[Algorithm] Inorder Successor in a binary search tree
Posted answer1215
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[Algorithm] Inorder Successor in a binary search tree相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
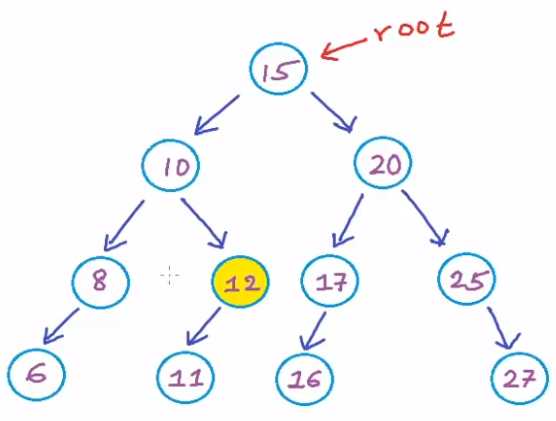
For the given tree, in order traverse is:
- visit left side
- root
- visit right side
// 6,8,10,11,12,15,16,17,20,25,27
The successor is the one right next to the target:
// target 8 --> succossor is 10
So, given the tree and target node, to find its successor.
Require knowledge how recurise call work, mainly it should reach the leaf node, then print it from bottom to top. For the node which has both right and left side, it visits left first, then itself, then right side.
function findCurrent(root, val) { let current = root; let found = null; while (current !== null) { if (current.val === val) { found = current; break; } else if (current.val < val) { current = current.right; } else { current = current.left; } } return found; } function findMin(root) { // min should be on the left side while (root.left != null) { root = root.left; } return root; } function findSuccsor(root, val) { const current = findCurrent(root, val); if (current == null) { return null; } // case 1: Node has right subtree // Find min on the right part of the node // the min should be on the left most if (current.right != null) { return findMin(current.right); } // case 2: Node has no right subtree // --> A. target node can be on the left side like 8 // --> B. target node can be on the right side like 12 else { let parent = root; let found = null; while (parent !== current) { // A: if target is smaller than parent, means on the left side // then we keep going down to find target, its parent should be // the successor if (current.val < parent.val) { found = parent; parent = parent.left; } // B: it target is larger than parent, means on the right side // then it means the parent node should already been visited // so we should not set successor in this case else { parent = parent.right; } } return found; } } function Node(val) { return { val, left: null, right: null }; } function Tree() { return { root: null, addLeft(val, root) { const node = Node(val); root.left = node; return root.left; }, addRight(val, root) { const node = Node(val); root.right = node; return root.right; } }; } const tree = new Tree(); const root = Node(15); tree.root = root; const n1 = tree.addLeft(10, tree.root); const n2 = tree.addRight(20, tree.root); const n3 = tree.addLeft(8, n1); tree.addLeft(6, n3); const n4 = tree.addRight(12, n1); tree.addLeft(11, n4); const n5 = tree.addLeft(17, n2); const n6 = tree.addLeft(16, n5); const n7 = tree.addRight(25, n2); tree.addRight(27, n7); // inorder // 6,8,10,11,12,15,16,17,20,25,27 // successor is the one next to the target // target 8 --> succossor is 10 console.log(findSuccsor(tree.root, 27));
以上是关于[Algorithm] Inorder Successor in a binary search tree的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章