基于cache和不拆点的优化算法
Posted hyc2026
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于cache和不拆点的优化算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一直对ds课上晏海华老师讲的dijkstra算法印象深刻,苦于一直没有地方施展,这次终于有了机会,于是第二次和第三次我都用了dijkstra算法莽到底。Dijkstra是单源的最短路径算法,主要特点是以起点为中心向外层层扩展(广度优先搜索思想),直至遍历完所有点,算出源点到其余所有点的最短距离。其具体算法思想在此不做过多阐述,不清楚的可以移步此网站。
存储图
要想遍历图,首先得存图,我用邻接表来存 private HashMap<Integer, HashMap<Edge, Integer>>
第一个Integer为起始节点(fromNodeId),第二个Integert为相同边的条数(为了防止在删边时一次删去了所有相同的边),Edge类中保存了 toNodeId 和 weight (Edge类需要重写hashCode和equals方法以作为hashMap的key;需要继承Comparable接口并重写compareTo方法,使得Edge可以放入优先队列中;可以重写toSrting方法方便debug)
为什么一个叫Edge的类只保存了 toNodeId 和 weight ,而没有保存 fromNodeId 呢,因为在邻接表中 formNodeId 是作为索引的存在。在之后的 Dijkstra 算法中以起点为中心向外层层扩展,因为起点已经存在,每次只扩展 weight 和 toNodeId。所以在Edge类中根本用不到 fromNodeId。
1 public class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> { 2 3 private int toNodeId; 4 private int weight; 5 6 public Edge(int toNodeId, int weight) { 7 this. toNodeId= toNodeId; 8 this.weight = weight; 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public int compareTo(Edge o) { 13 return this.weight - o.getWeight(); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public String toString() { 18 return (toNodeId + " " + weight); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public int hashCode() { 23 int result = 17; 24 result = result * 37 + toNodeId; 25 result = result * 37 + weight; 26 return result; 27 } 28 29 @Override 30 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 31 if (obj != null && (obj instanceof Edge)) { 32 return (((Edge) obj).getTo() == toNodeId 33 && ((Edge) obj).getWeight() == weight); 34 } else { 35 return false; 36 } 37 } 38 39 public int getToNodeId() { 40 return toNodeId; 41 } 42 43 public int getWeight() { 44 return weight; 45 } 46 }
我们得明确一点就是,要算的PATH_LENGTH、TICKET_PRICE、TRANSFER_COUNT和UNPLEASANT_VALUE是不相同的,而CONNECTED_BLOCK_COUNT可以利用上面任何一个来计算,我用的是PATH_LENGTH。接下来要解决的两个问题是如何构建邻接表和在何时利用Dijkstra算法。
何时使用Dijkstra
第二次作业结构变更指令有20条,第三次作业结构变更指令有50条,虽然有所增加,但是还是只占指令总数的很小一部分。所以最先能想到的方法就是在结构变更指令中计算出之后所有可能要用到的信息并存储起来,但仔细一想这种做法其实是不可取的,因为这种做法可能会计算很多用不到的信息,浪费时间。因此我们可以在add和remove之后只构建好邻接表,在查询时知道具体的起点和终点之后再利用Dijkstra算法的可以算出起点到所有点的最短路径的特点,建立四个类似于cache的hashMap来保存先前计算出的结果。
我们利用Connect类来保存两个节点的信息。(Connect类同样需要重写hashCode和equals方法,可以重写toString方法,在这里运用一个小技巧,就是在构造方法中把较小的作为fromNodeId,较大的作为toNodeId,这样在查询时可以不用考虑fromNodeId和toNodeId的顺序)
1 public class Connect { 2 3 private int fromNodeId; 4 private int toNodeId; 5 6 public Connect(int a, int b) { 7 if (a <= b) { 8 this.fromNodeId = a; 9 this.toNodeId = b; 10 } else { 11 this.fromNodeId = b; 12 this.toNodeId = a; 13 } 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public int hashCode() { 18 int result = 17; 19 result = result * 37 + fromNodeId; 20 result = result * 37 + toNodeId; 21 return result; 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 26 if (obj != null && (obj instanceof Connect)) { 27 return (((Connect) obj).getFromId() == fromNodeId 28 && ((Connect) obj).getToId() == toNodeId); 29 } else { 30 return false; 31 } 32 } 33 34 @Override 35 public String toString() { 36 return (fromNodeId + " " + toNodeId); 37 } 38 39 40 public int getFromIdNodeId () { 41 return fromNodeId; 42 } 43 44 public int getToIdNodeId () { 45 return toNodeId; 46 } 47 }
我们在使用完Dijkstra后,将原点到各个点的距离保存在HashMap<Integer, Integer>中,前一个Integer为toNodeId,后一个Integer为计算出的最短距离。然后将计算结果保存在cache中cache.put(new Connect(fromNodeId, a), dis.get(a)),a为用Iterator遍历的dis的keySet()。
构建邻接表
邻接表的构建需要分别考虑PATH_ADD和PATH_REMOVE两个过程,shortCount、transferCount、priceCount和valueCout分别代表四种图的邻接表。
a. shortCount
求最短路径就只需要按一般思路构建邻接表,即遍历一条路径,将相邻的两个点加入邻接表中。只用一次循环,path上两个点之间的权重设为1,需要更新相同边的num。
1 public HashMap<Integer, HashMap<Edge, Integer>> addShort(Path path) { 2 for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) { 3 if (shortCount.containsKey(path.getNode(i))) { 4 HashMap<Edge, Integer> value 5 = shortCount.get(path.getNode(i)); 6 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(i + 1), 1); 7 if (value.containsKey(edge)) { 8 int num = value.get(edge); 9 num++; 10 value.put(edge, num); 11 } else { 12 value.put(edge, 1); 13 } 14 shortCount.put(path.getNode(i), value); 15 } else { 16 HashMap<Edge, Integer> value = new HashMap<>(); 17 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(i + 1), 1); 18 value.put(edge, 1); 19 shortCount.put(path.getNode(i), value); 20 } 21 if (shortCount.containsKey(path.getNode(i + 1))) { 22 HashMap<Edge, Integer> value 23 = shortCount.get(path.getNode(i + 1)); 24 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(i), 1); 25 if (value.containsKey(edge)) { 26 int num = value.get(edge); 27 num++; 28 value.put(edge, num); 29 } else { 30 value.put(edge, 1); 31 } 32 shortCount.put(path.getNode(i + 1), value); 33 } else { 34 HashMap<Edge, Integer> value = new HashMap<>(); 35 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(i), 1); 36 value.put(edge, 1); 37 shortCount.put(path.getNode(i + 1), value); 38 } 39 } 40 return shortCount; 41 }
1 public HashMap<Integer, HashMap<Edge, Integer>> 2 removeShort(Path path) { 3 for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) { 4 HashMap<Edge, Integer> value = shortCount.get(path.getNode(i)); 5 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(i + 1), 1); 6 int num = value.get(edge); 7 num--; 8 if (num == 0) { 9 value.remove(edge); 10 if (value.size() == 0) { 11 shortCount.remove(path.getNode(i)); 12 } else { 13 shortCount.put(path.getNode(i), value); 14 } 15 } else { 16 value.put(edge, num); 17 shortCount.put(path.getNode(i), value); 18 } 19 value = shortCount.get(path.getNode(i + 1)); 20 edge = new Edge(path.getNode(i), 1); 21 num = value.get(edge); 22 num--; 23 if (num == 0) { 24 value.remove(edge); 25 if (value.size() == 0) { 26 shortCount.remove(path.getNode(i + 1)); 27 } else { 28 shortCount.put(path.getNode(i + 1), value); 29 } 30 } else { 31 value.put(edge, num); 32 shortCount.put(path.getNode(i + 1), value); 33 } 34 } 35 return shortCount; 36 }
在后面的三种情况中,因为涉及到了不同路径之间的换乘,所以按照之前的方法构建邻接表是不可取的。我们尝试构建一种新的、重构的图,将一条路径之间任意两点的都建立一条路径,那么在重构的图中,两个点之间有几条路径,就可以表示换乘了几次,我们开可以通过给重构的图的边赋不同的值,来最终得到我们想要的结果。
b. transferCount
为了计算换乘次数,需要将同一条路径之间任意两点之间都构建一条路径,所以要用两重循环,每两点之间的权重仍为1。换乘的次数即为求出的最短路径减1。
e.g.对于路径1 2 3和路径4 2 5
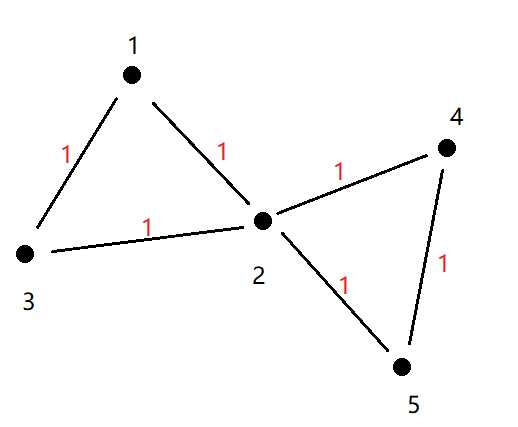
1到3换乘1-1=0次
1到5换乘2-1=1次
1 public HashMap<Integer, HashMap<Edge, Integer>> 2 addTransfer(Path path) { 3 for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) { 4 for (int j = i + 1; j < path.size(); j++) { 5 if (transferCount.containsKey(path.getNode(i))) { 6 HashMap<Edge, Integer> value 7 = transferCount.get(path.getNode(i)); 8 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(j), 1); 9 if (value.containsKey(edge)) { 10 int num = value.get(edge); 11 num++; 12 value.put(edge, num); 13 } else { 14 value.put(edge, 1); 15 } 16 transferCount.put(path.getNode(i), value); 17 } else { 18 HashMap<Edge, Integer> value = new HashMap<>(); 19 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(j), 1); 20 value.put(edge, 1); 21 transferCount.put(path.getNode(i), value); 22 } 23 if (transferCount.containsKey(path.getNode(j))) { 24 HashMap<Edge, Integer> value 25 = transferCount.get(path.getNode(j)); 26 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(i), 1); 27 if (value.containsKey(edge)) { 28 int num = value.get(edge); 29 num++; 30 value.put(edge, num); 31 } else { 32 value.put(edge, 1); 33 } 34 transferCount.put(path.getNode(j), value); 35 } else { 36 HashMap<Edge, Integer> value = new HashMap<>(); 37 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(i), 1); 38 value.put(edge, 1); 39 transferCount.put(path.getNode(j), value); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 return transferCount; 44 }
(remove同理)
在后两种邻接表的构建过程中仍然仿照transfer方法,但是对weight需要有新的计算方法,这里采用floyd算法。price的边权为1,value的边权为F(fromNodeId,toNodeId)(F定义如下),switching为开关,true为price,false为value。
1 private int[] aa = {1, 4, 16, 64, 256}; 2 private int F(int x, int y) { 3 return aa[Math.max(((x % 5 + 5) % 5), ((y % 5 + 5) % 5))]; 4 }
1 private void flord(Path path, boolean switching) { 2 HashMap<Integer, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); 3 int n = 0; 4 int max = 120; 5 int[][] matrix = new int[max][max]; 6 for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) { 7 for (int j = 0; j < max; j++) { 8 if (i == j) { 9 matrix[i][j] = 0; 10 } else { 11 matrix[i][j] = 1000000; 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) { 16 if (!hashMap.containsKey(path.getNode(i))) { 17 hashMap.put(path.getNode(i), n); 18 n++; 19 } 20 if (!hashMap.containsKey(path.getNode(i + 1))) { 21 hashMap.put(path.getNode(i + 1), n); 22 n++; 23 } 24 if (path.getNode(i) == path.getNode(i + 1)) { 25 matrix[hashMap.get(path.getNode(i))] 26 [hashMap.get(path.getNode(i + 1))] = 0; 27 } else { 28 if (switching) { 29 matrix[hashMap.get(path.getNode(i))] 30 [hashMap.get(path.getNode(i + 1))] = 1; 31 matrix[hashMap.get(path.getNode(i + 1))] 32 [hashMap.get(path.getNode(i))] = 1; 33 } else { 34 matrix[hashMap.get(path.getNode(i))] 35 [hashMap.get(path.getNode(i + 1))] 36 = F(path.getNode(i), path.getNode(i + 1)); 37 matrix[hashMap.get(path.getNode(i + 1))] 38 [hashMap.get(path.getNode(i))] 39 = F(path.getNode(i), path.getNode(i + 1)); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 for (int k = 0; k < max; k++) { 44 for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) { 45 for (int j = 0; j < max; j++) { 46 if (matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j] < matrix[i][j]) { 47 matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j]; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 if (switching) { 53 priceMatrix = matrix; 54 priceMap = hashMap; 55 } else { 56 valueMatrix = matrix; 57 valueMap = hashMap; 58 } 59 }
计算出的两两之间的权值保存在matrix中,因为nodeId并不是按照从零开始递增的,但是为了利用二维数组,需要建立一个映射表,存在hashMap中。因为在删除边是还要利用映射关系和权值,所以matrix和hashMap需要分别保存在HashMap<Path, int[][]>和HashMap<Path, HashMap<Integer, Integer>>中。
c. priceCount
计算出一条路径中任意两点之间的权重后,构建邻接表就比较简单了。边权为一条path内最短路径加2,票价为最终求出的最短路径减2
e.g.对于路径1 2 3和路径4 2 5
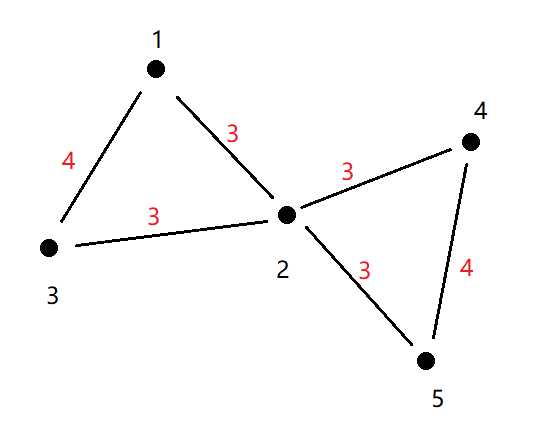
1到2的边权为1+2=3,票价为3-2=1
1到3的边权为2+2=4,票价为4-2=2
1到5的票价为3+3-2=4
相对于transfer,有改动的地方是 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(j), 2 + priceMatrix[priceMap.get(path.getNode(i))][priceMap.get(path.getNode(j))]);
d. valueCout
计算出一条路径中任意两点之间的权重后,构建邻接表就比较简单了。边权为一条path内最短路径加32,票价为最终求出的最短路径减32
e.g.对于路径1 2 3和路径4 2 5
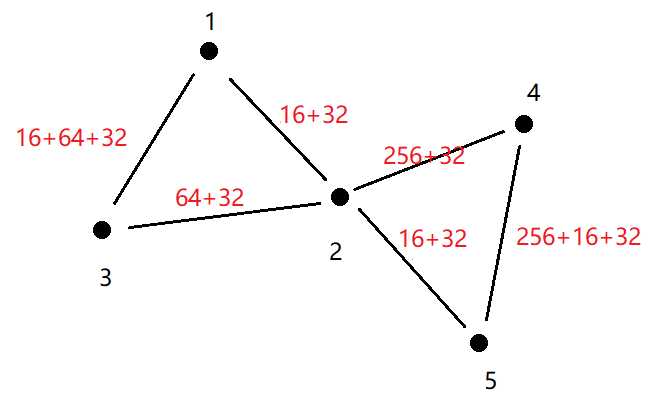
1到2的边权为16+32=48,不满意度为48-32=16
1到3的边权为16+64+32=112,票价为112-32=80
1到5的票价为48+48-32=64
相对于transfer,有改动的地方是 Edge edge = new Edge(path.getNode(j), 32 + valueMatrix[valueMap.get(path.getNode(i))][valueMap.get(path.getNode(j))]);
add和remove
1 public int addPath(Path path) { 2 if (path != null && path.isValid()) { 3 if (pidList.containsKey(path)) { 4 return pidList.get(path); 5 } 6 id++; 7 pathList.put(id, path); 8 pidList.put(path, id); 9 shortCount = addShort(path); 10 transferCount = addTransfer(path); 11 priceCount = addPrice(path); 12 priceMatrixPath.put(path, priceMatrix); 13 priceMapPath.put(path, priceMap); 14 valueCount = addRemove.addValue(path); 15 valueMatrixPath.put(path, valueMatrix); 16 valueMapPath.put(path, valueMap); 17 shorrt = new HashMap<>(); 18 transfer = new HashMap<>(); 19 price = new HashMap<>(); 20 value = new HashMap<>(); 21 block = connectedBlock(); 22 return id; 23 } else { 24 return 0; 25 } 26 }
1 public int removePath(Path path) throws PathNotFoundException { 2 if (path == null || !path.isValid() || !pidList.containsKey(path)) { 3 throw new PathNotFoundException(path); 4 } else { 5 shortCount = addRemove.removeShort(path); 6 transferCount = addRemove.removeTransfer(path); 7 priceCount = addRemove.removePrice(path); 8 valueCount = addRemove.removeValue(path); 9 int pathId = pidList.get(path); 10 pidList.remove(path); 11 pathList.remove(pathId); 12 shorrt = new HashMap<>(); 13 transfer = new HashMap<>(); 14 price = new HashMap<>(); 15 value = new HashMap<>(); 16 block = connectedBlock(); 17 return pathId; 18 } 19 }
(removePathById同理)
注意到有一句是 block = connectedBlock(),connectBlock是计算连通块个数的,在遍历所有点的基础上调用了几次Dijkstra算法,便有几个连通块,并将结果保存在cache中。因为连通块的个数在add和remove之后会变动,并且不能利用缓存中的信息,所以在结构变更指令后直接计算connectBlock的个数,并将结果保存在cache中。
事实上用四种算法都可以计算连通块的个数,但是在我的程序中isConnect也是用short来算的,这样short的cache命中率会大大增加。
查询
在查询时先查cache,若cache命中则直接输出结果,若未命中再用dijkstra算法算出结果,保存在cache中并输出结果。(shorrt即为cache)
1 public int getShortestPathLength(int fromNodeId, int toNodeId) 2 throws NodeIdNotFoundException, NodeNotConnectedException { 3 if (!shortCount.containsKey(fromNodeId)) { 4 throw new NodeIdNotFoundException(fromNodeId); 5 } else if (!shortCount.containsKey(toNodeId)) { 6 throw new NodeIdNotFoundException(toNodeId); 7 } else if (!isConnected(fromNodeId, toNodeId)) { 8 throw new NodeNotConnectedException(fromNodeId, toNodeId); 9 } else { 10 Connect connect = new Connect(fromNodeId, toNodeId); 11 if (shorrt.containsKey(connect)) { 12 return shorrt.get(connect); 13 } else { 14 dis = dijkstra(fromNodeId); 15 Iterator<Integer> iterator = dis.keySet().iterator(); 16 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 17 int a = iterator.next(); 18 shorrt.put(new Connect(fromNodeId, a), dis.get(a)); 19 } 20 return shorrt.get(connect); 21 } 22 } 23 }
Dijkstra
最后贴上我的dijkstra算法。
1 public HashMap<Integer, Integer> dijkstra(int s) { 2 HashMap<Integer, Integer> visit = new HashMap<>(); 3 HashMap<Integer, Integer> dis = new HashMap<>(); 4 Iterator<Integer> iterator = shortCount.keySet().iterator(); 5 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 6 int key = iterator.next(); 7 dis.put(key, 1000000); 8 visit.put(key, 0); 9 } 10 Queue<Edge> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(); 11 queue.add(new Edge(s, 0)); 12 dis.put(s, 0); 13 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 14 Edge now = queue.poll(); 15 if (dis.get(now.getTo()) < now.getWeight()) { 16 continue; 17 } 18 if (visit.get(now.getTo()) == 1) { 19 continue; 20 } 21 visit.put(now.getTo(), 1); 22 Iterator<Edge> i 23 = shortCount.get(now.getTo()).keySet().iterator(); 24 while (i.hasNext()) { 25 Edge edge = i.next(); 26 if (visit.get(edge.getTo()) == 0 && dis.get(edge.getTo()) 27 > dis.get(now.getTo()) + edge.getWeight()) { 28 dis.put(edge.getTo(), 29 dis.get(now.getTo()) + edge.getWeight()); 30 queue.add( 31 new Edge(edge.getTo(), dis.get(edge.getTo()))); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 return dis; 36 }
以上是关于基于cache和不拆点的优化算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章