Java初学——输出和输入处理
Posted wuxuewei
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java初学——输出和输入处理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、文件
1.什么是文件
相关记录或放在一起的数据的集合.input输入数据 output输出文件,在java程序中访问文件的属性需要 JAVAAPI:java.io.File
2.怎样操作文件
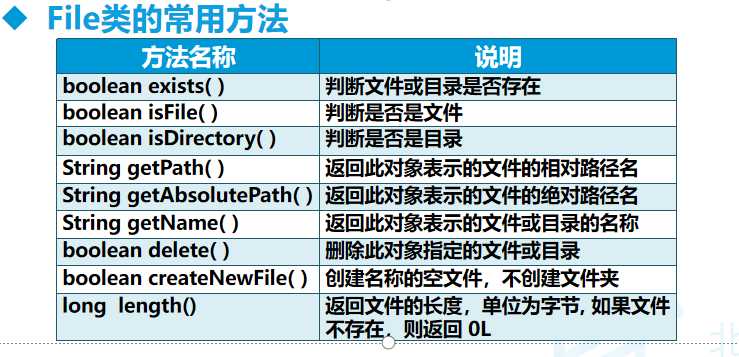
绝对路径:我们平时使用计算机时要找到需要的文件就必须知道文件的位置,而表示文件的位置的方式就是路径,例如只要看到这个路径:c:/website/img/photo.jpg我们就知道photo.jpg文件是在c盘的website目录下的img子目录中。这样完整的描述文件位置的路径就是绝对路径。我们不需要知道其他任何信息就可以根据绝对路径判断出文件的位置。
相对路径: 所谓相对路径,顾名思义就是自己相对与目标位置。不论将这些文件放到哪里,只要他们的相对关系没有变,就不会出错。 另外我们使用“../”来表示上一级目录,“../../”表示上上级的目录,以此类推。
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; /** * 在文件类中, 在写文件名是可以用文件名"c:\\\\test.java"或者("c:/test.java")两种方式 * 还可以是物理文件和目录 * @author 61483 * */ public class Test //如果文件不存在就创建文件,查看文件信息,删除信息 //创建文件方法 public void creat(File file) //文件不存在就创建方法 if (!file.exists()) //判断文件或目录是否存在的方法 try //创建文件的方法 file.createNewFile(); System.out.println("文件以经创建"); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); //查看文件相关信息的方法 public void show(File file) //如果文件存在 if (file.exists()) //查看文件 if (file.isFile()) System.out.println("该文件的名字是"+file.getName()); System.out.println("该文件的相对路径是:"+file.getPath()); System.out.println("该文件的绝对路径是:"+file.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println("文件大小:"+file.length()+"KB"); if (file.isDirectory()) System.out.println("此文件是目录"); else System.out.println("该文件不存在"); //删除文件 public void delefile(File file) if(file.exists()) file.delete(); System.out.println("文件已删除"); public static void main(String[] args) Test test=new Test(); File file=new File("d:/wuxuewei.txt"); test.creat(file); test.show(file); test.delefile(file);
二、输入输出流
1.Java流的分类
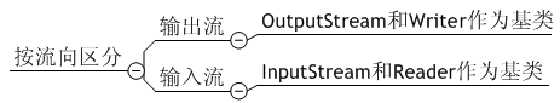
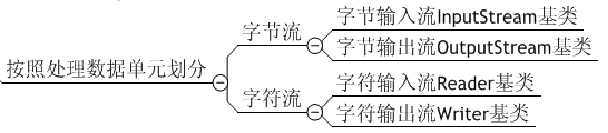
三、字节流
1.FileInputStream
FileInputStream是InputStream的子类:构造方法有两种
FileInputStream(File flie)绝对路径
FileInputStream(String name)相对路径
InputStream类常用方法
int read( ):在数据源一个字节读,返回时时该字节的整数形式
int read(byte[] b) 从输入流读取若干字节,把字节保存在数组中,返回读取到的是字节数如果到了输入流末尾返回-1
int read(byte[] b,int off,int len)从输入流读取若干字节,把字节保存在数组中,off指的是字节数组中开始保存数据的起始下标,len指的是读取字节数目.返回读取到的是字节数目,如果到了输入流末尾返回-1.
void close( ):读取数据流完毕后关闭流
int available():可以读取的字节数目.
package readfile; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; public class Readfile public void creat(File file) if (!file.exists()) try file.createNewFile(); System.out.println("文件已创建"); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); else System.out.println("文件已存在"); public static void main(String[] args) // 创建文件 File file = new File("d:/wuxuewei.txt"); Readfile t1 = new Readfile(); FileInputStream fis = null; t1.creat(file); // 输入流 try fis = new FileInputStream("d:/wuxuewei.txt"); System.out.println("开始读取:字节数共" + fis.available()); int data; //利用read()方法读取 // while ((data = fis.read()) != -1) // System.out.print((char) data); // // //借助Read(byte[])去读取文件 byte[] b=new byte[1024]; while ((data=fis.read(b))!=-1) for (int i = 0; i < data; i++) System.out.print((char)b[i]); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try fis.close(); System.out.println("数据流已关闭"); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
2.FileOutStream
void write(int c)
void write(byte[] buf)
void write(byte[] b,int off,int len)
void close():关闭输出流
void flush():强制把缓冲区的数据写到输出流中
构造方法
FileOutputStream (File file)
FileOutputStream(String name)
前两种构造方法在向文件写数据时将覆盖文件中原有的内容 2.创建FileOutputStream实例时,如果相应的文件并不存在,则会自动创建一个空的文件.
FileOutputStream(String name,boolean append)append如果为true不会覆盖 追加内容
package readfile; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Outfiledome public static void main(String[] args) FileOutputStream fos = null; try fos = new FileOutputStream("d:/wuxuewei.txt"); String str = "你好 世界"; byte[] b = str.getBytes(); fos.write(b, 0, b.length); System.out.println("文件已被更新"); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try fos.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
四、字符流
1.字符输入流
Reader类常用方法
int read( )
int read(char[] c)
read(char[] c,int off,int len)
void close( )
子类InputStreamReader常用的构造方法
InputStreamReader(InputStream in)
InputStreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName)
2.字符输出流
Writer类常用方法 :
write(String str)
write(String str,int off,int len)
void close()
void flush() 强制清空缓存,在流输出完之后清空
子类OutputStreamWriter常用的构造方法
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out)
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out,String charsetName)
FileWriter类是OutputStreamWriter的子类
FileWriter (File file)
FileWriter (String name)
该类只能按照本地平台的字符编码来写数据,用户不能指定其他的字符编码类型
五、常见问题
1.中文乱码
出现的原因:文件编码格式和程序环境的编码格式不一样
解决方法:
方法一:window→p‘references→General→Workspace→Textile encoding选择编码格式
方法二:输入流运用InputStreamReader
FileReader类是InputStreamReader的子类
FileReader(File file)
FileReader(String name) 该类只能按照本地平台的字符编码来读取数据,用户不能指定其他的字符编码类型 System.out.println(System.getProperty("file.encoding")); 获得本地平台的字符编码类型。
package filereader; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.Reader; public class FileReaderDome public static void main(String[] args) // FileReader fr = null; Reader reader=null; try StringBuffer sbf=new StringBuffer(); //文件输入流 FileInputStream ins=new FileInputStream( "d:/wuxuewei.txt"); //利用InputStreamReader来控制文件读取时的编码格式 reader=new InputStreamReader(ins,"UTF-8"); // fr = new FileReader("d:/wuxuewei.txt"); char ca[] = new char[1024]; int len=-1; while ((len=reader.read(ca))!=-1) sbf.append(ca); System.out.println(sbf); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try reader.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
2.BufferddReader类
FileReader类是InputStreamReader的子类
FileReader(File file)
FileReader(String name)
该类只能按照本地平台的字符编码来读取数据,用户不能指定其他的字符编码类型 System.out.println(System.getProperty("file.encoding")); 获得本地平台的字符编码类型
BufferddReader缓冲区可以成组的将字符串输入,相对之前的读取方式更加效率便捷
BufferedReader常用的构造方法 BufferedReader(Reader in) BufferedReader特有的方法 readLine()可以成行的读取字符串
package filereader; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.Reader; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; public class BufferReaderDome public static void main(String[] args) Reader reader = null;// 创建Read类 FileInputStream fis = null; BufferedReader br = null; try // 找到文件对象 fis = new FileInputStream("d:/wuxuewei.txt"); // 包装文件格式 reader = new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8"); // 创建字符缓冲池 br = new BufferedReader(reader); String line; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) // 读取输出每一行 System.out.println(line); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try br.close(); fis.close(); reader.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
缓冲池输入输出小练习
package Wtite; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.io.Reader; import java.io.Writer; //借助字符流写内容 public class Writedome public static void main(String[] args) // 写入类 Writer wr = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; // 读取类 Reader reader = null; BufferedReader bfr = null; try // 开始写入内容 wr = new FileWriter("d:/wuxuewei.txt", true); bw = new BufferedWriter(wr); bw.write("你好"); bw.newLine(); bw.write("内容写入完毕"); wr.flush(); // 读取内容 reader = new FileReader("d:/wuxuewei.txt"); bfr = new BufferedReader(reader); String line; while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) System.out.println(line); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try bw.close(); wr.close(); bfr.close(); reader.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
六、读取二进制文件
1.什么是二进制文件
例如视频音频
DataInputStream类 FileInputStream的子类 与FileInputStream类结合使用读取二进制文件
DataOutputStream类 FileOutputStream的子类 与FileOutputStream类结合使用写二进制文件
package erjinzhi; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Copypic public static void main(String[] args) //读取二进制图片 DataInputStream dis=null; FileInputStream fis=null; //输出二进制图片 FileOutputStream fos = null; DataOutputStream dos=null; try //读取 fis=new FileInputStream("d:/hashiqi.jpg"); dis=new DataInputStream(fis); //输出 fos=new FileOutputStream("d:/hashiqicopy.jpg"); dos=new DataOutputStream(fos); int temp; while ((temp=dis.read())!=0) dos.write(temp); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try dos.close(); fos.close(); dis.close(); fis.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
七、序列化和反序列化
序列化是将对象的状态写入到特定的流中的过程
反序列化则是从特定的流中获取数据重新构建对象的过程
如果要将对象序列化和反序列化则需要实现Serializable的接口 否则会报错
具体实现代码:
创建学生类
package xuliehua; import java.io.Serializable; public class Student implements Serializable private String name; private String sex; private transient int age;//不需要序列化的成员 加traansient public String getName() return name; public void setName(String name) this.name = name; public String getSex() return sex; public void setSex(String sex) this.sex = sex; public int getAge() return age; public void setAge(int age) this.age = age; public Student(String name, String sex, int age) this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.age = age;
开始序列化和反序列化
package xuliehua; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutput; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import com.sun.xml.internal.ws.message.stream.StreamAttachment; public class Xuliehua public static void main(String[] args) // 实例化创建对象 进行序列化 Student st1 = new Student("张三", "男", 12); ObjectOutputStream oos = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; // 反序列化 ObjectInputStream ois = null; FileInputStream fis = null; try // 开始序列化 fos = new FileOutputStream("d:/xuesheng.txt"); oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos); oos.writeObject(st1); // 反序列化 fis = new FileInputStream("d:/xuesheng.txt"); ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis); Student st2 = (Student) ois.readObject(); System.out.println("反序列化的信息" + st2.getName() + st2.getAge() + st2.getSex()); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (ClassNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try oos.close(); fos.close(); ois.close(); fis.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace();
以上是关于Java初学——输出和输入处理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章