代码示例_网络编程_select_内核链表
Posted panda-w
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了代码示例_网络编程_select_内核链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
select_list
1.头文件
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <sys/select.h> 7 #include <sys/time.h> 8 #include <sys/socket.h> 9 #include <strings.h> 10 #include <string.h> 11 #include <arpa/inet.h> 12 #include "list.h" 13 14 #define IP "192.168.2.150" 15 #define PORT 9999 16 #define SIZE 128 17 18 struct cli_info 19 20 struct list_head list; 21 int cli_fd; 22 ;
2.client_delect.c
1 #include "net.h" 2 3 int main(void) 4 5 //1.创建套接字 6 int fd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); 7 if(fd<0) 8 perror("socket failed"); 9 exit(1); 10 11 12 13 //2.初始服务器地址 14 struct sockaddr_in cli; 15 cli.sin_family = AF_INET; 16 cli.sin_port = htons(PORT); 17 cli.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(IP); 18 19 20 //3.发送连接请求 21 if( connect(fd,(struct sockaddr*)&cli,sizeof(cli))<0 ) 22 perror("connect failed"); 23 exit(1); 24 25 26 27 //4.写 28 char buf[SIZE]; 29 while(1) 30 bzero(buf,SIZE); 31 printf("please input:\\t"); 32 fgets(buf,SIZE,stdin); 33 write(fd,buf,strlen(buf)); 34 if(!strncmp(buf,"quit",4)) 35 break; 36 37 38 39 //5.关闭 40 close(fd); 41 42 43 return 0 ; 44
3.server_select.c
1 #include "net.h" 2 3 int main(void) 4 5 char buf[SIZE]; 6 int newfd = -1; 7 8 9 //*****定义初始头结点 10 struct cli_info head; 11 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&head.list); 12 13 14 //1.创建套接字 15 int fd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); 16 if(fd<0) 17 perror("socket failed"); 18 exit(1); 19 20 21 22 //2.初始本地地址 23 struct sockaddr_in ser; 24 bzero(&ser,sizeof(ser)); 25 ser.sin_family = AF_INET; 26 ser.sin_port = htons(PORT); 27 ser.sin_addr.s_addr=htonl(INADDR_ANY); 28 29 30 //3.绑定 31 if( bind(fd,(struct sockaddr*)&ser,sizeof(ser))<0 ) 32 perror("bind failed"); 33 exit(1); 34 35 36 37 //4.监听 38 if( listen(fd,5)<0 ) 39 perror("listen failed"); 40 exit(1); 41 42 43 int len = sizeof(ser); 44 int maxfd = -1; 45 46 //5.多路复用 47 fd_set read_fds; //定义读集合 48 FD_ZERO(&read_fds); //清空读集合 49 maxfd = fd; //最大描述符 50 51 52 //***** 53 struct cli_info *cur=NULL; 54 struct list_head *ptr,*q; 55 56 57 //6.加入监听处理 读集合 58 while(1) 59 FD_SET(0,&read_fds); //将标准输入加入读集合 60 FD_SET(fd,&read_fds); //将fd加入读集合 61 maxfd = fd; //表示最大读集合 62 63 #if 0 64 if(maxfd < newfd) 65 FD_SET(newfd,&read_fds); 66 maxfd=newfd; 67 68 #endif 69 70 //*****将文件描述符加入到读集合 71 list_for_each(ptr,&head.list) 72 cur = list_entry(ptr,struct cli_info,list); 73 FD_SET(cur->cli_fd,&read_fds); 74 if(maxfd<cur->cli_fd) 75 maxfd = cur->cli_fd; 76 77 78 79 int ret = select(maxfd+1,&read_fds,NULL,NULL,NULL); 80 if(ret<0) 81 perror("select failed"); 82 exit(1); 83 84 else if(ret==0) 85 perror("time out"); 86 exit(1); 87 88 else 89 //6.1 判断输入端是否有相应 90 if(FD_ISSET(0,&read_fds)) 91 bzero(buf,SIZE); 92 fgets(buf,SIZE,stdin); 93 printf("shell :%s",buf); 94 95 96 97 //6.2 判断客户端是否有相应 98 if(FD_ISSET(fd,&read_fds)) 99 //*****给新节点申请空间 100 struct cli_info *temp=(struct cli_info*)malloc(sizeof(struct cli_info)); 101 if(temp==NULL) 102 perror("malloc failed"); 103 exit(1); 104 105 //接收 106 newfd=accept(fd,(struct sockaddr*)&ser,&len); 107 if(newfd<0) 108 perror("accept failed"); 109 exit(1); 110 111 printf("client connect succsee : ip=%s port=%d 用户上线啦 ^.^ ...\\n",inet_ntoa(ser.sin_addr),ntohs(ser.sin_port)); 112 //*****将连接的新客户文件描述符加入到新节点 113 temp->cli_fd=newfd; 114 //*****把新节点插入到链表 115 list_add(&temp->list,&head.list); 116 117 118 119 //6.3 判断客户端是否有数据 120 list_for_each_safe(ptr,q,&head.list) 121 cur = list_entry(ptr,struct cli_info,list); 122 if(FD_ISSET(cur->cli_fd,&read_fds)) 123 bzero(buf,SIZE); 124 int val = read(cur->cli_fd,buf,SIZE); 125 if(val<0) 126 perror("read failed"); 127 exit(1); 128 129 else if(val==0) 130 FD_CLR(cur->cli_fd,&read_fds); 131 list_del(&cur->list); 132 close(cur->cli_fd); 133 free(cur); 134 cur->cli_fd = -1; 135 136 else 137 printf("client info :\\nip=%s port=%d\\ndata=%s\\n",inet_ntoa(ser.sin_addr),ntohs(ser.sin_port),buf); 138 if(!strncmp(buf,"quit",4)) 139 printf("client info :\\nip=%s port=%d 用户下线啦 ^.^ ...\\n",inet_ntoa(ser.sin_addr),ntohs(ser.sin_port)); 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 return 0 ; 149
4.list.h
1 #ifndef _LINUX_LIST_H 2 #define _LINUX_LIST_H 3 4 /* 5 * Simple doubly linked list implementation. 6 * 7 * Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when 8 * manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as 9 * sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can 10 * generate better code by using them directly rather than 11 * using the generic single-entry routines. 12 */ 13 14 struct list_head 15 struct list_head *next,*prev; 16 ; 17 18 #define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100 + 0) 19 #define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200 + 0) 20 21 #define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER) 22 #define container_of(ptr, type, member) ( 23 const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); 24 (type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );) 25 #define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) &(name), &(name) 26 27 #define LIST_HEAD(name) 28 struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) 29 30 static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list) 31 32 list->next = list; 33 list->prev = list; 34 35 36 /* 37 * Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries. 38 * 39 * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know 40 * the prev/next entries already! 41 */ 42 #ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST 43 static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new, 44 struct list_head *prev, 45 struct list_head *next) 46 47 next->prev = new; 48 new->next = next; 49 new->prev = prev; 50 prev->next = new; 51 52 #else 53 extern void __list_add(struct list_head *new, 54 struct list_head *prev, 55 struct list_head *next); 56 #endif 57 58 /** 59 * list_add - add a new entry 60 * @new: new entry to be added 61 * @head: list head to add it after 62 * 63 * Insert a new entry after the specified head. 64 * This is good for implementing stacks. 65 */ 66 static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) 67 68 __list_add(new, head, head->next); 69 70 71 72 /** 73 * list_add_tail - add a new entry 74 * @new: new entry to be added 75 * @head: list head to add it before 76 * 77 * Insert a new entry before the specified head. 78 * This is useful for implementing queues. 79 */ 80 static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) 81 82 __list_add(new, head->prev, head); 83 84 85 /* 86 * Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries 87 * point to each other. 88 * 89 * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know 90 * the prev/next entries already! 91 */ 92 static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next) 93 94 next->prev = prev; 95 prev->next = next; 96 97 98 /** 99 * list_del - deletes entry from list. 100 * @entry: the element to delete from the list. 101 * Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is 102 * in an undefined state. 103 */ 104 #ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST 105 static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry) 106 107 __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); 108 109 110 static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry) 111 112 __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); 113 entry->next = LIST_POISON1; 114 entry->prev = LIST_POISON2; 115 116 #else 117 extern void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry); 118 extern void list_del(struct list_head *entry); 119 #endif 120 121 /** 122 * list_replace - replace old entry by new one 123 * @old : the element to be replaced 124 * @new : the new element to insert 125 * 126 * If @old was empty, it will be overwritten. 127 */ 128 static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old, 129 struct list_head *new) 130 131 new->next = old->next; 132 new->next->prev = new; 133 new->prev = old->prev; 134 new->prev->next = new; 135 136 137 static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old, 138 struct list_head *new) 139 140 list_replace(old, new); 141 INIT_LIST_HEAD(old); 142 143 144 /** 145 * list_del_init - deletes entry from list and reinitialize it. 146 * @entry: the element to delete from the list. 147 */ 148 static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry) 149 150 __list_del_entry(entry); 151 INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry); 152 153 154 /** 155 * list_move - delete from one list and add as another‘s head 156 * @list: the entry to move 157 * @head: the head that will precede our entry 158 */ 159 static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) 160 161 __list_del_entry(list); 162 list_add(list, head); 163 164 165 /** 166 * list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another‘s tail 167 * @list: the entry to move 168 * @head: the head that will follow our entry 169 */ 170 static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list, 171 struct list_head *head) 172 173 __list_del_entry(list); 174 list_add_tail(list, head); 175 176 177 /** 178 * list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head 179 * @list: the entry to test 180 * @head: the head of the list 181 */ 182 static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list, 183 const struct list_head *head) 184 185 return list->next == head; 186 187 188 /** 189 * list_empty - tests whether a list is empty 190 * @head: the list to test. 191 */ 192 static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head) 193 194 return head->next == head; 195 196 197 /** 198 * list_empty_careful - tests whether a list is empty and not being modified 199 * @head: the list to test 200 * 201 * Description: 202 * tests whether a list is empty _and_ checks that no other CPU might be 203 * in the process of modifying either member (next or prev) 204 * 205 * NOTE: using list_empty_careful() without synchronization 206 * can only be safe if the only activity that can happen 207 * to the list entry is list_del_init(). Eg. it cannot be used 208 * if another CPU could re-list_add() it. 209 */ 210 static inline int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head) 211 212 struct list_head *next = head->next; 213 return (next == head) && (next == head->prev); 214 215 216 /** 217 * list_rotate_left - rotate the list to the left 218 * @head: the head of the list 219 */ 220 static inline void list_rotate_left(struct list_head *head) 221 222 struct list_head *first; 223 224 if (!list_empty(head)) 225 first = head->next; 226 list_move_tail(first, head); 227 228 229 230 /** 231 * list_is_singular - tests whether a list has just one entry. 232 * @head: the list to test. 233 */ 234 static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head) 235 236 return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev); 237 238 239 static inline void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list, 240 struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry) 241 242 struct list_head *new_first = entry->next; 243 list->next = head->next; 244 list->next->prev = list; 245 list->prev = entry; 246 entry->next = list; 247 head->next = new_first; 248 new_first->prev = head; 249 250 251 /** 252 * list_cut_position - cut a list into two 253 * @list: a new list to add all removed entries 254 * @head: a list with entries 255 * @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself 256 * and if so we won‘t cut the list 257 * 258 * This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and 259 * including @entry, from @head to @list. You should 260 * pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list 261 * should be an empty list or a list you do not care about 262 * losing its data. 263 * 264 */ 265 static inline void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list, 266 struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry) 267 268 if (list_empty(head)) 269 return; 270 if (list_is_singular(head) && 271 (head->next != entry && head != entry)) 272 return; 273 if (entry == head) 274 INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); 275 else 276 __list_cut_position(list, head, entry); 277 278 279 static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list, 280 struct list_head *prev, 281 struct list_head *next) 282 283 struct list_head *first = list->next; 284 struct list_head *last = list->prev; 285 286 first->prev = prev; 287 prev->next = first; 288 289 last->next = next; 290 next->prev = last; 291 292 293 /** 294 * list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks 295 * @list: the new list to add. 296 * @head: the place to add it in the first list. 297 */ 298 static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list, 299 struct list_head *head) 300 301 if (!list_empty(list)) 302 __list_splice(list, head, head->next); 303 304 305 /** 306 * list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue 307 * @list: the new list to add. 308 * @head: the place to add it in the first list. 309 */ 310 static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list, 311 struct list_head *head) 312 313 if (!list_empty(list)) 314 __list_splice(list, head->prev, head); 315 316 317 /** 318 * list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list. 319 * @list: the new list to add. 320 * @head: the place to add it in the first list. 321 * 322 * The list at @list is reinitialised 323 */ 324 static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list, 325 struct list_head *head) 326 327 if (!list_empty(list)) 328 __list_splice(list, head, head->next); 329 INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); 330 331 332 333 /** 334 * list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list 335 * @list: the new list to add. 336 * @head: the place to add it in the first list. 337 * 338 * Each of the lists is a queue. 339 * The list at @list is reinitialised 340 */ 341 static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list, 342 struct list_head *head) 343 344 if (!list_empty(list)) 345 __list_splice(list, head->prev, head); 346 INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); 347 348 349 350 /** 351 * list_entry - get the struct for this entry 352 * @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer. 353 * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. 354 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 355 */ 356 #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) 357 container_of(ptr, type, member) 358 359 /** 360 * list_first_entry - get the first element from a list 361 * @ptr: the list head to take the element from. 362 * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. 363 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 364 * 365 * Note, that list is expected to be not empty. 366 */ 367 #define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) 368 list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member) 369 370 /** 371 * list_for_each - iterate over a list 372 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 373 * @head: the head for your list. 374 */ 375 #define list_for_each(pos, head) 376 for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next) 377 378 /** 379 * __list_for_each - iterate over a list 380 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 381 * @head: the head for your list. 382 * 383 * This variant doesn‘t differ from list_for_each() any more. 384 * We don‘t do prefetching in either case. 385 */ 386 #define __list_for_each(pos, head) 387 for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next) 388 389 /** 390 * list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards 391 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 392 * @head: the head for your list. 393 */ 394 #define list_for_each_prev(pos, head) 395 for (pos = (head)->prev; pos != (head); pos = pos->prev) 396 397 /** 398 * list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry 399 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 400 * @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage 401 * @head: the head for your list. 402 */ 403 #define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) 404 for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); 405 pos = n, n = pos->next) 406 407 /** 408 * list_for_each_prev_safe - iterate over a list backwards safe against removal of list entry 409 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 410 * @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage 411 * @head: the head for your list. 412 */ 413 #define list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, head) 414 for (pos = (head)->prev, n = pos->prev; 415 pos != (head); 416 pos = n, n = pos->prev) 417 418 /** 419 * list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type 420 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 421 * @head: the head for your list. 422 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 423 */ 424 #define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) 425 for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); 426 &pos->member != (head); 427 pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member)) 428 429 /** 430 * list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type. 431 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 432 * @head: the head for your list. 433 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 434 */ 435 #define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) 436 for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member); 437 &pos->member != (head); 438 pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member)) 439 440 /** 441 * list_prepare_entry - prepare a pos entry for use in list_for_each_entry_continue() 442 * @pos: the type * to use as a start point 443 * @head: the head of the list 444 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 445 * 446 * Prepares a pos entry for use as a start point in list_for_each_entry_continue(). 447 */ 448 #define list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member) 449 ((pos) ? : list_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member)) 450 451 /** 452 * list_for_each_entry_continue - continue iteration over list of given type 453 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 454 * @head: the head for your list. 455 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 456 * 457 * Continue to iterate over list of given type, continuing after 458 * the current position. 459 */ 460 #define list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member) 461 for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); 462 &pos->member != (head); 463 pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member)) 464 465 /** 466 * list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse - iterate backwards from the given point 467 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 468 * @head: the head for your list. 469 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 470 * 471 * Start to iterate over list of given type backwards, continuing after 472 * the current position. 473 */ 474 #define list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse(pos, head, member) 475 for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); 476 &pos->member != (head); 477 pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member)) 478 479 /** 480 * list_for_each_entry_from - iterate over list of given type from the current point 481 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 482 * @head: the head for your list. 483 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 484 * 485 * Iterate over list of given type, continuing from current position. 486 */ 487 #define list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member) 488 for (; &pos->member != (head); 489 pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member)) 490 491 /** 492 * list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry 493 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 494 * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage 495 * @head: the head for your list. 496 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 497 */ 498 #define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) 499 for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member), 500 n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); 501 &pos->member != (head); 502 pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member)) 503 504 /** 505 * list_for_each_entry_safe_continue - continue list iteration safe against removal 506 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 507 * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage 508 * @head: the head for your list. 509 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 510 * 511 * Iterate over list of given type, continuing after current point, 512 * safe against removal of list entry. 513 */ 514 #define list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member) 515 for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member), 516 n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); 517 &pos->member != (head); 518 pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member)) 519 520 /** 521 * list_for_each_entry_safe_from - iterate over list from current point safe against removal 522 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 523 * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage 524 * @head: the head for your list. 525 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 526 * 527 * Iterate over list of given type from current point, safe against 528 * removal of list entry. 529 */ 530 #define list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member) 531 for (n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); 532 &pos->member != (head); 533 pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member)) 534 535 /** 536 * list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse - iterate backwards over list safe against removal 537 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 538 * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage 539 * @head: the head for your list. 540 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 541 * 542 * Iterate backwards over list of given type, safe against removal 543 * of list entry. 544 */ 545 #define list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member) 546 for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member), 547 n = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); 548 &pos->member != (head); 549 pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.prev, typeof(*n), member)) 550 551 /** 552 * list_safe_reset_next - reset a stale list_for_each_entry_safe loop 553 * @pos: the loop cursor used in the list_for_each_entry_safe loop 554 * @n: temporary storage used in list_for_each_entry_safe 555 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 556 * 557 * list_safe_reset_next is not safe to use in general if the list may be 558 * modified concurrently (eg. the lock is dropped in the loop body). An 559 * exception to this is if the cursor element (pos) is pinned in the list, 560 * and list_safe_reset_next is called after re-taking the lock and before 561 * completing the current iteration of the loop body. 562 */ 563 #define list_safe_reset_next(pos, n, member) 564 n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member) 565 566 /* 567 * Double linked lists with a single pointer list head. 568 * Mostly useful for hash tables where the two pointer list head is 569 * too wasteful. 570 * You lose the ability to access the tail in O(1). 571 */ 572 #endif
测试:
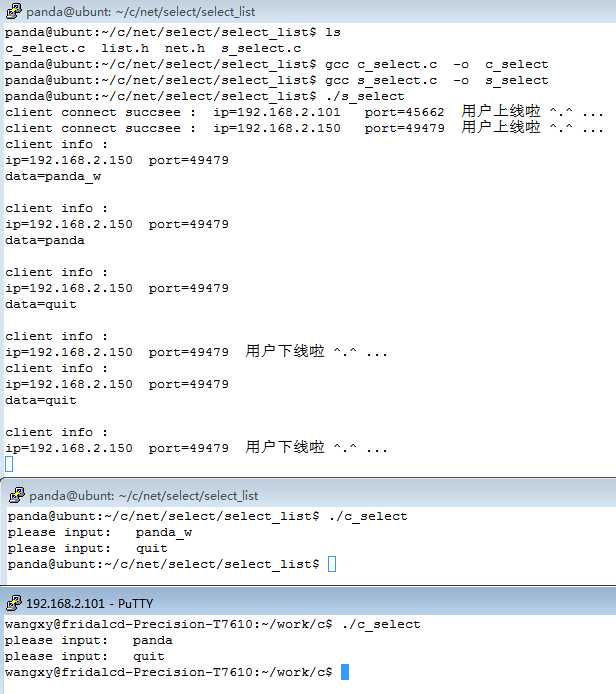
success !
以上是关于代码示例_网络编程_select_内核链表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章