Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications | 1 CHAPTER The Foundations: Logic and Proofs | 1.3 Propos
Posted minost
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications | 1 CHAPTER The Foundations: Logic and Proofs | 1.3 Propos相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
DEFINITION 1
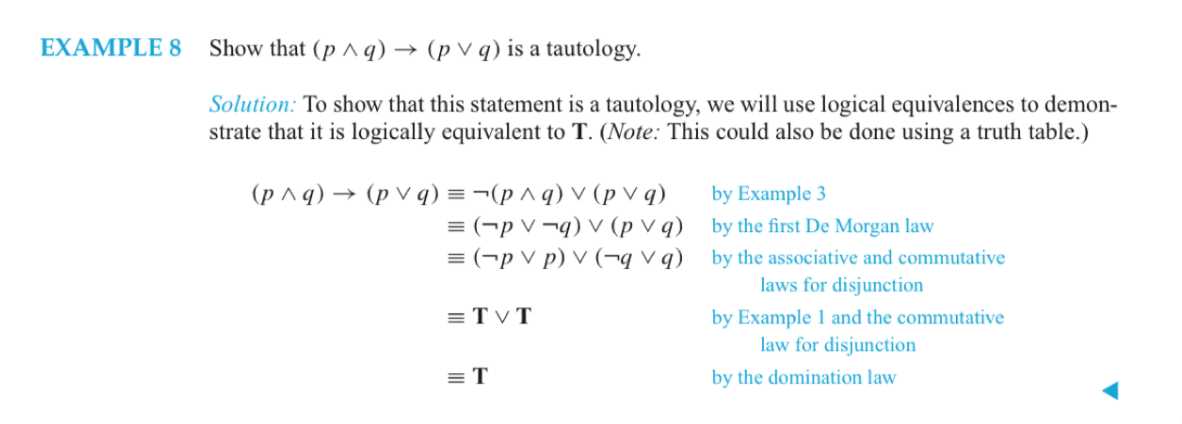
A compound proposition that is always true,no matter what the truth values of the proposi-tional variables that occur in it, is called atautology.
A compound proposition that is always false iscalled a contradiction.
A compound proposition that is neither a tautology nor a contradiction is called contingency.
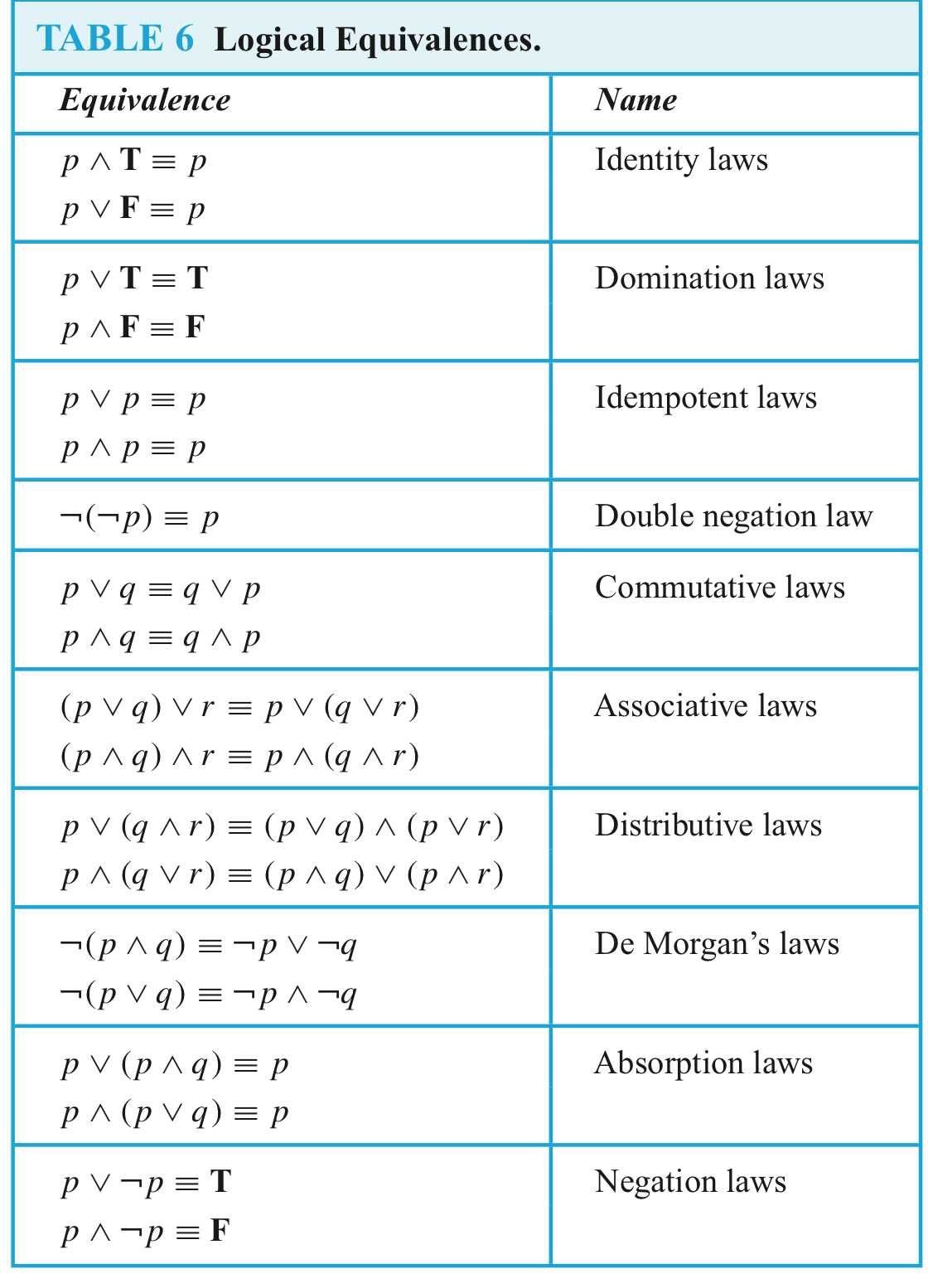
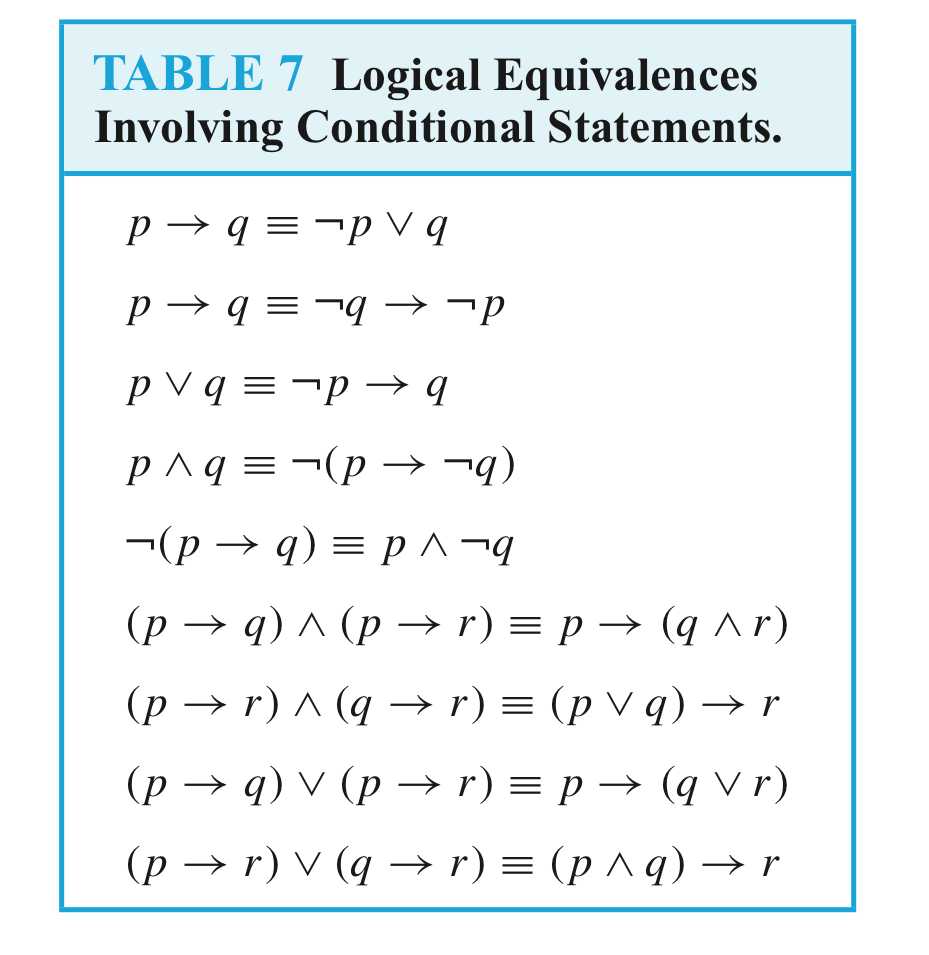
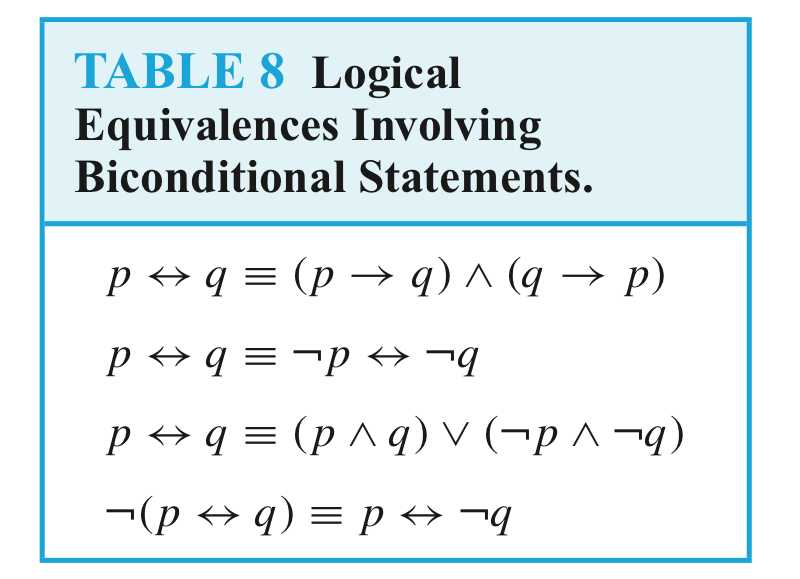
Logical Equivalences
Compound propositions that have the same truth values in all possible cases are called logically equivalent.
DEFINITION 2
The compound propositions p and q are called logically equivalent if p ↔ q is a tautology.
The notation p ≡ q denotes that p and q are logically equivalent.
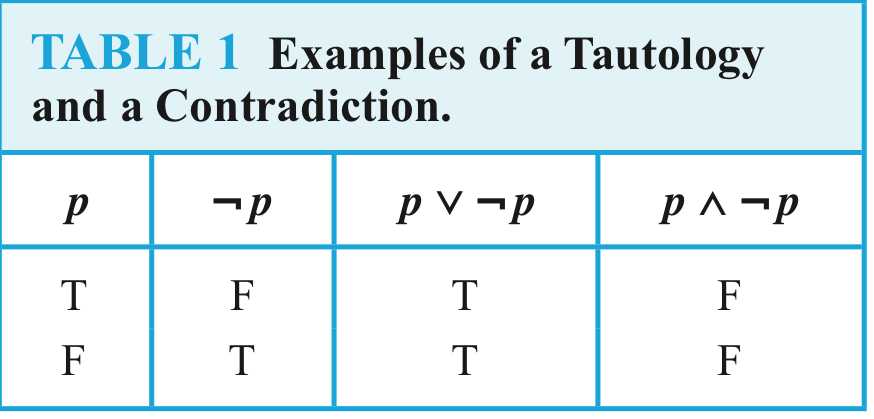

In general, 2**n rows are required if a compound proposition involves n propositional variables.
以上是关于Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications | 1 CHAPTER The Foundations: Logic and Proofs | 1.3 Propos的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章