双栈模拟队列与双队列模拟栈
Posted duwenze
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了双栈模拟队列与双队列模拟栈相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.两个队列共享一个环形向量空间,将这两个队列模拟成栈,并实现十进制转化为二进制
程序如下:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #define maxSize 20 4 typedef int DataType; 5 typedef struct 6 { 7 DataType elem[maxSize]; 8 int front[2],rear[2]; 9 }DualQueue; 10 void InitQueue(DualQueue *Q) 11 { 12 Q->front[0]=Q->rear[0]=0; 13 Q->front[1]=Q->rear[1]=maxSize/2; 14 } 15 int EnQueue(DualQueue *Q,DataType x,int flag) 16 { 17 if(flag<0||flag>1) 18 { 19 return 0; 20 } 21 if(Q->front[flag]==Q->rear[1-flag]) 22 { 23 if(Q->front[1-flag]==Q->rear[flag]) //假设另一个队列也满 24 { 25 return 0; 26 } 27 //不满则将另一个队列向前挪动一位置 28 for(int i=Q->rear[1-flag];i!=Q->front[1-flag];i=(i-1)%maxSize) 29 { 30 Q->elem[(i+1)%maxSize]=Q->elem[i-1]; 31 } 32 Q->rear[1-flag]=(Q->rear[1-flag]+1)%maxSize; 33 Q->front[1-flag]=(Q->front[1-flag]+1)%maxSize; 34 35 Q->rear[flag]=(Q->rear[flag]+1)%maxSize; 36 Q->elem[Q->rear[flag]]=x; 37 return 1; 38 } 39 Q->rear[flag]=(Q->rear[flag]+1)%maxSize; 40 Q->elem[Q->rear[flag]]=x; 41 return 1; 42 } 43 int DeQueue(DualQueue *Q,DataType *x,int flag) 44 { 45 if(flag<0||flag>1) 46 { 47 return 0; 48 } 49 if(Q->front[flag]==Q->rear[flag]) 50 { 51 return 0; 52 } 53 Q->front[flag]=(Q->front[flag]+1)%maxSize; 54 *x=Q->elem[Q->front[flag]]; 55 return 1; 56 } 57 void QStackInit(DualQueue *Q) 58 { 59 InitQueue(Q); 60 } 61 bool QStackEmpty(DualQueue *Q) 62 { 63 if(Q->front[0]==Q->rear[0]&&Q->front[1]==Q->rear[1]) 64 { 65 return true; 66 } 67 else 68 { 69 return false; 70 } 71 } 72 bool QStackFull(DualQueue *Q) 73 { 74 if(Q->front[0]==Q->rear[1]&&Q->front[1]==Q->rear[0]) 75 { 76 return true; 77 } 78 else 79 { 80 return false; 81 } 82 } 83 bool QStackPush(DualQueue *Q,int x) 84 { 85 if(QStackFull(Q)) 86 { 87 return false; 88 } 89 if(QStackEmpty(Q)) 90 { 91 EnQueue(Q,x,0); 92 } 93 else if(!(Q->front[0]==Q->rear[0])) 94 { 95 EnQueue(Q,x,0); 96 } 97 else 98 { 99 EnQueue(Q,x,1); 100 } 101 return true; 102 } 103 bool QStackPop(DualQueue *Q,int *x) 104 { 105 if(QStackEmpty(Q)) 106 { 107 return false; 108 } 109 if(!(Q->front[0]==Q->rear[0])) 110 { 111 while(1) 112 { 113 DeQueue(Q,x,0); 114 if(!(Q->front[0]==Q->rear[0])) 115 { 116 EnQueue(Q,*x,1); 117 } 118 else 119 { 120 break; 121 } 122 } 123 } 124 else 125 { 126 while(1) 127 { 128 DeQueue(Q,x,1); 129 if(!(Q->front[1]==Q->rear[1])) 130 { 131 EnQueue(Q,*x,0); 132 } 133 else 134 { 135 break; 136 } 137 } 138 } 139 return true; 140 } 141 int main() 142 { 143 DualQueue Q; 144 QStackInit(&Q); 145 int x,i,result=0; 146 printf("请输入一个十进制数:\\n"); 147 scanf("%d",&x); 148 while(x!=0) 149 { 150 i=x%2; 151 x=x/2; 152 QStackPush(&Q,i); 153 } 154 while(!QStackEmpty(&Q)) 155 { 156 QStackPop(&Q,&i); 157 result=result*10+i; 158 } 159 printf("二进制为:%d\\n",result); 160 }
运行结果如下:
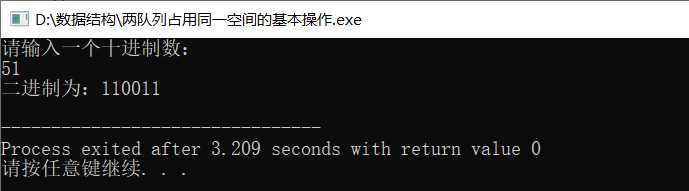
在此程序中,应注意如果一个队列满了,而另一个队列未满,则可以移动元素位置,改变队列空间,与栈浮动技术相似。同时在挪动位置的过程中,循环控制条件不应设为>,而应该为!=。
2.使用两栈模拟一个队列,并实现输出杨辉三角
程序如下:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 typedef int SElemType; 4 typedef struct node 5 { 6 SElemType data; 7 struct node *link; 8 }LinkNode,*LinkStack; 9 void StackInit(LinkStack *S) 10 { 11 (*S)=NULL; 12 } 13 int StackEmpty(LinkStack *S) 14 { 15 return (*S)==NULL; 16 } 17 int StackPush(LinkStack *S,SElemType x) 18 { 19 LinkNode *p=(LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode)); 20 p->data=x; 21 p->link=(*S); 22 (*S)=p; 23 return 1; 24 } 25 int StackPop(LinkStack *S,SElemType *x) 26 { 27 if(S==NULL) 28 { 29 return 0; 30 } 31 LinkNode *p=(*S); 32 *x=p->data; 33 (*S)=p->link; 34 free(p); 35 return 1; 36 } 37 void SQueueInit(LinkStack *S1,LinkStack *S2) 38 { 39 StackInit(S1); 40 StackInit(S2); 41 } 42 bool SQueueEmpty(LinkStack *S1,LinkStack *S2) 43 { 44 if(StackEmpty(S1)&&StackEmpty(S2)) 45 { 46 return true; 47 } 48 return false; 49 } 50 int EnSQueue(LinkStack *S1,LinkStack *S2,int x) 51 { 52 if(SQueueEmpty(S1,S2)) 53 { 54 StackPush(S1,x); 55 } 56 else if(!StackEmpty(S1)) 57 { 58 StackPush(S1,x); 59 } 60 else 61 { 62 StackPush(S2,x); 63 } 64 return 1; 65 } 66 int DeSQueue(LinkStack *S1,LinkStack *S2,int *x) 67 { 68 if(SQueueEmpty(S1,S2)) 69 { 70 return 0; 71 } 72 if(!StackEmpty(S1)) 73 { 74 while(1) 75 { 76 StackPop(S1,x); 77 if(!StackEmpty(S1)) 78 { 79 StackPush(S2,*x); 80 } 81 else 82 { 83 break; 84 } 85 } 86 int temp; 87 while(1) 88 { 89 StackPop(S2,&temp); 90 StackPush(S1,temp); 91 if(StackEmpty(S2)) 92 { 93 break; 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 else 98 { 99 while(1) 100 { 101 StackPop(S2,x); 102 if(!StackEmpty(S2)) 103 { 104 StackPush(S1,*x); 105 } 106 else 107 { 108 break; 109 } 110 } 111 int temp; 112 while(1) 113 { 114 StackPop(S1,&temp); 115 StackPush(S2,temp); 116 if(StackEmpty(S1)) 117 { 118 break; 119 } 120 } 121 } 122 } 123 void YangHvi(int n) 124 { 125 LinkStack S1,S2; 126 SQueueInit(&S1,&S2); 127 EnSQueue(&S1,&S2,1); 128 EnSQueue(&S1,&S2,1); 129 int i,j; 130 int s=0,t; 131 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 132 { 133 printf("\\n"); 134 EnSQueue(&S1,&S2,0); 135 for(int j=i;j<=n-1;j++) 136 { 137 printf("%2c",‘ ‘); 138 } 139 for(int j=1;j<=i+2;j++) 140 { 141 DeSQueue(&S1,&S2,&t); 142 EnSQueue(&S1,&S2,s+t); 143 s=t; 144 if(j!=i+2) 145 { 146 printf("%4d",s); 147 } 148 } 149 } 150 } 151 main() 152 { 153 int n; 154 printf("请输入行数:\\n"); 155 scanf("%d",&n); 156 YangHvi(n); 157 }
运行结果如下:
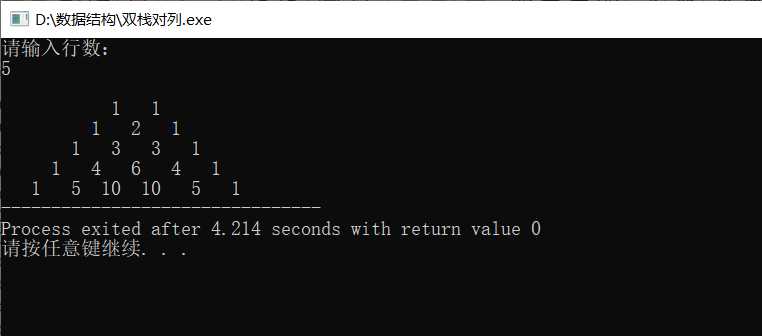
在此程序中应注意的是,模拟队列与模拟栈的细微区别(仅依据这两个程序而言):输入元素基本一样,输出元素,在模拟栈中还多了一步,将栈1的元素(除最后一个元素)全部传给栈2,然后输出元素,最后还需要将栈2的全部元素又传回给栈1.
以上是关于双栈模拟队列与双队列模拟栈的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章