dfs与dp算法之关系与经典入门例题
Posted fromneptune
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了dfs与dp算法之关系与经典入门例题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
声明
本文不介绍dfs、dp算法的基础思路,有想了解的可以自己找资源学习。
本文适合于刚刚接触dfs和dp算法的人,发现两种算法间的内在联系。
本人算法之路走之甚短,如果理解出现问题欢迎大家的指正,我会分享基于我目前理解到的算法思想。
dfs与dp的关系
很多情况下,dfs和dp两种解题方法的思路都是很相似的,这两种算法在一定程度上是可以互相转化的。
想到dfs也就常常会想到dp,当然在一些特定的适用场合下除外。
dp主要运用了预处理的思想,而dfs则是类似于白手起家,一步步探索。一般来讲,能够预处理要好些,好比战争前做好准备。
dfs和dp都是十分重要的基础算法,在各个竞赛中都有涉及,务必精通。
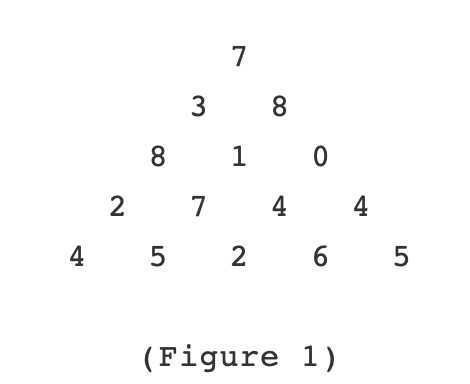
经典例题-数字三角形 - POJ 1163
题目
The Triangle
Description
Figure 1 shows a number triangle. Write a program that calculates the highest sum of numbers passed on a route that starts at the top and ends somewhere on the base. Each step can go either diagonally down to the left or diagonally down to the right.
Input
Your program is to read from standard input. The first line contains one integer N: the number of rows in the triangle. The following N lines describe the data of the triangle. The number of rows in the triangle is > 1 but <= 100. The numbers in the triangle, all integers, are between 0 and 99.
Output
Your program is to write to standard output. The highest sum is written as an integer.
Sample Input
5 7 3 8 8 1 0 2 7 4 4 4 5 2 6 5Sample Output
30
dfs思路
解题思路
自顶向下,将每种路径都走一遍。
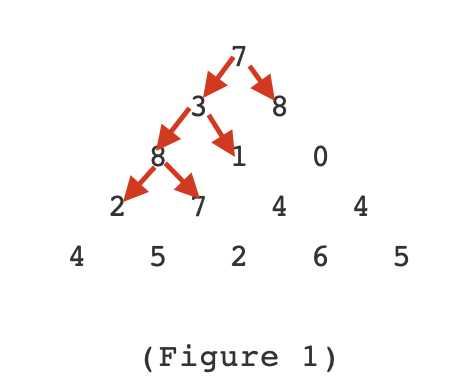
通过迭代计算到最后一层,记录最后一层的所有值。
最后一层中的最大值即为所求。
具体代码
#include <iostream>
// use vector vessel to write down the final level
#include <vector>
// use 'sort' method in <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
// use 'greater<T>' functional template in <functional>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
// the maximum of the triangle ordinal
const int max_ordinal = 100;
// the depth
int num_of_rows;
// save data
int data[max_ordinal][max_ordinal];
// save the data of the final level
vector<int> ans;
void dfs(int level, int sum, int column)
{
// avoid multi calculate
int current_sum = sum+data[level][column];
// save data which was in final level
if(level+1 == num_of_rows)
{
ans.push_back(current_sum);
return;
}
// binary tree
dfs(level+1, current_sum, column);
dfs(level+1, current_sum, column+1);
}
int main()
{
cin >> num_of_rows;
for(int i = 0; i < num_of_rows; i++)
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
scanf("%d", &data[i][j]);
dfs(0, 0, 0);
cout << "output data:" << endl;
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end(), greater<int>());
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)
{
cout << ans[i] << "\\t";
if(!((i+1) % 5)) cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}dp思路
解题思路
dfs的思路是从上到下,而dp的思路是:从第二层开始,每下去一次往回看一下并取上一层相邻两个大的那个。
具体代码
#include <iostream>
// use 'max' method and 'sort' method
#include <algorithm>
// use 'greater<T>' functional template
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
// same as DFS
const int max_ordinal = 100;
int num_of_rows;
int data[max_ordinal][max_ordinal];
// the array of the dp method
int dp[max_ordinal][max_ordinal];
int main()
{
cin >> num_of_rows;
for(int i = 0; i < num_of_rows; i++)
for(int j = 0; j<= i; j++)
scanf("%d", &data[i][j]);
// dp now
dp[0][0] = data[0][0];
for(int i = 1; i < num_of_rows; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
if(j-1 >= 0)
{
dp[i][j] = data[i][j] + max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1]);
} else {
dp[i][j] = data[i][j] + dp[i-1][j];
}
}
}
// calling 'sort' method
sort(dp[num_of_rows-1], &dp[num_of_rows-1][num_of_rows], greater<int>());
for(int i = 0; i < num_of_rows; i++)
cout << dp[num_of_rows-1][i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "answer is: ";
cout << dp[num_of_rows-1][0] << endl;
return 0;
}以上是关于dfs与dp算法之关系与经典入门例题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章