无同步方案
Posted yjxyy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了无同步方案相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
??要保证线程安全,并不一定就要进行同步,如果一个方法本来就不涉及共享数据,那么它就不需要任何的同步措施去保证数据的安全。
1.栈封闭
??多个线程访问同一个方法的局部变量时,不会出现线程安全问题,因为局部变量保存在虚拟机栈中,属于线程的私有区域,所以不会出现线程安全性。
package ConcurrentExemple;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class StackClosedExemple
public void add100()
int cnt=0; //方法内的局部变量保存在每个线程私有的虚拟机栈中,所以在多线程情况下不会发生数据不安全。
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
cnt++;
System.out.println(cnt);
public static void main(String[]args)
StackClosedExemple stackClosedExemple=new StackClosedExemple();
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executorService.execute(()->stackClosedExemple.add100());
executorService.execute(()->stackClosedExemple.add100());
executorService.shutdown();
100
1002.线程本地存储
??如果一段代码中所需要的数据必须与其他的代码共享,那就看看这些共享数据是否能在一个线程内执行,如果可以保证,那么我们就可以将共享数据的可见范围限制在同一个线程之中,这样无需同步,也可以保证多个线程之间不出现数据争用的情况。
??可以使用java.lang.ThreadLocal类来实现线程本地存储功能。
???ThreadLocal变量是一个不同线程可以拥有不同值的变量,所有的线程可以共享同一个ThreadLocal对象。但是不同的线程的ThreadLocal变量可以取不同的值,而且任意一个线程的值发生变化,不会影响其他的线程,分别用set()和get()方法对ThreadLocal变量进行赋值和查看其值。
???对于以下代码,thread1中设置threadLocal为1,而thread2设置threadLocal为2,过一段时间thread1访问threadLocal仍然是1,不受thread2的影响。
package ConcurrentExemple;
public class ThreadLocalExemple
public static void main(String[]args)
ThreadLocal threadLocal=new ThreadLocal();
Thread thread1=new Thread(()->
threadLocal.set(1);
try
Thread.sleep(3000);
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.remove();
);
Thread thread2=new Thread(()->
threadLocal.set(2);
threadLocal.remove();
);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
public class ThreadLocaExemple1
public static void main(String[]args)
ThreadLocal threadLocal1=new ThreadLocal();
ThreadLocal threadLocal2=new ThreadLocal();
Thread thread1=new Thread(()->
threadLocal1.set(1);
threadLocal2.set(2);
System.out.println(threadLocal1.get());
System.out.println(threadLocal2.get());
);
Thread thread2=new Thread(()->
threadLocal1.set(3);
threadLocal2.set(4);
);
thread1.start();
thread1.start();
它对应的底层结构图为:
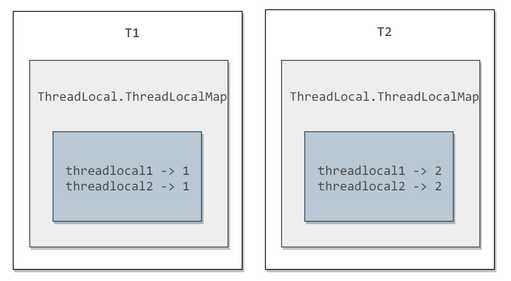
??每个Thread都有一个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap对象。
??当调用一个ThreadLocal的set(T value)方法时,先得到当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象,然后将ThreadLocal->value键值对放进Map中。
set()方法源码如下:
public void set(T value)
Thread t=Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map=getMap(t);
if(map!=null)
map.set(this,value);
else
creatMap(t,value);
get()方法源码如下:
public T get()
Thread t=Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap=getMap(t);
if(map!=nulll)
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e=map.getEntry(this)
if(e!=null)
T result=(T)e.value;
return result;
return setInitialValue();
??ThreadLcoal从理论上来讲不是用来解决多线程并发问题的,因为根本不存在多线程竞争。
??在一些场景下(尤其是使用线程池),由于ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap的底层数据结构导致ThreadLocal有内存泄露的情况,所以我们应该尽可能的在使用ThreadLocal后手动的调用remove()方法,以避免这种情况的发生。
以上是关于无同步方案的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章