JVM 字节码的结构
Posted linlf03
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JVM 字节码的结构相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
编译的.class文件,可以用javap进行反编译
javap Test.class
javap -c Test.class
javap -verbose Test.class
1、创建MyTest1.java
public class MyTest1
private int a = 1;
public MyTest1()
public int getA()
return this.a;
public void setA(int a)
this.a = a;
使用D:\\workspace\\study\\ jvm_demo\\build\\classes\\java\\main\\com\\example\\jvm\\bytecode>javap -verbose MyTest1.class
Classfile /D:/workspace/study/ jvm_demo/build/classes/java/main/com/example/jvm/bytecode/MyTest1.class
Last modified 2019-6-23; size 495 bytes
MD5 checksum 54c0850cfabb7f115919c93e556e3630
Compiled from "MyTest1.java"
public class com.example.jvm.bytecode.MyTest1
SourceFile: "MyTest1.java"
minor version: 0
major version: 51
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #4.#20 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
#2 = Fieldref #3.#21 // com/example/jvm/bytecode/MyTest1.a:I
#3 = Class #22 // com/example/jvm/bytecode/MyTest1
#4 = Class #23 // java/lang/Object
#5 = Utf8 a
#6 = Utf8 I
#7 = Utf8 <init>
#8 = Utf8 ()V
#9 = Utf8 Code
#10 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#11 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable
#12 = Utf8 this
#13 = Utf8 Lcom/example/jvm/bytecode/MyTest1;
#14 = Utf8 getA
#15 = Utf8 ()I
#16 = Utf8 setA
#17 = Utf8 (I)V
#18 = Utf8 SourceFile
#19 = Utf8 MyTest1.java
#20 = NameAndType #7:#8 // "<init>":()V
#21 = NameAndType #5:#6 // a:I
#22 = Utf8 com/example/jvm/bytecode/MyTest1
#23 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
public com.example.jvm.bytecode.MyTest1();
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: aload_0
5: iconst_1
6: putfield #2 // Field a:I
9: return
LineNumberTable:
line 6: 0
line 8: 4
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 10 0 this Lcom/example/jvm/bytecode/MyTest1;
public int getA();
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: getfield #2 // Field a:I
4: ireturn
LineNumberTable:
line 12: 0
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 5 0 this Lcom/example/jvm/bytecode/MyTest1;
public void setA(int);
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=2, args_size=2
0: aload_0
1: iload_1
2: putfield #2 // Field a:I
5: return
LineNumberTable:
line 16: 0
line 17: 5
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 6 0 this Lcom/example/jvm/bytecode/MyTest1;
0 6 1 a I
2、使用WinHex打开MyTest1.class文件
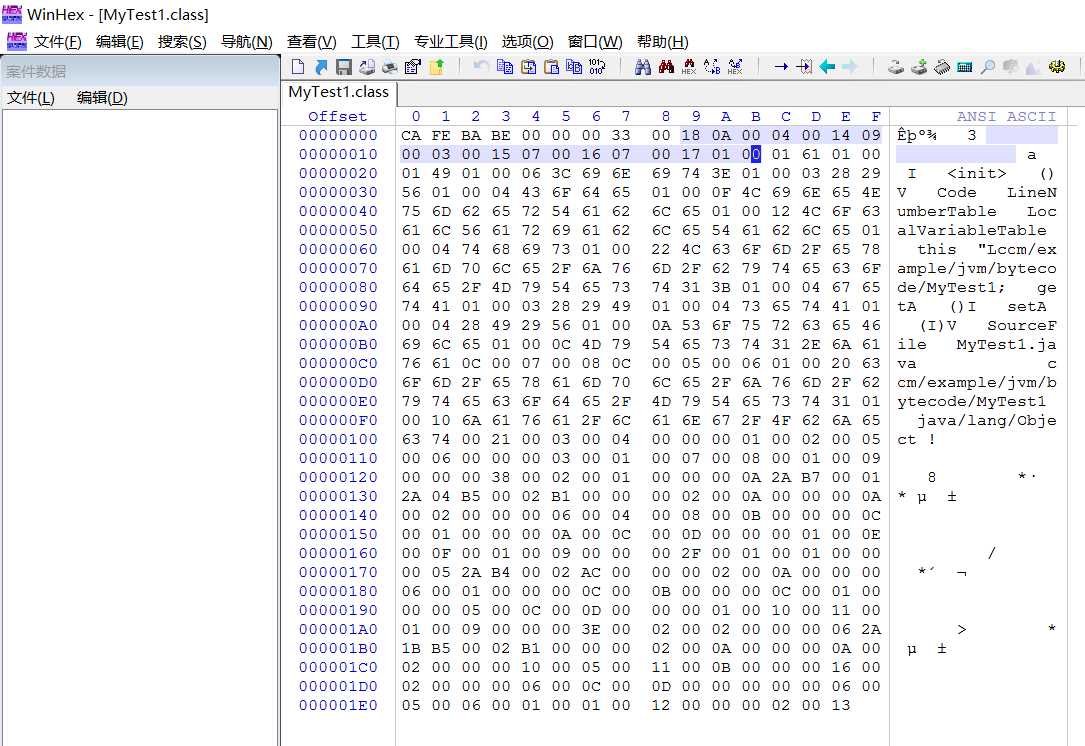
1、使用javap -verbose命令分析一个字节码文件时,将会分析该字节码文件的魔数、版本号、常量池、类的构造方法、类中的方法信息、类变量与成员变量等信息。
2、魔数: 所有的.class字节码文件的前4个字节都是魔数,魔数值为固定值: 0xCAFEBABE.
3、
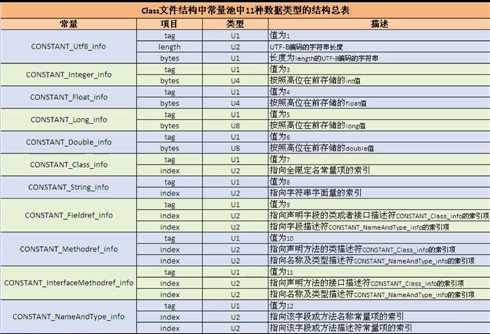
3、Class文件结构中常量池中11种数据类型的结构总表
以上是关于JVM 字节码的结构的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章