spring源码阅读 Bean加载之默认标签加载
Posted aquariusm
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring源码阅读 Bean加载之默认标签加载相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
接着上文的内容,我们经历了xml资源文件的校验/解析/终于要进入到Bean的加载中了。
上文进行到:
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for(int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); ++i) Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) Element ele = (Element)node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) this.parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); else delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); else delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
这里,加载代理类的一个判断是否是默认命名空间的标签,把过程分为两个步骤,我们先来看第一个分支,即默认标签的解析。
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, "import")) this.importBeanDefinitionResource(ele); else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, "alias")) this.processAliasRegistration(ele); else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, "bean")) this.processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate); else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, "beans")) this.doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
默认的这几个根标签的解析,我们就从最关注的"bean"标签解析开始吧。即:this.processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate)。
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele); // 1 if (bdHolder != null) bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder); // 2 try BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, this.getReaderContext().getRegistry()); // 3 catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException var5) this.getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name ‘" + bdHolder.getBeanName() + "‘", ele, var5); this.getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder)); // 4
这里分为几个步骤:
1: 把ele元素解析为我们需要的 BeanDefinitionHolder 对象。
2: 判断子元素中,是否有自定义标签,如果有调用自定义标签的处理Handle进行处理,并获取返回的bdHolder
3: 将解析到的bdHolder注册到我们的配置读取上下文的注册表中
4: 触发Bean注册完成的事件通知
理完思路,那我们就从第一个步骤开始,即把ele xml节点翻译成我们的BeanDefinition对象。
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) String id = ele.getAttribute("id"); String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute("name"); List<String> aliases = new ArrayList(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, ",; "); aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr)); String beanName = id; if (!StringUtils.hasText(id) && !aliases.isEmpty()) beanName = (String)aliases.remove(0); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) this.logger.debug("No XML ‘id‘ specified - using ‘" + beanName + "‘ as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases"); if (containingBean == null) this.checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele); AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = this.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean); if (beanDefinition != null) if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) try if (containingBean != null) beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true); else beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition); String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName(); if (beanClassName != null && beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() && !this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) aliases.add(beanClassName); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) this.logger.debug("Neither XML ‘id‘ nor ‘name‘ specified - using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]"); catch (Exception var9) this.error(var9.getMessage(), ele); return null; String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases); return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray); else return null;
这里首先获取AbstractBeanDefinition对象,然后组装成BeanDefinitionHolder。查看parseBeanDefinitionElement 的代码
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName)); String className = null; if (ele.hasAttribute("class")) className = ele.getAttribute("class").trim(); try String parent = null; if (ele.hasAttribute("parent")) parent = ele.getAttribute("parent"); AbstractBeanDefinition bd = this.createBeanDefinition(className, parent); this.parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd); bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, "description")); this.parseMetaElements(ele, bd); this.parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); this.parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); this.parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd); this.parsePropertyElements(ele, bd); this.parseQualifierElements(ele, bd); bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource()); bd.setSource(this.extractSource(ele)); AbstractBeanDefinition var7 = bd; return var7; catch (ClassNotFoundException var13) this.error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, var13); catch (NoClassDefFoundError var14) this.error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, var14); catch (Throwable var15) this.error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, var15); finally this.parseState.pop(); return null;
看这句createBeanDefinition(className, parent),跟进代码到BeanDefinitionReaderUtils的createBeanDefinition方法
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(String parentName, String className, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition(); bd.setParentName(parentName); if (className != null) if (classLoader != null) bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader)); else bd.setBeanClassName(className); return bd;
这里创建的是一个GenericBeanDefinition对象。AbstractBeanDefinition一共有三个子类
GenericBeanDefinition
ChildBeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition
暂时没看到Root和Child的应用,我们这里就只关注下这个GenericBeanDefinition。className不为空,classLoader为空,那么只设置下BeanCassName属性。
继续解析:
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean, AbstractBeanDefinition bd) if (ele.hasAttribute("singleton")) this.error("Old 1.x ‘singleton‘ attribute in use - upgrade to ‘scope‘ declaration", ele); else if (ele.hasAttribute("scope")) bd.setScope(ele.getAttribute("scope")); else if (containingBean != null) bd.setScope(containingBean.getScope()); if (ele.hasAttribute("abstract")) bd.setAbstract("true".equals(ele.getAttribute("abstract"))); String lazyInit = ele.getAttribute("lazy-init"); if ("default".equals(lazyInit)) lazyInit = this.defaults.getLazyInit(); bd.setLazyInit("true".equals(lazyInit)); String autowire = ele.getAttribute("autowire"); bd.setAutowireMode(this.getAutowireMode(autowire)); String dependencyCheck = ele.getAttribute("dependency-check"); bd.setDependencyCheck(this.getDependencyCheck(dependencyCheck)); String autowireCandidate; if (ele.hasAttribute("depends-on")) autowireCandidate = ele.getAttribute("depends-on"); bd.setDependsOn(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(autowireCandidate, ",; ")); autowireCandidate = ele.getAttribute("autowire-candidate"); String destroyMethodName; if (!"".equals(autowireCandidate) && !"default".equals(autowireCandidate)) bd.setAutowireCandidate("true".equals(autowireCandidate)); else destroyMethodName = this.defaults.getAutowireCandidates(); if (destroyMethodName != null) String[] patterns = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(destroyMethodName); bd.setAutowireCandidate(PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(patterns, beanName)); if (ele.hasAttribute("primary")) bd.setPrimary("true".equals(ele.getAttribute("primary"))); if (ele.hasAttribute("init-method")) destroyMethodName = ele.getAttribute("init-method"); if (!"".equals(destroyMethodName)) bd.setInitMethodName(destroyMethodName); else if (this.defaults.getInitMethod() != null) bd.setInitMethodName(this.defaults.getInitMethod()); bd.setEnforceInitMethod(false); if (ele.hasAttribute("destroy-method")) destroyMethodName = ele.getAttribute("destroy-method"); if (!"".equals(destroyMethodName)) bd.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName); else if (this.defaults.getDestroyMethod() != null) bd.setDestroyMethodName(this.defaults.getDestroyMethod()); bd.setEnforceDestroyMethod(false); if (ele.hasAttribute("factory-method")) bd.setFactoryMethodName(ele.getAttribute("factory-method")); if (ele.hasAttribute("factory-bean")) bd.setFactoryBeanName(ele.getAttribute("factory-bean")); return bd;
这里解析各种bd的属性,并设置到bd对象里。这些属性比如init-method / destroy-method / lazy-init 这些我们经常使用的,还有些不熟悉的,可以到时候用到的时候查看了解下。
下面解析META元素:
public void parseMetaElements(Element ele, BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor attributeAccessor) NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes(); for(int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); ++i) Node node = nl.item(i); if (this.isCandidateElement(node) && this.nodeNameEquals(node, "meta")) Element metaElement = (Element)node; String key = metaElement.getAttribute("key"); String value = metaElement.getAttribute("value"); BeanMetadataAttribute attribute = new BeanMetadataAttribute(key, value); attribute.setSource(this.extractSource(metaElement)); attributeAccessor.addMetadataAttribute(attribute);
遍历所有meta标签,创建BeanMetaAttribute属性,并添加到bd中,这里向上转型到了BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor类。这里还是很清晰的,接口该做什么事情,还是分开的很清楚的。这里是架构设计里 接口隔离原则的体现。不同接口里,做的事情是不一样的,并不混在一起,这样当一个部分需要改动的时候,不会影响另一个部分。我的理解。
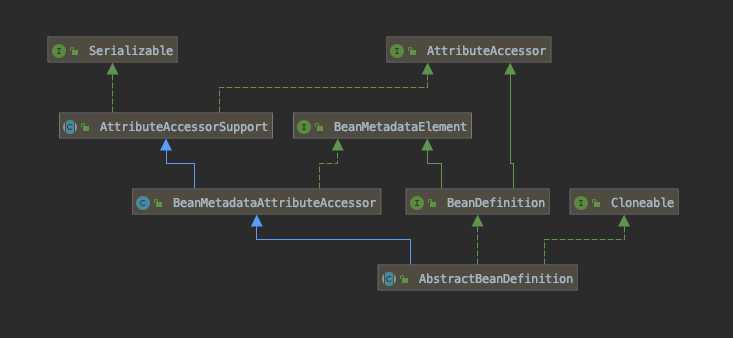
继续:解析lookup-method元素
public void parseLookupOverrideSubElements(Element beanEle, MethodOverrides overrides) NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes(); for(int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); ++i) Node node = nl.item(i); if (this.isCandidateElement(node) && this.nodeNameEquals(node, "lookup-method")) Element ele = (Element)node; String methodName = ele.getAttribute("name"); String beanRef = ele.getAttribute("bean"); LookupOverride override = new LookupOverride(methodName, beanRef); override.setSource(this.extractSource(ele)); overrides.addOverride(override);
添加到db的overrides属性里了。
解析:replaced-method 根look-method标签类似不再赘述
解析:constructor-arg 标签,构造函数标签比较常见,这里也相对复杂些,至少从代码上看
public void parseConstructorArgElements(Element beanEle, BeanDefinition bd) NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes(); for(int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); ++i) Node node = nl.item(i); if (this.isCandidateElement(node) && this.nodeNameEquals(node, "constructor-arg")) this.parseConstructorArgElement((Element)node, bd);
先遍历元素,然后具体的操作,由parseConstructorArgElement方法来负责
public void parseConstructorArgElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) String indexAttr = ele.getAttribute("index"); String typeAttr = ele.getAttribute("type"); String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute("name"); if (StringUtils.hasLength(indexAttr)) try int index = Integer.parseInt(indexAttr); if (index < 0) this.error("‘index‘ cannot be lower than 0", ele); else try this.parseState.push(new ConstructorArgumentEntry(index)); Object value = this.parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, (String)null); ValueHolder valueHolder = new ValueHolder(value); if (StringUtils.hasLength(typeAttr)) valueHolder.setType(typeAttr); if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) valueHolder.setName(nameAttr); valueHolder.setSource(this.extractSource(ele)); if (bd.getConstructorArgumentValues().hasIndexedArgumentValue(index)) this.error("Ambiguous constructor-arg entries for index " + index, ele); else bd.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(index, valueHolder); finally this.parseState.pop(); catch (NumberFormatException var19) this.error("Attribute ‘index‘ of tag ‘constructor-arg‘ must be an integer", ele); else try this.parseState.push(new ConstructorArgumentEntry()); Object value = this.parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, (String)null); ValueHolder valueHolder = new ValueHolder(value); if (StringUtils.hasLength(typeAttr)) valueHolder.setType(typeAttr); if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) valueHolder.setName(nameAttr); valueHolder.setSource(this.extractSource(ele)); bd.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(valueHolder); finally this.parseState.pop();
先获取index/type/name属性,然后根据有没有index属性类分别处理
如果有index属性,那么获取value,并创建valueHolder最终添加到constructorArgumentValues 中。
来看具体的获取value的过程
public Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String propertyName) String elementName = propertyName != null ? "<property> element for property ‘" + propertyName + "‘" : "<constructor-arg> element"; NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes(); Element subElement = null; for(int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); ++i) Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element && !this.nodeNameEquals(node, "description") && !this.nodeNameEquals(node, "meta")) if (subElement != null) this.error(elementName + " must not contain more than one sub-element", ele); else subElement = (Element)node; boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.hasAttribute("ref"); boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.hasAttribute("value"); if (hasRefAttribute && hasValueAttribute || (hasRefAttribute || hasValueAttribute) && subElement != null) this.error(elementName + " is only allowed to contain either ‘ref‘ attribute OR ‘value‘ attribute OR sub-element", ele); if (hasRefAttribute) String refName = ele.getAttribute("ref"); if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) this.error(elementName + " contains empty ‘ref‘ attribute", ele); RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName); ref.setSource(this.extractSource(ele)); return ref; else if (hasValueAttribute) TypedStringValue valueHolder = new TypedStringValue(ele.getAttribute("value")); valueHolder.setSource(this.extractSource(ele)); return valueHolder; else if (subElement != null) return this.parsePropertySubElement(subElement, bd); else this.error(elementName + " must specify a ref or value", ele); return null;
获取value的过程分为几个主要部分,根据是ref类型,还是value类型不同,或者是子元素类型,操作不同
如果是ref类型,创建RuntimeBeanReference对象;如果是value类型,则封装为TypedStringVlue类型。如果是子元素类型,则继续由parsePropertySubElement处理
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) return this.parsePropertySubElement(ele, bd, (String)null); public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String defaultValueType) if (!this.isDefaultNamespace((Node)ele)) return this.parseNestedCustomElement(ele, bd); else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "bean")) BeanDefinitionHolder nestedBd = this.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, bd); if (nestedBd != null) nestedBd = this.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, nestedBd, bd); return nestedBd; else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "ref")) String refName = ele.getAttribute("bean"); boolean toParent = false; if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) refName = ele.getAttribute("local"); if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) refName = ele.getAttribute("parent"); toParent = true; if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) this.error("‘bean‘, ‘local‘ or ‘parent‘ is required for <ref> element", ele); return null; if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) this.error("<ref> element contains empty target attribute", ele); return null; else RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName, toParent); ref.setSource(this.extractSource(ele)); return ref; else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "idref")) return this.parseIdRefElement(ele); else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "value")) return this.parseValueElement(ele, defaultValueType); else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "null")) TypedStringValue nullHolder = new TypedStringValue((String)null); nullHolder.setSource(this.extractSource(ele)); return nullHolder; else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "array")) return this.parseArrayElement(ele, bd); else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "list")) return this.parseListElement(ele, bd); else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "set")) return this.parseSetElement(ele, bd); else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "map")) return this.parseMapElement(ele, bd); else if (this.nodeNameEquals(ele, "props")) return this.parsePropsElement(ele); else this.error("Unknown property sub-element: [" + ele.getNodeName() + "]", ele); return null;
这里可以看到,所有支持的子类的分类处理都有了,里边的具体内容,就感兴趣的进去看了。
待续。。。
以上是关于spring源码阅读 Bean加载之默认标签加载的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章