类String
Posted wurengen
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了类String相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
String类概述
java.lang.String 类代表字符串。Java程序中所有的字符串文字(例如 "abc" )都可以被看作是实现此类的实例。类 String 中包括用于检查各个字符串的方法,比如用于比较字符串,搜索字符串,提取子字符串以及创建具有翻译为大写或小写的所有字符的字符串的副本。
特点:
- 字符串不变:字符串的值在创建后不能被更改。
- 因为String对象是不可变的,所以它们可以被共享。
- 字符串效果相当于是char[];例如:"abc" 等效于 char[] data={ ‘a‘ , ‘b‘ , ‘c‘ } 。但底层原理都是byte[]字节数组。
使用步骤
查看类
- java.lang.String :此类不需要导入。
查看构造方法()
- public String() :初始化新创建的 String对象,以使其表示空字符序列。
- public String(char[] value) :通过当前参数中的字符数组来构造新的String。
- public String(byte[] bytes) :通过使用平台的默认字符集解码当前参数中的字节数组来构造新的String。
创建字符串的常见4种方式:
代码举例:
package demo01; public class Demo01String { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建字符串方式一: 无参构造 String str1 = new String(); System.out.println("我的第一个字符串" + str1); //创建字符串方式二:通过字符数组构造 char chars[] = {‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘}; String str2 = new String(chars); System.out.println("我的第二个字符串" + str2); // 创建字符串方式三:通过字节数组构造 byte bytes[] = {97, 98, 99}; String str3 = new String(bytes); System.out.println("我的第三个字符串" + str3); //创建字符串方式四:直接创建 System.out.println("我的第四个字符串" +"abc"); } }
执行结果:
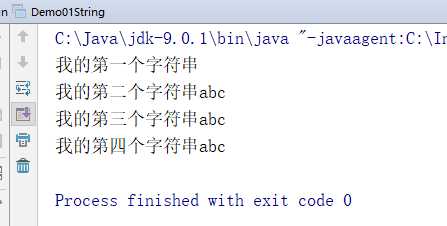
字符串常量:
程序当中直接写上的双引号字符串,就在常量池当中,常量池中的对象共享。通过构造方法创建的字符串,不共享对象。
查看字符串当中的常用方法:
判断功能的方法
- public boolean equals (Object anObject) :将此字符串与指定对象进行比较。只有参数是一个字符串并且内容相同的才会返回true,否则返回false
- public boolean equalsIgnoreCase (String anotherString) :将此字符串与指定对象进行比较,忽略大小 写。
代码举例
package demo01; public class Demo02String { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建字符串对象 String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "hello"; String s3 = "HELLO"; // boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同 System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); //boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写 System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); } }
执行结果:
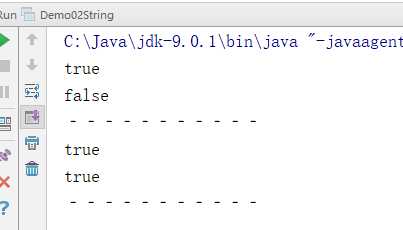
注意事项:
- Object 是” 对象”的意思,也是一种引用类型。作为参数类型,表示任意对象都可以传递到方法中。
- equals具有对称性。a.equals(b)等价于b.equalse(a)。如果字符串常量,参与比较,建议写在前面
获取功能的方法
- public int length () :返回此字符串的长度。
- public String concat (String str) :将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾。
- public char charAt (int index) :返回指定索引处的 char值
- public int indexOf (String str) :返回指定子字符串第一次出现在该字符串内的索引。没有返回‐1
代码举例:
package demo01; public class Demo03String { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建字符串对象 String s = "helloworld123"; // int length():获取字符串的长度,其实也就是字符个数 System.out.println(s.length()); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // String concat (String str):将将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾. String s2 = s.concat("werhello aww"); System.out.println(s2); // char charAt(int index):获取指定索引处的字符 System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); System.out.println(s.charAt(1)); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // int indexOf(String str):获取str在字符串对象中第一次出现的索引,没有返回‐1 System.out.println(s.indexOf("l")); System.out.println(s.indexOf("owo")); System.out.println(s.indexOf("ak")); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); } }
执行结果:
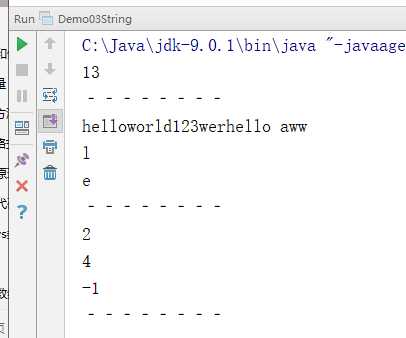
字符串的截取方法:
- public String substring (int beginIndex) :返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex开始截取字符串到字符 串结尾。
- public String substring (int beginIndex, int endIndex) :返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex到 endIndex截取字符串。含beginIndex,不含endIndex。
代码举例:
package demo02; public class Demo01String { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "12356789abc"; // String substring(int start):从start开始截取字符串到字符串结尾 System.out.println(s.substring(0)); System.out.println(s.substring(5)); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // String substring(int start,int end):从start到end截取字符串。含start,不含end。 System.out.println(s.substring(0, s.length())); System.out.println(s.substring(3, 8)); } }
执行结果:

转换功能的方法
- public char[] toCharArray () :将此字符串转换为新的字符数组。
- public byte[] getBytes () :使用平台的默认字符集将该 String编码转换为新的字节数组。
- public String replace (CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) :将与target匹配的字符串使用replacement字符串替换。
代码举例:
package demo02; public class Demo02String { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建字符串对象 String s = "abc"; // char[] toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组 char[] chs = s.toCharArray(); for (int x = 0; x < chs.length; x++) { System.out.println(chs[x]); } System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // byte[] getBytes ():把字符串转换为字节数组 byte[] bytes = s.getBytes(); for (int x = 0; x < bytes.length; x++) { System.out.println(bytes[x]); } System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // 替换字母it为大写IT String str = "123456abc123"; String replace = str.replace("123", "abc"); System.out.println(replace); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); } }
执行结果:
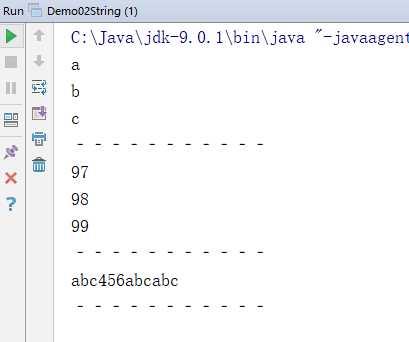
分割功能的方法
- public String[] split(String regex) :将此字符串按照给定的regex(规则)拆分为字符串数组。
注意事项:此方法的参数是正则表达式,需要符合正则表达式规则
package demo02; public class Demo03String { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建字符串对象 String s = "aa,bb,cc"; // 调用切割方法 String[] strArray = s.split(","); // 遍历数组 for (int x = 0; x < strArray.length; x++) { System.out.print(strArray[x] + " "); } } }
执行结果:
以上是关于类String的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
如何通过单击片段内的线性布局从片段类开始新活动?下面是我的代码,但这不起作用