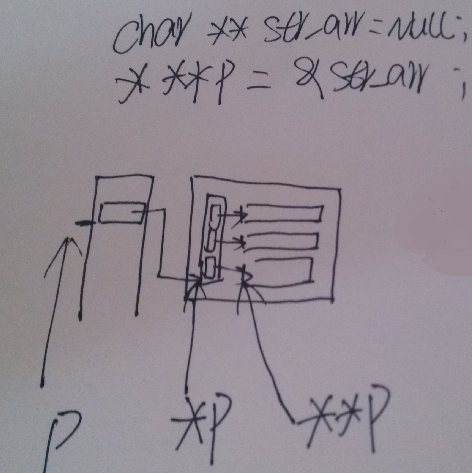
C提高4 多维数组,结构体与二级指针
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C提高4 多维数组,结构体与二级指针相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
昨天的试题:原题见昨天作业题
[email protected]:~/high/day03$ cat main.c /* 二级指针,绝佳训练题1 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int spitspring(char *buf1,char *c,char **myp,int *total) { char *p_head = buf1; char *p_tail = buf1; int count = 0; while(*p_head != ‘\0‘) { p_head = strstr(p_head,c); if(p_head == NULL) { break; } if(p_head - p_tail > 0) { strncpy(myp[count],p_tail,p_head - p_tail); myp[count][p_head - p_tail] = ‘\0‘; count ++; p_head = p_head+1; p_tail = p_head; } } *total = count; return 0; } int main() { int ret = 0; int i = 0; char *string = "abcd,efg,accd,2313,3,42,4"; char *split_char = ","; int count = 0; //在主函数中手动分配malloc空间,用来存放10个子串 char **str_arr = NULL; str_arr = (char **)malloc(10* sizeof(char *)); //str_arr指针的步长是 char * if(str_arr == NULL) { return -1; } //为10个子串分别分配30个char的长度空间 for(i = 0;i<10;i++) { *(str_arr + i) = (char *)malloc(30 * sizeof(char)); } //调用函数,将处理的结果返回到str_arr中 ret = spitspring(string,split_char,str_arr,&count); if(ret != 0) { printf("ERROR IN spitspring %d",ret); return ret; } //打印输出 for(i = 0;i<10;i++) { printf("%s \n",*(str_arr + i)); } //释放空间 for(i = 0;i<10;i++) { free(*(str_arr + i) ); } free(str_arr); printf("Hello End!\n"); return ret; } [email protected]:~/high/day03$ [email protected]:~/high/day03$ [email protected]:~/high/day03$ gcc -g -o main main.c && ./main abcd efg accd 2313 3 42 Hello End! [email protected]:~/high/day03$
还是上面这道题,主调函数不分配内存,被调函数返回malloc
[email protected]:~/high/day03$ cat main.c /* 二级指针,绝佳训练题1 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> char ** spitspring(char *str,char *c,int *total) { //1先求出有多少个子串,count char *p_head = str;//向字符串右跑 char *p_tail = str;// int count = 0; while(p_head) { p_head = strstr(p_head,c); if(p_head - p_tail > 0) { count ++; p_tail = p_head = p_head+1; } } *total = count; //根据子串数目,精确分配个数 char **str_arr = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * count); if(str_arr == NULL) { return NULL; } p_head = str; p_tail = str; count = 0; while(p_head) { p_head = strstr(p_head,c); if(p_head - p_tail > 0) { int len = p_head - p_tail +1; //存放字符串的‘\0‘ *(str_arr + count) = malloc(len * sizeof(char)); if(*(str_arr + count) == NULL) { return NULL; } strncpy(*(str_arr + count),p_tail,p_head - p_tail); *(*(str_arr + count) + (p_head - p_tail) ) = ‘\0‘; count ++; p_head = p_head+1; p_tail = p_head; } } return str_arr; } int main() { int ret = 0; int i = 0; char *string = "abcd,efg,"; char *split_char = ","; int count = 0; char **str_arr = spitspring(string,split_char,&count); if(str_arr == NULL) { printf("ERROR IN spitspring %d \n",ret); return ret; } //打印输出 for(i = 0;i<count;i++) { printf("%s \n",*(str_arr + i)); } //释放空间 for(i = 0;i<count;i++) { free(*(str_arr + i) ); } free(str_arr); return ret; } [email protected]:~/high/day03$ [email protected]:~/high/day03$ [email protected]:~/high/day03$ gcc -g -o main main.c && ./main abcd efg [email protected]:~/high/day03$
我的练习
[email protected]:~/high$ cat my.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> /* 涉及的知识点: 两个指针挖字符串 多级指针内存分配 多级指针内存分配出错的处理 多级指针释放内存空间 */ void free_two_level_pointer(char ***p,int count) { if(p == NULL) return ; int i; for(i = 0;i<count;i++)//先释放几个子串的空间 { if(*(p + i) != NULL) { free(*(*(p) + i));//此处相当于数组 第p[i] 行 *(*(p) + i) = NULL; } } if(*p != NULL)//再释放存放子串数目的空间 { free(*p); *p = NULL; } return ; } int splitstr(const char *str/*in*/,const char *split_str/*in*/,char ***str_arr/*out*/,int *count/*in*/) { if(str == NULL) return -1; if(split_str == NULL) return -2; if(str_arr == NULL) return -3; if(count == NULL) return -4; const char *p_head = str; const char *p_tail = str; int my_count = 0; int i =0; int ret = 0; //1找出子串的个数 while(p_head = strstr(p_head,split_str)) { p_head += strlen(split_str);; my_count++; } *count = my_count; //printf("[]%d \n",*count); //创建二维数组的行数,有几个子串就创建几行 char **my_str_arr = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * my_count); if(my_str_arr == NULL) { ret = -1; goto END; } char **tmp_str_arr =my_str_arr;//只有当分配成功时才执行 //这一步非常重要,将申请到的空间置0,为判断下一级指针分配是否成功,埋下伏笔 memset(tmp_str_arr,0,sizeof(char *) * my_count); //给把分割的子串存放起来 p_head = str; p_tail = str; my_count = 0; while(p_head = strstr(p_head,split_str)) { *(tmp_str_arr + my_count) = (char * )malloc(sizeof(char) * (p_head - p_tail + 1 )); //为‘\0‘分配存储空间 if(*(tmp_str_arr + my_count) == NULL) { ret = -2; goto END; } strncpy(*(tmp_str_arr + my_count),p_tail,p_head - p_tail); *(*(tmp_str_arr + my_count) + (p_head - p_tail +1)) = ‘\0‘; my_count ++; p_head += strlen(split_str);; p_tail = p_head; } END: if(ret != 0) { //释放堆内存 free_two_level_pointer(&my_str_arr,*count); printf("ERROR in splitstr :%d \n",ret); return -1; } *str_arr = my_str_arr; return 0; } int main() { int ret = 0; int i = 0; char *str = "ab123,ad456,qwedc,123,12wsx,"; char *split_str = ","; int count = 0; char **str_arr = NULL; //调用这个函数 ret = splitstr(str,split_str,&str_arr,&count); if(ret != 0) { printf("ERROR in splitstr :%d\n",ret); return ret; } //遍历 for(i = 0;i<count;i++) { printf("[%d] -> %s \n",i+1,*(str_arr + i)); } //释放堆内存 free_two_level_pointer(&str_arr,count); return ret ; } [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g my.c && ./a.out [1] -> ab123 [2] -> ad456 [3] -> qwedc [4] -> 123 [5] -> 12wsx [email protected]:~/high$
【数组指针】【数组指针】【数组指针】【数组指针】【数组指针】
数组类型:
数组地址,自定义数组:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int a[] = {1,2}; //长度为2
int b[100] = {1,3}; //长度为100,后面全是0
int c[200] = {0}; //长度为200,编译器自动全部置0
memset(c,0,sizeof(c)); //显式重置内存块
// c是数组的首地址 步长为 4个字节
// &c是数组的地址,步长为200 *4个字节
printf("%p ,%p \n",c,c+1);
printf("%p ,%p \n",&c,&c+1);
typedef int (MyArrayType)[5]; //定义了一个数据类型,数组数据类型
MyArrayType myArray; //相当于 int myArray[5];
int i = 0;
for (i = 0;i < 5;i++ )
{
myArray[i] = i*i;
}
for (i = 0;i < 5;i++ )
{
printf("%d \n",myArray[i]);
}
return 0;
}
编译:
[email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out
0x7ffd6f70b700 ,0x7ffd6f70b704
0x7ffd6f70b700 ,0x7ffd6f70ba20
0
1
4
9
16【压死初学者的三座大山】
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//定义数组指针变量的方法1
//用自定义数组类型 *
int main()
{
int i = 0;
//指针数组
char *arr1[] = {"hehe","haha","123456"};//指针数组,三个指针指向不同的字符串
//数组的指针
typedef int (MyArrayType)[5]; //定义了一个数据类型,int [5]数组数据类型
MyArrayType arr2; //相当于 int myArray[5];
MyArrayType *arr3;
int arr4[5]; //普通数组
arr3 = &arr4;
for(i = 0;i<5;i++)
{
*((*arr3) + i) = i * i;
}
for(i = 0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("%d \n",*((*arr3) + i));
}
return 0;
}
编译:
[email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out
0
1
4
9
16//定义数组指针变量的方法2
//定义声明一个数组指针类型
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//定义数组指针变量的方法2
//定义声明一个数组指针类型
int main()
{
int i = 0;
typedef int (*P_arr)[5]; //申明一种数据类型,相当于二级指针
P_arr arr1 = NULL; //告诉编译器,给我分配一个指针变量
int arr2[5] ; //定义了一个普通的数组
arr1 = &arr2;
for(i = 0;i<5;i++)
{
*((*arr1) + i) = i * i;
}
for(i = 0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("%d \n",*((*arr1) + i));
}
return 0;
}
[email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out
0
1
4
9
16直接定义数组指针
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//定义数组指针变量的方法3
//前两种方法通过类型定义变量 比较麻烦
int main()
{
int (*p)[5] = 0; //定义了一个指向数组的 ,数组指针变量
int arr[5];
p = &arr;
int i = 0;
for(i = 0;i < 5;i++)
{
*((*p) + i) = i * i + i;
}
for(i = 0;i < 5;i++)
{
printf("%d \n",*((*p) + i));
}
return 0;
}
编译:
[email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out
0
2
6
12
20//多维数组的本质推演
//看图
[email protected]:~/high$ cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> //多维数组的本质推演 //看图 int main() { int arr1[3][5]; int i = 0; int j = 0; for(i = 0;i < 3;i++) { for(j = 0;j < 5;j++) { arr1[i][j] = i + j; } } for(i = 0;i < 3;i++) { for(j = 0;j < 5;j++) { printf("%d\t",arr1[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } //探索 printf("%p ,%p ,(跳过了20个字节)\n",arr1,arr1 + 1); printf("%p ,%p ,(跳过了60个字节)\n",&arr1,(&arr1) + 1); int (*p)[5];//这个指针的步长是5 * int p = arr1; for(i = 0;i < 3;i++) { for(j = 0;j < 5;j++) { printf("%d\t",p[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out 0 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 6 0x7ffc3f09a490 ,0x7ffc3f09a4a4 ,(跳过了20个字节) 0x7ffc3f09a490 ,0x7ffc3f09a4cc ,(跳过了60个字节) 0 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 6 [email protected]:~/high$
//证明:二维数组做函数形参 退化
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//证明:二维数组做函数形参 退化
void printf_arr(int (*p)[5]) //p的步长的int 5
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for(i = 0;i < 3;i++)
{
for(j = 0;j<5;j++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*(p + i) + j) );
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr1[3][5];
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for(i = 0;i < 3;i++)
{
for(j = 0;j < 5;j++)
{
arr1[i][j] = i + j;
}
}
printf_arr(arr1);
return 0;
}
编译:
[email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out
0 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 6 [email protected]:~/high$
[email protected]:~/high$//证明:二维数组在内存中是线性存储的
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//证明:二维数组在内存中是线性存储的
int main()
{
int arr1[3][5];
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for(i = 0;i < 3;i++)
{
for(j = 0;j < 5;j++)
{
arr1[i][j] = i + j;
}
}
int *p = (int *) arr1;
for(i = 0;i < 3* 5;i++)
{
printf("%d ",*(p + i));
}
return 0;
}
编译:
[email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out
0 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 6 [email protected]:~/high$
[email protected]:~/high$多维数组当函数参数,退化为指针的证明:
[email protected]:~/high$ cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> //返回关键字所在菜单列表的位置 int searchKeyTable(char* table[],const int size, const char *key,int *pos) { printf("数组大小 %ld \n",sizeof(table)/sizeof(*table)); printf("这个就可以证明,多维数组当函数参数,退化为一个指针\n"); return 0; } #define DIM(a) (sizeof(a)/sizeof(*a)) int main() { int inum = 0; int pos = 0; int a[10]; int i = 0; char *c_keyword[] = { "while", "case", "static", "do" }; printf("数组大小 %ld \n",sizeof(c_keyword)/sizeof(*c_keyword)); searchKeyTable(c_keyword,DIM(c_keyword),"do",&pos); return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out 数组大小 4 数组大小 1 这个就可以证明,多维数组当函数参数,退化为一个指针 [email protected]:~/high$
【指针数组的应用 】
返回关键字所在菜单列表的位置
[email protected]:~/high$ cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> //返回关键字所在菜单列表的位置 int searchKeyTable(char* table[],const int size, const char *key,int *pos) { int rv = 0; int i = 0 ; int inum = 0; if(table == NULL) return -1; if(key == NULL) return -1; if(pos == NULL) return -1; for(i = 0;i<size;i++) { if(strcmp(key,table[i]) == 0) { *pos = i; return rv; } } if(i == size) { *pos = -1; } return 0; } #define DIM(a) (sizeof(a)/sizeof(*a)) int main() { int inum = 0; int pos = 0; int a[10]; int i = 0; char *c_keyword[] = { "while", "case", "static", "do" }; searchKeyTable(c_keyword,DIM(c_keyword),"do",&pos); printf("%d \n",pos); return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out 3 [email protected]:~/high
指针数组的命令行模式
[email protected]:~/high$ cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(int num,char **str1,char **str2) //操作系统在调用之前,为参数的存储提供空间 { int i = 0; for(i = 0;i<num;i++) { printf("%s \n",str1[i]); } printf("--------------------------\n"); for(i = 0;str2[i] != NULL;i++) { printf("%s \n",str2[i]); } return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out 123 345 ./a.out 123 345 -------------------------- XDG_SESSION_ID=2 TERM=xterm SHELL=/bin/bash SSH_CLIENT=10.11.12.1 9479 22 SSH_TTY=/dev/pts/1 USER=chunli LD_LIBRARY_PATH=:. MAIL=/var/mail/chunli PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games PWD=/home/chunli/high LANG=en_US.UTF-8 SHLVL=1 HOME=/home/chunli LANGUAGE=en_US:en LOGNAME=chunli SSH_CONNECTION=10.11.12.1 9479 10.11.12.4 22 XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/1000 OLDPWD=/home/chunli _=./a.out [email protected]:~/high$
具有自我结束能力的指针数组
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//具有自我结束能力的指针数组
int main()
{
int i = 0;
char *str_arr[] = {
"1234",
"5678",
"1357",
"2468",
‘\0‘
};
while( *(str_arr + i) )
{
printf("%s \n",*(str_arr + i));
i++;
}
}
编译:
[email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out
1234
5678
1357
2468更深层次:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//具有自我结束能力的指针数组
int main()
{
int i = 0;
char *str_arr[] = {
"1234",
"5678",
"1357",
"2468",
‘\0‘, // ‘\0‘ 0 NULL 都是一样的效果,都是字符结束标志
0, // ‘\0‘ 0 NULL 都是一样的效果,都是字符结束标志
NULL // ‘\0‘ 0 NULL 都是一样的效果,都是字符结束标志
};
while( *(str_arr + i) )
{
printf("%s \n",*(str_arr + i));
i++;
}
}--------------结构体------
【结构体 提高】
【1】结构体类型的定义
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//定义了一个数据类型。固定大小内存块的别名,此时还没有分配内存
struct Teacher
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
};
int main()
{
struct Teacher t1; //告诉编译器,给我分配内存
return 0;
}//定义了一个数据类型。固定大小内存块的别名,此时还没有分配内存
typedef struct Teacher //别名
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
} struct_teacher;
int main()
{
struct_teacher t1; //使用typedef之后,可以省略struct 直接这样定义
return 0;
}结构体变量的定义3中方法:
1,直接定义
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//结构体定义变量,有3种
typedef struct Teacher
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
} struct_teacher;
int main()
{
struct_teacher t1; //定义结构体方法1
return 0;
}2,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//结构体定义变量,有3种
//2 定义类型的同时,定义变量
struct Teacher
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
} teacher1,teacher2;
int main()
{
return 0;
}3,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//结构体定义变量,有3种
//2 定义类型的同时,定义隐式变量
struct
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
} teacher1,teacher2;
int main()
{
return 0;
}【初始化变量的3中方法】
1,定义变量的时候初始化;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
} s_teacher;
int main()
{
s_teacher t1 = {"chunli",22,007};
return 0;
}2,定义结构体时就定义两个变量
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Teacher
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
}
teacher1 = {"chunli",22,7},
teacher2 = {"chunli",22,7};
int main()
{
return 0;
}3,匿名结构体
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
}
teacher1 = {"chunli",22,7},
teacher2 = {"chunli",22,7};
int main()
{
return 0;
}结构体变量的引用:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Teacher
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
};
int main()
{
struct Teacher t1;
struct Teacher t2;
t1.age = 12; //.点是寻址操作,计算age相对于t1大变量的偏移量
t1.id = 1;
strcpy(t1.name,"chunli");
printf("%s,%d,%d \n",t1.name,t1.age,t1.id);
return 0;
}
编译:
[email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out
chunli,12,1结构体指针的引用:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Teacher
{
char name[64];
int age;
int id;
};
int main()
{
struct Teacher t1;
struct Teacher t2;
t1.age = 12; //.点是寻址操作,计算age相对于t1大变量的偏移量,计算过程在CPU,不在内存
t1.id = 1;
strcpy(t1.name,"chunli");
//通过指针的方式操作内存
struct Teacher *p;
p = &t1;
p -> id = 2; //.点是寻址操作,计算age相对于t1大变量的偏移量,计算过程在CPU,不在内存
printf("%s,%d,%d \n",t1.name,t1.age,t1.id);
printf("%s,%d,%d \n",p -> name,p -> age,p -> id);
return 0;
}
编译:
[email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out
chunli,12,2
chunli,12,2结构体浅拷贝:
[email protected]:~/high$ cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> struct Teacher { char name[64]; int age; int id; }; //浅拷贝 void my_copy(struct Teacher *to,struct Teacher *from) { *to = *from; } int main() { struct Teacher t1 = {"chunli",2,22}; struct Teacher t2; my_copy(&t2,&t1); printf("%s,%d,%d \n",t2.name,t2.age,t2.id); return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out chunli,2,22 [email protected]:~/high$
结构体在栈空间:按照年龄排序:
[email protected]:~/high$ cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> struct Teacher { char name[64]; int age; int id; }; void printf_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { while(num--) { printf("%d \n",p[num-1].age); } } void sort_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { int i = 0; int j = 0; struct Teacher tmp; for(i = 0;i<num; i++) { for(j = i+1;j<num;j++) if(p[i].age > p[j].age ) { tmp = p[i]; p[i] = p[j]; p[j] = tmp; } } } int main() { int i = 0; struct Teacher teacher_arr[3]; for(i = 0;i < 3;i++) { printf("[%d]Enter age: ",i+1); scanf("%d",&teacher_arr[i].age); } sort_teacher(teacher_arr,3); for(i = 0;i < 3;i++) { printf("age = %d \n",teacher_arr[i].age); } return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out [1]Enter age: 12 [2]Enter age: 11 [3]Enter age: 23 age = 11 age = 12 age = 23 [email protected]:~/high$
结构体指针做函数参数基本应用,内存分配,释放内存
[email protected]:~/high$ cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> struct Teacher { char name[64]; int age; int id; }; struct Teacher *create_teacher(int num) { struct Teacher *p = (struct Teacher *)malloc(sizeof(struct Teacher ) * num); if(p == NULL) { return NULL; } } void printf_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { while(num--) { printf("%d \n",p[num].age); } } void free_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { while(num--) { if(p+num != NULL) { free(p + num); } } } void sort_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { if(p == NULL) { return ; } int i = 0; int j = 0; struct Teacher tmp; for(i = 0;i<num; i++) { for(j = i+1;j<num;j++) if(p[i].age < p[j].age ) { tmp = p[i]; p[i] = p[j]; p[j] = tmp; } } } int main() { int i = 0; struct Teacher *teacher_arr = create_teacher(3);; for(i = 0;i < 3;i++) { printf("[%d]Enter age: ",i+1); scanf("%d",&(teacher_arr[i]).age); //printf("%d \n",teacher_arr[i].age); } sort_teacher(teacher_arr,3); printf_teacher(teacher_arr,3); return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out [1]Enter age: 99 [2]Enter age: 11 [3]Enter age: 66 11 66 99
结构体指针做函数参数,进阶
[email protected]:~/high$ cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> struct Teacher { char name[64]; int age; int id; }; int create_teacher( struct Teacher **pt,int num) { int ret = 0; struct Teacher *p = NULL; p = (struct Teacher *)malloc(sizeof(struct Teacher ) * num); if(p == NULL) { return -1; } *pt = p; return ret; } void printf_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { while(num--) { printf("%d \n",p[num].age); } } void free_teacher(struct Teacher **p,int num) { if(*p != NULL) { free(*p); *p = NULL; } } void sort_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { if(p == NULL) { return ; } int i = 0; int j = 0; struct Teacher tmp; for(i = 0;i<num; i++) { for(j = i+1;j<num;j++) if(p[i].age < p[j].age ) { tmp = p[i]; p[i] = p[j]; p[j] = tmp; } } } int main() { int i = 0; int ret = 0; int num = 3; struct Teacher *teacher_arr = NULL; ret = create_teacher(&teacher_arr,num);; if(ret != 0) { printf("ERROR IN create_teacher %d \n",ret); return ret; } for(i = 0;i < num;i++) { printf("[%d]Enter age: ",i+1); scanf("%d",&(teacher_arr[i]).age); } sort_teacher(teacher_arr,num); printf_teacher(teacher_arr,num); free_teacher(&teacher_arr,num); return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g main.c && ./a.out [1]Enter age: 33 [2]Enter age: 22 [3]Enter age: 88 22 33 88 [email protected]:~/high$
结构体套一级指针:
[email protected]:~/high$ cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> struct Teacher { char name[64]; char *alias; int age; int id; }; int create_teacher( struct Teacher **pt,int num) { int ret = 0; int i = 0; struct Teacher *p = NULL; p = (struct Teacher *)malloc(sizeof(struct Teacher ) * num); if(p == NULL) { return -1; } memset(p,0,sizeof(struct Teacher) * num); for(i = 0;i<num;i++) //为每一个节点分配内存空间 { p[i].alias = (char *)malloc( 100); if(p[i].alias == NULL) { return -2; } memset(p[i].alias,0,100); } *pt = p; return ret; } void printf_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { while(num--) { printf("%d \n",p[num].age); } } void free_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { if(p == NULL) return ; int i = 0; for(i = 0;i<num;i++) { if(p[i].alias != NULL) { free(p[i].alias); p[i].alias = NULL; } } if(p != NULL) { free(p); p = NULL; } } void sort_teacher(struct Teacher *p,int num) { if(p == NULL) { return ; } int i = 0; int j = 0; struct Teacher tmp; for(i = 0;i<num; i++) { for(j = i+1;j<num;j++) if(p[i].age < p[j].age ) { tmp = p[i]; p[i] = p[j]; p[j] = tmp; } } } int main() { int i = 0; int ret = 0; int num = 3; struct Teacher *teacher_arr = NULL; ret = create_teacher(&teacher_arr,num);; if(ret != 0) { printf("ERROR IN create_teacher %d \n",ret); return ret; } for(i = 0;i < num;i++) { printf("\n[%d]Enter age: ",i+1); scanf("%d",&(teacher_arr[i]).age); printf("\n[%d]Enter name: ",i+1); scanf("%s",teacher_arr[i].name); printf("\n[%d]Enter alias: ",i+1); scanf("%s",teacher_arr[i].alias); } sort_teacher(teacher_arr,num); printf_teacher(teacher_arr,num); free_teacher(teacher_arr,num); return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g -Wall main.c && ./a.out [1]Enter age: 11 [1]Enter name: 11 [1]Enter alias: 11 [2]Enter age: 22 [2]Enter name: 22 [2]Enter alias: 22 [3]Enter age: 33 [3]Enter name: 33 [3]Enter alias: 33 11 22 33 [email protected]:~/high$
教师结构体 二级指针训练
1,在堆中分配结构体空间
2,每个老师有一个别名,存在堆中
3,每个老师带领3名学生,学生的名字分别存在堆中
4,初始化每个老师与学生的信息
5,按照老师的名字,把结构体排序
6,打印出全部结构体信息
7,堆中结构体释放
[email protected]:~/high$ cat my_struct.c #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> /* 堆内存分配好习惯: 1,执行分配 2,判断分配是否成功 3,内存清零 4,分配异常处理 */ typedef struct Teacher { int age; char name[60]; char *alias_name; char **students_name; } master; void free_master(master *p_head,int teacher_num,int student_num) { int i = 0; int j = 0; if(p_head == NULL) { return ; } for(i = 0;i<teacher_num;i++) { if( p_head[i].alias_name != NULL) { free(p_head[i].alias_name); //释放别名一级指针 p_head[i].alias_name = NULL; } for(j=0;j<student_num;j++) { if(p_head[i].students_name[j] == NULL) { free(p_head[i].students_name[j]); //释放学生姓名二级指针的第二维 p_head[i].students_name[j] = NULL; } } if(p_head[i].students_name != NULL) { free(p_head[i].students_name); //释放学生个数二级指针的第一维 p_head[i].students_name = NULL; } } if(p_head != NULL) { p_head = NULL; } } int create_master(master **p_head,int teacher_num,int student_num) { int ret = 0; int i = 0; int j = 0; if(p_head == NULL) { return -1; } master *master_head = (master *)malloc(teacher_num * sizeof(master));//创建teacher_num个老师的空间 if(master_head == NULL) { return -2; } memset(master_head,0,teacher_num * sizeof(master)); for(i = 0;i<teacher_num;i++) //有几个老师, { master_head[i].alias_name = (char *)malloc(100 * sizeof(char)); if(master_head[i].alias_name == NULL) { return -3; } //memset((master_head +i ,0,100 * sizeof(char)); 这儿不能这么写,害我查bug好久 char **my_students = (char **)malloc(student_num * sizeof(char *));//每个导师带领student_num 名学生 if(my_students == NULL) { return -4; } memset(my_students,0,student_num * sizeof(char *)); for(j = 0;j<student_num;j++) { my_students[j] = (char *)malloc(100); if(my_students[j] == NULL) { return -5; } } master_head[i].students_name = my_students; } *p_head = master_head; return ret; } void sort_teacher(master *p,int num) { int i = 0; int j = 0; for(i = 0;i<num;i++) { for(j=i+1;j<num;j++) { if(strcmp(p[i].name,p[j].name) >0) { master tmp = p[i]; p[i] = p[j]; p[j] = tmp; } } } } void printf_teacher(master *p,int teacher_num,int student_num) { int i =0; int j =0; printf("------------------------\n"); for(i = 0;i<teacher_num;i++) { printf("[%d] %d,%s,%s -->",i+1,p[i].age,p[i].name,p[i].alias_name); for(j = 0;j<student_num;j++) { printf("%s ",p[i].students_name[j]); } printf("\n"); } } int main() { int ret = 0; int i = 0; int j = 0; int teacher_num = 3; int student_num = 3; master *p_head = NULL; ret = create_master(&p_head,teacher_num,student_num); if(ret != 0) { return -1; } for(i=0;i<teacher_num;i++) { printf("[%d]Enter age ",i+1); scanf("%d",&(p_head[i].age)); printf("[%d]Enter name ",i+1); scanf("%s",p_head[i].name); printf("[%d]Enter alias ",i+1); scanf("%s",p_head[i].alias_name); for(j = 0;j<student_num;j++) { printf("[%d][%d]Enter student_name ",i+1,j+1); scanf("%s",p_head[i].students_name[j]); } } sort_teacher(p_head,teacher_num); printf_teacher(p_head,teacher_num,student_num); free_master(p_head,teacher_num,student_num); return 0; } [email protected]:~/high$ [email protected]:~/high$ gcc -g -Wall my_struct.c && ./a.out [1]Enter age 32 [1]Enter name chunli [1]Enter alias chunli-1 [1][1]Enter student_name chunli-2 [1][2]Enter student_name chunli-3 [1][3]Enter student_name chunli-4 [2]Enter age 11 [2]Enter name kangkang [2]Enter alias kangkang-1 [2][1]Enter student_name kangkang-1^H2 [2][2]Enter student_name kangkang-2 [2][3]Enter student_name kangkang-3 [3]Enter age 99 [3]Enter name zhangsanfeng [3]Enter alias zhangsanfeng-1 [3][1]Enter student_name zhangsanfeng-2 [3][2]Enter student_name zhangsanfeng-3 [3][3]Enter student_name zhangsanfeng-4 ------------------------ [1] 32,chunli,chunli-1 -->chunli-2 chunli-3 chunli-4 [2] 11,kangkang,kangkang-1 -->kangkang-2 kangkang-2 kangkang-3 [3] 99,zhangsanfeng,zhangsanfeng-1 -->zhangsanfeng-2 zhangsanfeng-3 zhangsanfeng-4 [email protected]:~/high$
本文出自 “魂斗罗” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://990487026.blog.51cto.com/10133282/1790842
以上是关于C提高4 多维数组,结构体与二级指针的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章