多线程信号量的运用
Posted 我有一壶酒
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了多线程信号量的运用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、信号量的初始化sem_init()函数语法
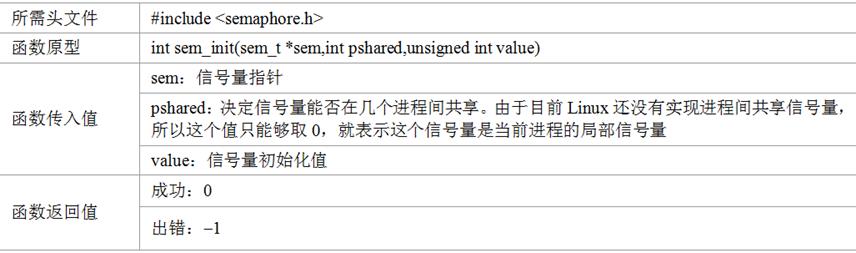
2、信号量sem_wait()操作,里面传递的参数首先-1,然后判断里面的参数-1之后是否>=0,是 则执行后面程序,否 则卡死在那里直到参数>=0 为止
信号量sem_post()操作,里面传递的参数+1,
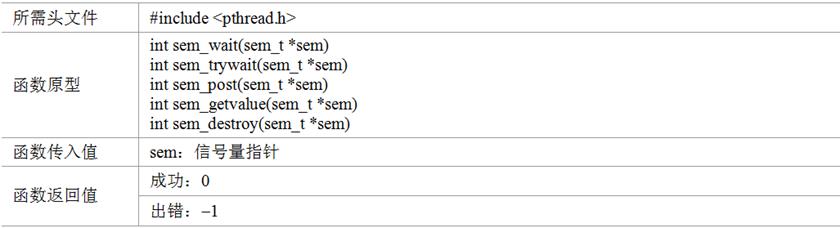
代码分析:生产者和消费者问题
/*producer-customer.c*/ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <errno.h> #include <semaphore.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #define MYFIFO "myfifo" /* 缓冲区有名管道的名字 */ #define BUFFER_SIZE 3 /* 缓冲区的单元数 */ #define UNIT_SIZE 5 /* 每个单元的大小 */ #define RUN_TIME 30 /* 运行时间 */ #define DELAY_TIME_LEVELS 5.0 /* 周期的最大值 */ int fd; time_t end_time; sem_t mutex, full, avail; /* 三个信号量 */ /*生产者线程*/ void *producer(void *arg) { int real_write; int delay_time = 0; while(time(NULL) < end_time) { delay_time = (int)(rand() * DELAY_TIME_LEVELS/(RAND_MAX) / 2.0) + 1; sleep(delay_time); /*P操作信号量avail和mutex*/ sem_wait(&avail); sem_wait(&mutex); printf("\\nProducer: delay = %d\\n", delay_time); /*生产者写入数据*/ if ((real_write = write(fd, "hello", UNIT_SIZE)) == -1) { if(errno == EAGAIN) { printf("The FIFO has not been read yet.Please try later\\n"); } } else { printf("Write %d to the FIFO\\n", real_write); } /*V操作信号量full和mutex*/ sem_post(&full); sem_post(&mutex); } pthread_exit(NULL); } /* 消费者线程*/ void *customer(void *arg) { unsigned char read_buffer[UNIT_SIZE]; int real_read; int delay_time; while(time(NULL) < end_time) { delay_time = (int)(rand() * DELAY_TIME_LEVELS/(RAND_MAX)) + 1; sleep(delay_time); /*P操作信号量full和mutex*/ sem_wait(&full); sem_wait(&mutex); memset(read_buffer, 0, UNIT_SIZE); printf("\\nCustomer: delay = %d\\n", delay_time); if ((real_read = read(fd, read_buffer, UNIT_SIZE)) == -1) { if (errno == EAGAIN) { printf("No data yet\\n"); } } printf("Read %s from FIFO\\n", read_buffer); /*V操作信号量avail和mutex*/ sem_post(&avail); sem_post(&mutex); } pthread_exit(NULL); } int main() { pthread_t thrd_prd_id,thrd_cst_id; pthread_t mon_th_id; int ret; srand(time(NULL)); end_time = time(NULL) + RUN_TIME; /*创建有名管道*/ if((mkfifo(MYFIFO, O_CREAT|O_EXCL) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST)) { printf("Cannot create fifo\\n"); return errno; } /*打开管道*/ fd = open(MYFIFO, O_RDWR); if (fd == -1) { printf("Open fifo error\\n"); return fd; } /*初始化互斥信号量为1*/ ret = sem_init(&mutex, 0, 1); /*初始化avail信号量为N*/ ret += sem_init(&avail, 0, BUFFER_SIZE); /*初始化full信号量为0*/ ret += sem_init(&full, 0, 0); if (ret != 0) { printf("Any semaphore initialization failed\\n"); return ret; } /*创建两个线程*/ ret = pthread_create(&thrd_prd_id, NULL, producer, NULL); if (ret != 0) { printf("Create producer thread error\\n"); return ret; } ret = pthread_create(&thrd_cst_id, NULL, customer, NULL); if(ret != 0) { printf("Create customer thread error\\n"); return ret; } pthread_join(thrd_prd_id, NULL); pthread_join(thrd_cst_id, NULL); close(fd); unlink(MYFIFO); return 0; }
简单点的代码,参考
http://www.cnblogs.com/yihujiu/p/5523814.html
以上是关于多线程信号量的运用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
求解答以下的java源代码,详细点,说明这个程序的设计思路,还有比如运用了多线程的话运用了多线程的啥