务器宕机的数据备份。应用场景
利用复制功能当Master服务器出现问题时,我们可以人工的切换到从服务器继续提供服务,此时服务器的数据和宕机时的数据几乎完全一致。
复制功能也可用作数据备份,但是如果人为的执行drop,delete等语句删除,那么从库的备份功能也就失效了.主从机制实现原理
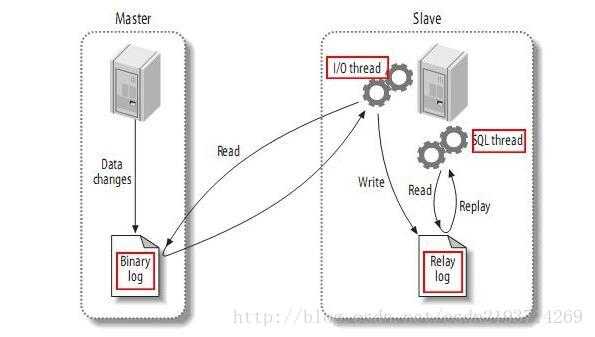
(1) master将改变记录到二进制日志(binary log)中(这些记录叫做二进制日志事件,binary log events);
(2) slave将master的binary log events拷贝到它的中继日志(relay log);
(3) slave重做中继日志中的事件,将改变反映它自己的数据。7.2:master主库配置
环境准备,两台机器分别安装好mariadb数据库
机器1:192.168.190.11 (master机器)
机器2:192.168.190.146 (slave机器)
#查看数据库状态
systemctl status mariadb
#停mariadb
systemctl stop mariadb
1.修改mysql的配置文件,开启binlog日志功能
vim /etc/my.cnf,写入如下信息
vim /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
server-id=1
log-bin=s20mysql-bin
# s20mysql-bin 这个名字随便起
修改完如下:
[mysqld]
server-id=1
log-bin=mysql-bin
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_general_ci
2.重启数据库生效binlog日志文件
systemctl start mariadb
[[email protected] opt]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show variables like '%log_bin%';
+---------------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------------------------+-------+
| log_bin | OFF |
| log_bin_trust_function_creators | OFF |
| sql_log_bin | ON |
+---------------------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 遇到一个坑 配置完vim /etc/my.cnf
# systemctl start mariadb 重启数据 还是不显示
# MariaDB [(none)]> show master status;
# Empty set (0.00 sec)
# 把数据库停止在重新开 就好了
#停mariadb
systemctl stop mariadb
# 再次查看状态信息
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status;
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
| File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB |
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
| mysql-bin.000001 | 245 | | |
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show variables like '%log_bin%';
+---------------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------------------------+-------+
| log_bin | ON |
| log_bin_trust_function_creators | OFF |
| sql_log_bin | ON |
+---------------------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.在主库上,创建一个用户,用于主从复制
新建用于主从同步的用户ivan,允许登录的从库是'%' 所有
create user 'ivan'@'%' identified by 'ivan123';
MariaDB [t1]> create user 'ivan'@'%' identified by 'ivan123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
# 补充
新建用于主从同步的用户ivan,允许登录的从库是'192.168.178.130'
create user 'ivan'@'192.168.178.130' identified by 'redhat';
# 题外话:如果提示密码太简单不复合策略加在前面加这句
mysql> set global validate_password_policy=0;4.给这个ivan账号,授予slave的身份
grant replication slave on *.* to 'ivan'@'%';
MariaDB [t1]> grant replication slave on *.* to 'ivan'@'%';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
#
.给从库账号授权,说明给ivan从库复制的权限,在192.168.178.130机器上复制
grant replication slave on *.* to 'ivan'@'192.168.178.130';
#检查主库创建的复制账号
select user,host from mysql.user;
#检查授权账号的权限
show grants for [email protected]'192.168.178.130';5.进行锁表,防止数据写入
# 实现对主数据库锁表只读,防止数据写入,数据复制失败
flush table with read lock;
# 锁上 就没法 crate database了
# 没有锁表之前 插入数据 就会变位置信息
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status;
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
| File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB |
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
| mysql-bin.000001 | 245 | | |
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> create database t2;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
# 检查主库的状态
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status;
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
| File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB |
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
| mysql-bin.000001 | 324 | | |
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
# File是二进制日志文件名,Position 是日志开始的位置。
MariaDB [(none)]> flush table with read lock;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> create database t3;
ERROR 1223 (HY000): Can't execute the query because you have a conflicting read lock
# 锁上 就没法 crate database了6.导出此时的主库数据,发送给从库,保证起点一致性
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases > /tmp/alldb.sql
scp /tmp/alldb.sql [email protected]:/tmp/
scp /tmp/alldb.sql [email protected]:/tmp/
[[email protected] opt]# mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases > /tmp/alldb.sql
Enter password: # 密码是数据库的密码 123
[[email protected] opt]# scp /tmp/alldb.sql [email protected]:/tmp/
[email protected]'s password:
alldb.sql 100% 504KB 4.6MB/s 00:00
[[email protected] opt]#
# 此步骤 注意传输的文件大小 如果传输的为0k ,需要重新传输
7.当从库配置好复制之后,回到这里解锁,写入数据,查看从库数据是否写入
unlock tables;
MariaDB [(none)]> unlock tables;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
7.3:slave从库配置
机器2:192.168.190.146 (slave主机)
1.修改从库机器的配置文件,开启id,以及只读模式
vim /etc/my.cnf 如下
[mysqld]
server-id=1000
read-only=true
# 修改完如下:
[mysqld]
server-id=1000
read-only=true
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
# 设置server-id值并关闭binlog功能参数
# 数据库的server-id在主从复制体系内是唯一的,Slave的server-id要与主库和其他从库不同,并且注释掉Slave的binlog参数。2.重启从库
systemctl restart mariadb
#1 把主发过来的导入过来
[[email protected] yum.repos.d]# mysql -uroot -p < /tmp/alldb.sql
Enter password:
# 此为数据库的密码 当前没有配置密码 直接回车就ok
# 2 查看导入过来的数据成功
[[email protected] tmp]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \\g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 10
Server version: 5.5.60-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\\h' for help. Type '\\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| t1 |
| t2 |
| test |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]>
# 默认的多一个test数据库 ,删除即可
MariaDB [(none)]> drop database test;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| t1 |
| t2 |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 此时把 主的数据库的密码也导入过来了
# 进入数据库的时候需要输入主库的密码
[[email protected] tmp]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
# 进入数据库的时候需要输入主的密码
# 检查Slava从数据库的各项参数
show variables like 'log_bin';
show variables like 'server_id';
MariaDB [(none)]> show variables like 'log_bin';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| log_bin | OFF |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3.一条命令,建立主从之间的复制关系
# 配置复制的参数,Slave从库连接Master主库的配置
change master to master_host='192.168.190.11',
master_user='ivan',
master_password='ivan123',
master_log_file='mysql-bin.000001',
master_log_pos=324;
# 主库的名字
# 主库的位置 起始点
MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host='192.168.190.11',
-> master_user='ivan',
-> master_password='ivan123',
-> master_log_file='mysql-bin.000001',
-> master_log_pos=324;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)4.开启从库的slave功能
start slave;
MariaDB [(none)]> start slave;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)5.查看从库的状态,检测是否复制成功
show slave status\\G
"""
MariaDB [(none)]> show slave status\\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event
Master_Host: 192.168.190.11
Master_User: ivan
Master_Port: 3306
Connect_Retry: 60
Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000001
Read_Master_Log_Pos: 324
Relay_Log_File: mariadb-relay-bin.000002
Relay_Log_Pos: 529
Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000001
Slave_IO_Running: Yes
Slave_SQL_Running: Yes
Replicate_Do_DB:
....
"""
查看如下两个参数是否是yes,主从复制即为正确
Slave_IO_Running: Yes
Slave_SQL_Running: Yes
# 跳到主库配置第7部 解锁 写入数据 查看是否同步成功
注意一个问题:
# 此时从数据库是用root登录的 ,在从数据库创建数据 会创建成功,root的权限比较大
# 但是在主数据库不会显示,因为不会同步
解决
在主数据库上面操作
grant select on *.* to [email protected]"%";
MariaDB [(none)]> grant select on *.* to [email protected]"%";
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
从数据库:
[[email protected] tmp]# mysql -uivan -p
Enter password:
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| 同步成功 |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| t1 |
| t2 |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> create database t3;
ERROR 1290 (HY000): The MariaDB server is running with the --read-only option so it cannot execute this statement
MariaDB [(none)]> tip:
注意此处还未配置从库的只读模式,只需在slave服务器上配置/etc/my.cnf,加上以下配置,并且在slave上创建普通用户,使用普通用户主从同步即可达到只读的效果
如果用root用户,无法达到readonly,这是一个坑[mysqld]
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_general_ci
log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
server-id=3
read-only=true
[client]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysql]
default-character-set=utf8以上是关于Centos7安装Mysql(Mariadb)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章