Linux 性能检查命令总结
Posted larry-luo
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux 性能检查命令总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
iostat -x 1 查看磁盘的IO负载
Linux系统出现了性能问题,一般我们可以通过top.iostat,vmstat等命令来查看初步定位问题。其中iostat可以给我们提供丰富的IO状态数据
$ iostat -x -1
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
10.43 0.00 1.51 1.51 0.00 86.56
Device:rrqm/s wrqm/s r/s w/s rkB/s wkB/s avgrq-sz avgqu-sz await r_await w_await svctm %util
sda 4477.00 9.00 951.00 13.00 24288.00 2492.00 55.56 0.21 0.22 0.21 0.92 0.17 16.00
%user :Show the percentage of CPU utilization that occurred while executing at the user level (application).
%nice :Show the percentage of CPU utilization that occurred while executing at the user level with nice priority.
%system:Show the percentage of CPU utilization that occurred while executing at the system level (kernel).
%iowait:Show the percentage of time that the CPU or CPUs were idle during which the system had an outstanding disk I/O request.
%steal :Show the percentage of time spent in involuntary wait by the virtual CPU or CPUs while the hypervisor was servicing another virtual processor.
%idle :Show the percentage of time that the CPU or CPUs were idle and the system did not have an outstanding disk I/O request.
rrqm/s:每秒进行merge的读操作数目。即delta(rmerge)/s
wrqm/s:每秒进行merge的写操作数目。即delta(wmerge)/s
r/s:每秒完成的读I/O设备次数。即delta(rio)/s
w/s:每秒完成的写I/0设备次数。即delta(wio)/s
rsec/s:每秒读扇区数。即delta(rsect)/s
wsec/s:每秒写扇区数。即delta(wsect)/s
rKB/s:每秒读K字节数。是rsec/s的一半,因为每扇区大小为512字节
wKB/s:每秒写K字节数。是wsec/s的一半
avgrq-sz:平均每次设备I/O操作的数据大小(扇区)。即delta(rsect+wsect)/delta(rio+wio)
avgqu-sz:平均I/O队列长度。即delta(aveq)/s/1000(因为aveq的单位为毫秒)
await:平均每次设备I/O操作的等待时间(毫秒)。即delta(ruse+wuse)/delta(rio+wio)
svctm:平均每次设备I/O操作的服务时间(毫秒)。即delta(use)/delta(rio+wio)
%util:一秒中有百分之多少的时间用于I/O操作,或者说一秒中有多少时间I/O队列是非空的。即delta(usr)/s/1000(因为use的单位为毫秒)
如果%util接近100%,表明I/O请求太多,I/O系统已经满负荷,磁盘可能存在瓶颈,一般%util大于70%,I/O压力就比较大.
svctm一般要小于await(因为同时等待的请求的等待时间被重复计算了),svctm的大小一般和磁盘性能有关,CPU/内存的负荷也会对其有影响,请求过多也会间接导致svctm的增加。await的大小一般取决于服务时间(svctm)以及I/O队列的长度和I/O请求的发出模式。如果svctm比较接近await,说明I/O几乎没有等待时间;如果await远大于svctm,说明I/O队列太长,应用得到的响应时间变慢,如果响应时间超过了用户可以容许的范围,这时可以考虑更换更快的磁盘,调整内核elevator算法,优化应用,或者升级CPU
队列长度(avcqu-sz)也可作为衡量系统I/O负荷的指标,但由于avcqu-sz是按照单位时间的平均值,所以不能反映瞬间的I/O洪水。
来自 <https://blog.csdn.net/smileteo/article/details/40152271>
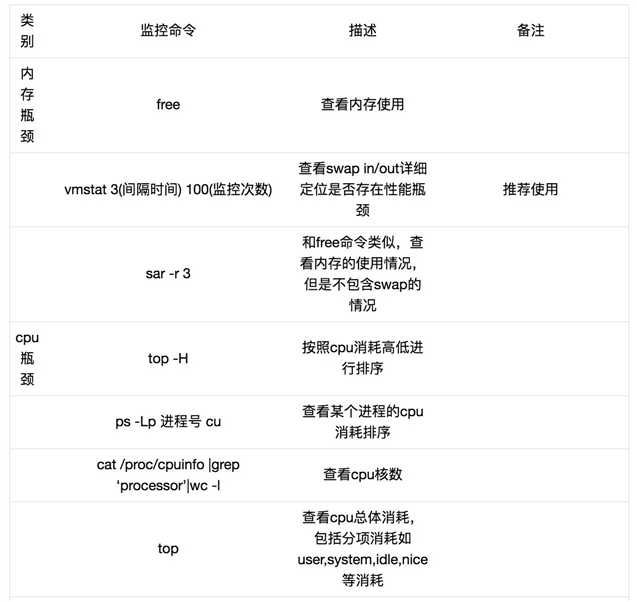

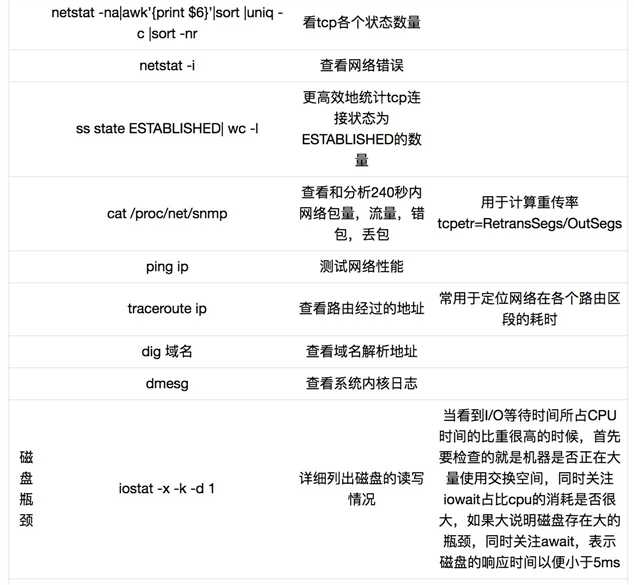
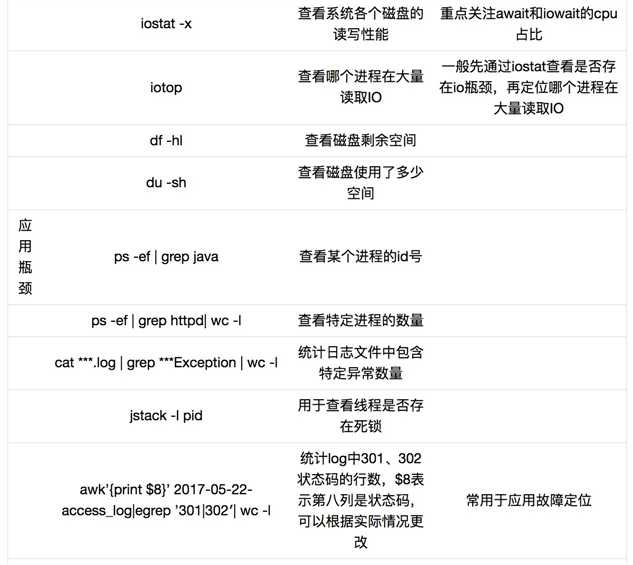
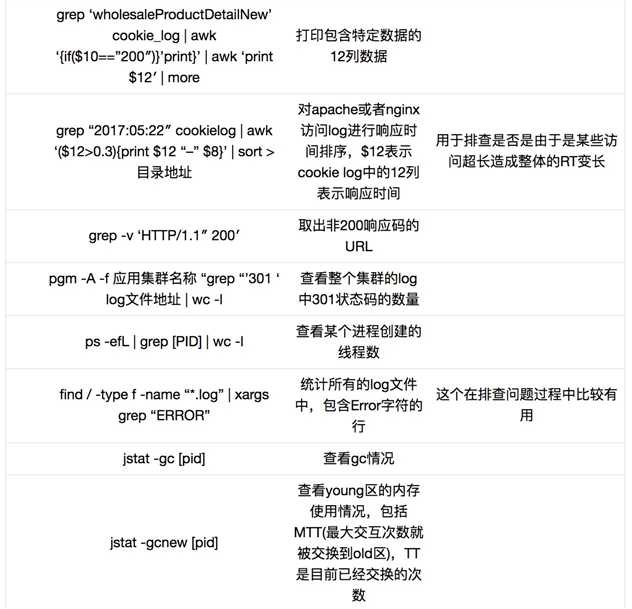

以上是关于Linux 性能检查命令总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章