14:多线程
Posted zwh820672664
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了14:多线程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.并发:万物都可以同时完成很多工作,我们把这些活动同时进行,这种同时进行的思想在Java中成为并发。
2.线程:将并发完成的每一件事情我们成为线程。
3.实现线程的2种方式:
- 继承java.lang.Thread 类:
- 实现java.lang.Runnable接口:
4.继承Thread类:
- 常用的两种构造方法:
- public Thread():创建一个新的线程对象。
- public Thread(String threadName):创建一个名为threadName的线程对象。
- 定义,实现方法,启动:
package xiancheng; /** * 创建线程 */ public class ThreaTest extends Thread { private int count = 10; //覆写run()方法,完成线程真正功能 public void run(){ System.out.println("创建了一个新线程ThreaTest,来实现业务!"); while (true){ System.out.print(count+" "); if(--count == 0){ return; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { //线程的启动是调用start()方法 ThreaTest threaTest = new ThreaTest(); threaTest.start(); } } 运行结果: 创建了一个新线程ThreaTest,来实现业务! 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
5.实现Runnable 接口:
- 使用Runnable 接口启动新的线程的步骤如下:
- 建立Runnable 对象
- 使用参数为Runnable 对象的构造方法创建Thread 实例
- 调用 start() 方法启动线程
package xiancheng; public class RunnableTest { private static Thread thread; private int count = 10; public void getInfo(){ thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true){ System.out.print(count+" "); if(--count == 0){ return; } } } }); thread.start(); } public static void main(String[] args) { RunnableTest runnableTest = new RunnableTest(); runnableTest.getInfo(); } } 运行结果: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
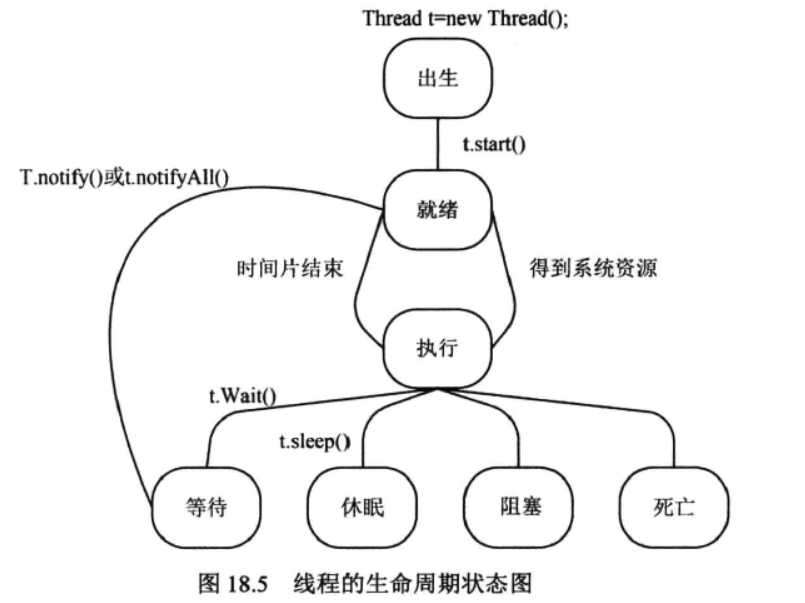
6.线程的生命周期的七种状态:
- 出生状态:线程被创建时的状态。
- 就绪状态:调用start()后的状态。
- 运行状态:得到系统资源后的状态。
- 等待状态:当调用wait()方法时就处于等待状态。处于此状态的线程需要调用notify()方法才能被唤醒。
- 休眠状态:当调用sleep()方法时进入休眠状态。
- 阻塞状态:线程在运行状态下发出输入\\输出请求,该线程将处于阻塞状态。在其等待输入\\输出结束时线程处于就绪状态。
- 死亡状态:当线程run()方法执行完毕时,线程进入死亡状态。
-
7.线程的加入:join()方法
- 例如:存在一个线程A,先需要插入一个线程B,并要求线程B先执行完再执行线程A:
package xiancheng; import static java.lang.Thread.*; public class JoinTest { private static Thread threadA; private static Thread threadB; public JoinTest(){ threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(10000); threadB.join(); System.out.println("线程threadA执行完毕"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); threadA.start(); threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("线程threadB执行完毕"); } }); threadB.start(); } public static void main(String[] args) { JoinTest joinTest = new JoinTest(); } } 运行结果: 线程threadB执行完毕 线程threadA执行完毕
7.线程中断 interrupt():
package xiancheng; public class InterruptedTest { private static Thread threadA; public InterruptedTest() { threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(10000); System.out.println("线程threadA执行中"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("线程被中断"); } } }); threadA.start(); threadA.interrupt(); } public static void main(String[] args) { InterruptedTest joinTest = new InterruptedTest(); } }
8:线程的礼让,使用yield()方法。
9:线程的优先级:Thread.MIN_PRIORITY(常量1),Thread.MAX_PRIORITY(常量10),Thread.NORM_PRIORITY(常量5),常量越大优先级越高。
10:线程同步:Java中提供线程同步的机制来防止访问资源的冲突。使用同步锁解决:
package xiancheng; public class ThreadSafeTest implements Runnable { int num = 10; @Override public void run() { while(true){ synchronized (""){ if(num >0 ){ try { Thread.sleep(000); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("tickets"+(--num)); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadSafeTest threadSafeTest = new ThreadSafeTest(); Thread threadA = new Thread(threadSafeTest); Thread threadB = new Thread(threadSafeTest); Thread threadC = new Thread(threadSafeTest); Thread threadD = new Thread(threadSafeTest); threadA.start(); threadB.start(); threadC.start(); threadD.start(); } } 运行结果: tickets9 tickets8 tickets7 tickets6 tickets5 tickets4 tickets3 tickets2 tickets1 tickets0
以上是关于14:多线程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章