记微软OpenHack机器学习挑战赛
Posted easymind223
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了记微软OpenHack机器学习挑战赛相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
有幸参加了微软OpenHack挑战赛,虽然题目难度不大,但是很有意思,学到了很多东西,还有幸认识了微软梁健老师,谢谢您的帮助!同时还认识同行的很多朋友,非常高兴,把这段难忘的比赛记录一下~~也分享一下代码,给那些没有参加的朋友,
数据集(文末链接)
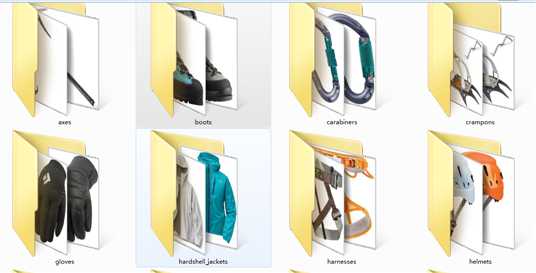
首先每支队伍会收到一个数据集,它是一个登山公司提供的装备图片,有登山镐,鞋子,登山扣,不知道叫什么的雪地爪?手套,冲锋衣,安全带。。。一共12个类别,每个类别几百个样本,我们的任务就是对这些图片分类和识别
简单看一下:
赛题:
赛题共有6道,简单描述一下:
1、搭建环境(略过)
2、图像正规化(包括颜色和大小)
3、通过机器学习方法对图像分类,precision>0.8
4、通过深度学习方法对图像分类,precision>0.9
5、部署(略过)
6、目标检测(用全新的数据集,检测雪地中的登山者是否带头盔!!航拍图像,有点难度~)
_______________________________________
下面是每道题目的详细描述和代码
题目2
完成以下任务:
选择一种基本颜色,例如白色并填充所有图片尺寸不是1:1比例的图像
不通过直接拉伸的方式,重塑至128x128x3像素的阵列形状
确保每个图像的像素范围从0到255(包含或[0,255]),也称为“对比度拉伸”(contrast stretching).
标准化或均衡以确保像素在[0,255]范围内.
成功完成的标准
团队将在Jupyter Notebook中运行一个代码单元,绘制原始图像,然后绘制填充后的像素值归一化或均衡图像, 展示给教练看.
团队将在Jupyter notebook 为教练运行一个代码单元,显示的像素值的直方图应该在0到255的范围内(包括0和255).

def normalize(src): arr = array(src) arr = arr.astype(‘float‘) # Do not touch the alpha channel for i in range(3): minval = arr[...,i].min() maxval = arr[...,i].max() if minval != maxval: arr[...,i] -= minval arr[...,i] *= (255.0/(maxval-minval)) arr = arr.astype(uint8) return Image.fromarray(arr,‘RGB‘) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from PIL import ImageColor from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow from PIL import Image from pylab import * import copy plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) #设置窗口大小 # src = Image.open("100974.jpeg") src = Image.open("rose.jpg") src_array = array(src) plt.subplot(2,2,1), plt.title(‘src‘) plt.imshow(src), plt.axis(‘off‘) ar=src_array[:,:,0].flatten() ag=src_array[:,:,1].flatten() ab=src_array[:,:,2].flatten() plt.subplot(2,2,2), plt.title(‘src hist‘) plt.axis([0,255,0,0.03]) plt.hist(ar, bins=256, normed=1,facecolor=‘red‘,edgecolor=‘r‘,hold=1) #原始图像直方图 plt.hist(ag, bins=256, normed=1,facecolor=‘g‘,edgecolor=‘g‘,hold=1) #原始图像直方图 plt.hist(ab, bins=256, normed=1,facecolor=‘b‘,edgecolor=‘b‘) #原g始图像直方图 dst = normalize(src) dst_array = array(dst) plt.subplot(2,2,3), plt.title(‘dst‘) plt.imshow(dst), plt.axis(‘off‘) ar=dst_array[:,:,0].flatten() ag=dst_array[:,:,1].flatten() ab=dst_array[:,:,2].flatten() plt.subplot(2,2,4), plt.title(‘dst hist‘) plt.axis([0,255,0,0.03]) plt.hist(ar, bins=256, normed=1,facecolor=‘red‘,edgecolor=‘r‘,hold=1) #原始图像直方图 plt.hist(ag, bins=256, normed=1,facecolor=‘g‘,edgecolor=‘g‘,hold=1) #原始图像直方图 plt.hist(ab, bins=256, normed=1,facecolor=‘b‘,edgecolor=‘b‘) #原g始图像直方图
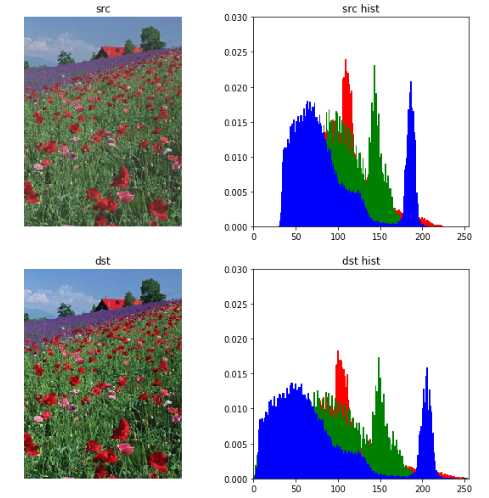
题目3
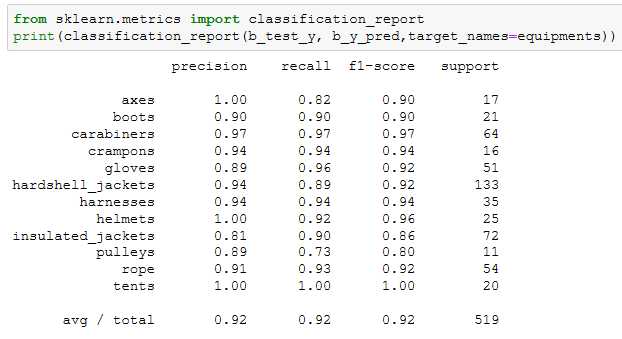
使用一个非参数化分类方法(参考 参考文档)来创建一个模型,预测新的户外装备图像的分类情况,训练来自挑战2的预处理过的128x128x3的装备图像。所使用的算法可以从scikit-learn库中挑选现有的非参数化算法来做分类。向教练展示所提供的测试数据集的精确度,并且精确度分数需要超过80%。

dir_data ="data/preprocess_images/" equipments = [‘axes‘, ‘boots‘, ‘carabiners‘, ‘crampons‘, ‘gloves‘, ‘hardshell_jackets‘, ‘harnesses‘, ‘helmets‘, ‘insulated_jackets‘, ‘pulleys‘, ‘rope‘, ‘tents‘] train_data = [] y = [] import os from PIL import Image for equip_name in equipments: dir_equip = dir_data + equip_name for filename in os.listdir(dir_equip): if(filename.find(‘jpeg‘)!=-1): name = dir_equip + ‘/‘ + filename img = Image.open(name).convert(‘L‘) train_data.append(list(img.getdata())) y.append(equip_name)

from sklearn import svm from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split train_X,test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(train_data, y, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 0) from sklearn import neighbors from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_fscore_support as score from sklearn.metrics import precision_score,recall_score clf_knn = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm=‘kd_tree‘) clf_knn.fit(train_X, train_y) y_pred = clf_knn.predict(test_X)

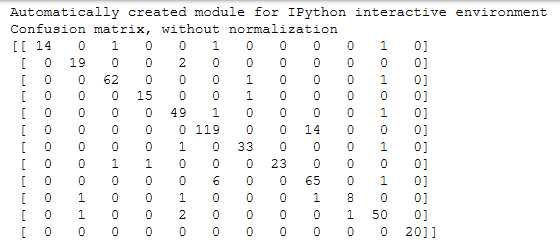
print(__doc__) import itertools import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import svm, datasets from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes, normalize=False, title=‘Confusion matrix‘, cmap=plt.cm.Blues): """ This function prints and plots the confusion matrix. Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`. """ if normalize: cm = cm.astype(‘float‘) / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis] print("Normalized confusion matrix") else: print(‘Confusion matrix, without normalization‘) print(cm) plt.imshow(cm, interpolation=‘nearest‘, cmap=cmap) plt.title(title) plt.colorbar() tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes)) plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45) plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes) fmt = ‘.2f‘ if normalize else ‘d‘ thresh = cm.max() / 2. for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])): plt.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt), horizontalalignment="center", color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black") plt.tight_layout() plt.ylabel(‘True label‘) plt.xlabel(‘Predicted label‘) # Compute confusion matrix # cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred) np.set_printoptions(precision=2) confusion_mat = confusion_matrix(test_y, y_pred, labels = equipments) # Plot non-normalized confusion matrix plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plot_confusion_matrix(confusion_mat, classes=equipments, title=‘Confusion matrix, without normalization‘) # Plot normalized confusion matrix plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plot_confusion_matrix(confusion_mat, classes=equipments, normalize=True, title=‘Normalized confusion matrix‘) plt.show()
因为要求精确度>0.8,sklearn中的很多算法应该都能满足,我选择了准确度比较高的KNN来建模,应该足够用了
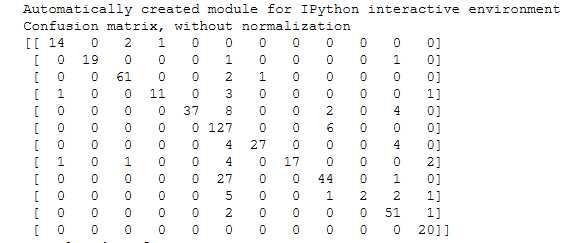
算一下presion和recall,轻松超越0.8
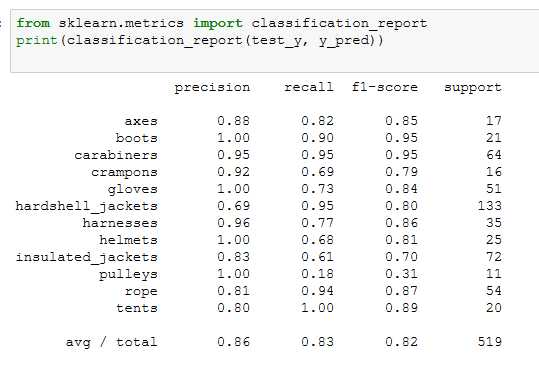
题目4
挑战完成标准,使用深度学习模型,如CNN分析复杂数据
团队将在Jupyter Notebook上为教练运行一个代码单元,展示模型的准确度为90%或更高
准确度如果要>0.9,sklearn中的机器学习算法就很难达到了,关键时刻只能上CNN

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from PIL import ImageColor from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow from PIL import Image from pylab import * dir_data ="data/preprocess_images/" equipments = [‘axes‘, ‘boots‘, ‘carabiners‘, ‘crampons‘, ‘gloves‘, ‘hardshell_jackets‘, ‘harnesses‘, ‘helmets‘, ‘insulated_jackets‘, ‘pulleys‘, ‘rope‘, ‘tents‘] train_data = [] y = [] import os from PIL import Image i=0 for equip_name in equipments: dir_equip = dir_data + equip_name for filename in os.listdir(dir_equip): if(filename.find(‘jpeg‘)!=-1): name = dir_equip + ‘/‘ + filename img = Image.open(name).convert(‘L‘) train_data.append(array(img).tolist()) y.append(i) i += 1 train_data = np.asarray(train_data)

from sklearn import svm from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split import numpy as np import keras num_classes=12 img_rows=128 img_cols=128 train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(train_data, y, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 0) train_X = train_X.reshape(train_X.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1) test_X = test_X.reshape(test_X.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1) train_X = train_X.astype(‘float32‘) test_X = test_X.astype(‘float32‘) train_X /= 255 test_X /= 255 print(‘x_train shape:‘, train_X.shape) print(train_X.shape[0], ‘train samples‘) print(test_X.shape[0], ‘test samples‘) # convert class vectors to binary class matrices train_y = keras.utils.to_categorical(train_y, num_classes) test_y = keras.utils.to_categorical(test_y, num_classes)

from keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Convolution2D,MaxPooling2D, Conv2D import keras model = Sequential() model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation=‘relu‘, input_shape=(128, 128, 1))) model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation=‘relu‘)) model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) # model.add(Dropout(0.25)) model.add(Flatten()) model.add(Dense(128, activation=‘relu‘)) # model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(12, activation=‘softmax‘)) model.compile(loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy, optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adadelta(), metrics=[‘accuracy‘]) model.fit(train_X, train_y, batch_size=128, epochs=50, verbose=1, validation_data=(test_X, test_y)) score = model.evaluate(test_X, test_y, verbose=0) print(‘Test loss:‘, score[0]) print(‘Test accuracy:‘, score[1])
CNN的混淆矩阵比KNN的好了不少
训练了好多次,不断调整各个卷积层和参数,终于达到了一个比较好的效果~~
题目6
使用深度学习框架,基于一个常用的模型,比如Faster R-CNN,训练一个目标检测的模型。这个模型需要能够检测并且使用方框框出图片中出现的每一个头盔。
这道题目首先要自己标注样本,几百张图像标注完累的半死。。。这里我们使用VOTT来标注,它会自动生成一个样本描述文件,很方便。Faster R-CNN的程序我们参考了git上的一个红细胞检测的项目,https://github.com/THULiusj/CosmicadDetection-Keras-Tensorflow-FasterRCNN,代码非常多就不贴了
最后来一张效果图

本文数据集和VOTT工具 链接:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1FFw0PLJrrOhwR6J1HexPJA
提取码 s242
以上是关于记微软OpenHack机器学习挑战赛的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
