设计模式-原型模式
Posted wenq001
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了设计模式-原型模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
原型模式概念:
所谓原型模式就是用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过复制这些原型创建新的对象的过程。
原型模式的使用:
在java中实现原形模式主要通过实现 Cloneable 接口,重新clone方法实现。
package com.dsx.design.prototype; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Date; public class Student implements Serializable ,Cloneable { private String name ; private Integer age ; private Date birthday ; private Teacher teacher ; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } public Teacher getTeacher() { return teacher; } public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) { this.teacher = teacher; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\\‘‘ + ", age=" + age + ", birthday=" + birthday + ", teacher=" + teacher + ‘}‘; } /** * 浅拷贝 * @return * @throws CloneNotSupportedException */ @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
需要获取新对象的时候,可以先new一个实例, 然后通过实例的clone方法获取新的拷贝对象。
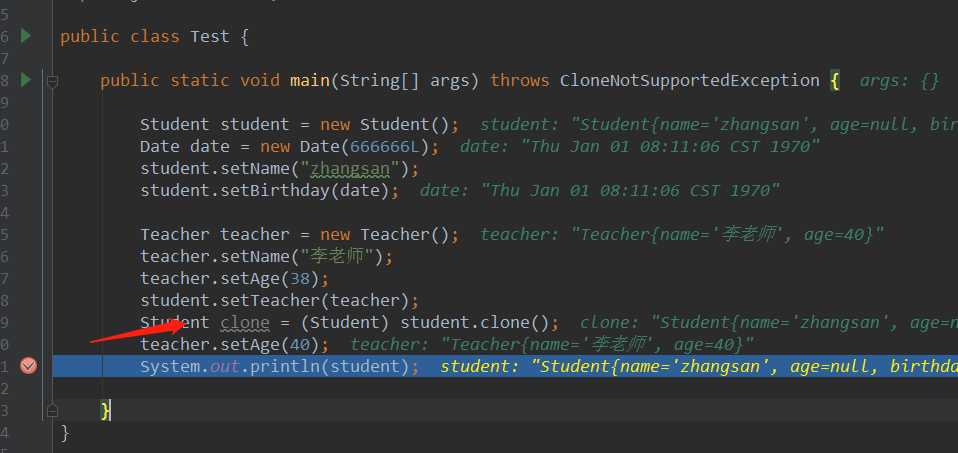
如图,调用student实例的clone方法获取新的拷贝对象。
但是使用原型模式有个点需要注意:
注意!!!!!!!!!
如上图代码所示:debug情况如下:
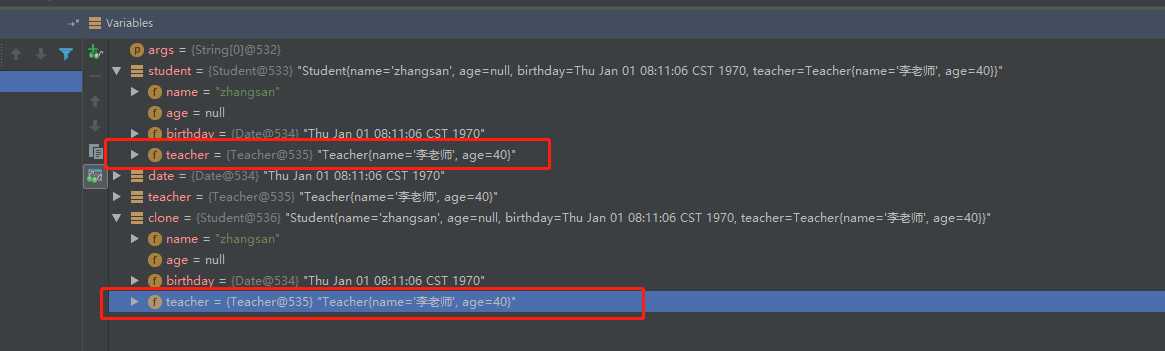
修改了teacher对象的Age信息,原对象和新拷贝的对象的属性的值都变成了新值。从上图中也可以看出,两个对象的属性teacher的地址相同。这是因为实现cloneable接口属于浅拷贝。
深拷贝和浅拷贝的概念:
浅拷贝:
被复制对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,而所有的对其他对象的引用仍然指向原来的对象。即对象的浅拷贝会对“主”对象进行拷贝,但不会复制主对象里面的对象。”里面的对象“会在原来的对象和它的副本之间共享。
简而言之,浅拷贝仅仅复制所考虑的对象,而不复制它所引用的对象。白话理解:浅拷贝就是说新产生的对象和原来对象的地址是不一样的,但是如果原来对象里面包含引用对象,拷贝完之后的新对象属性中的引用对象不会创建新的,还是和原先对象的属性中引用对象指向同一地址。
图示:
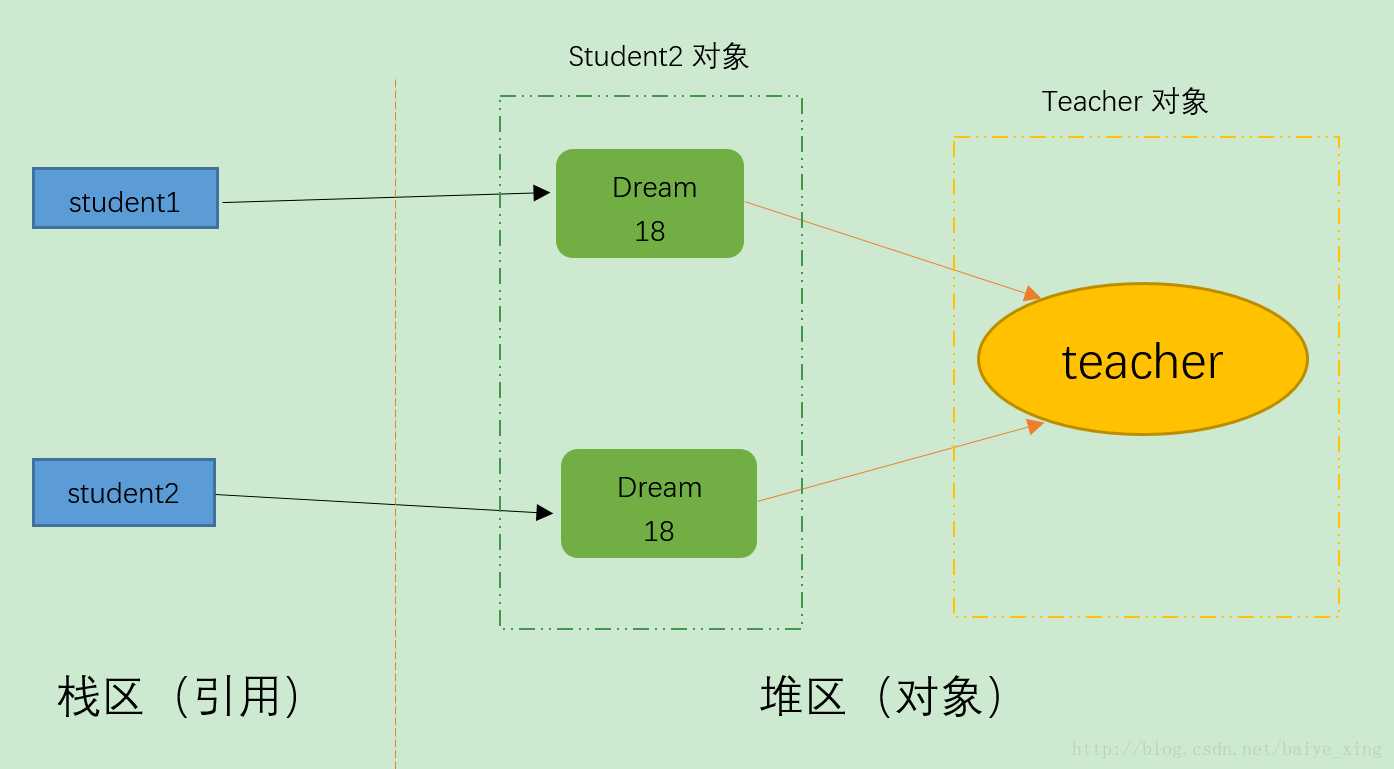
Student的拷贝,创建了新对象stu1,stu2,但是对象里面Teacher属性,stu1和stu2还是指向同一个Teacher地址。
深拷贝:
深拷贝是一个整个独立的对象拷贝,深拷贝会拷贝所有的属性,并拷贝属性指向的动态分配的内存。当对象和它所引用的对象一起拷贝时即发生深拷贝。深拷贝相比于浅拷贝速度较慢并且花销较大。
简而言之,深拷贝把要复制的对象所引用的对象都复制了一遍。白话理解:和浅拷贝对应起来理解,不仅是拷贝的对象是新对象,如果对象里面的属性是引用对象,那么拷贝对象的引用属性也是新对象。
图示: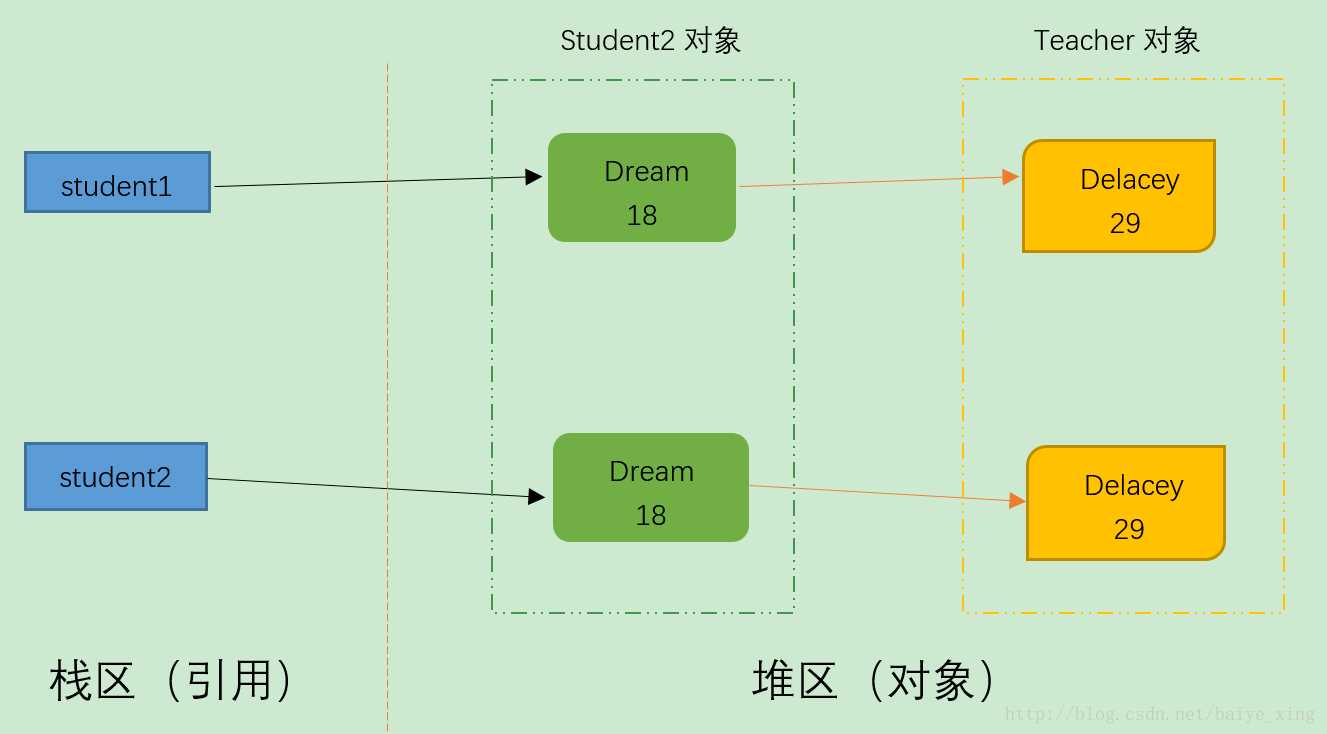
如上:深拷贝,不仅stu1和stu2是新对象,两个对象的属性teacher也是不同的地址引用.
原型模式中属于浅拷贝还是深度拷贝?
原型模式是属于浅拷贝 。
原型模式中如何实现深度拷贝?
圆形模式中如果需要实现深度拷贝,则需要对对象的属性都进行拷贝。
方式1:重写clone方法的时候,需要对每一个引用对象都重新赋值,例如Teacher的赋值
在student的 clone方法中重写Date和Teacher的拷贝:
/** * 深度拷贝 * @return * @throws CloneNotSupportedException */ @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student = (Student) super.clone(); student.setTeacher((Teacher) student.getTeacher().clone()); student.setBirthday((Date) student.getBirthday().clone()); return student ; }
当然如果对象的属性很多,我们也可以对对象实现Serializable ,使用序列化实现深拷贝:
public Object deepClone() throws Exception {
// 序列化
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);
// 反序列化
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
return ois.readObject();
}
附上该设计模式中的测试代码;
Student 类:
package com.dsx.design.prototype; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Date; public class Student implements Serializable ,Cloneable { private String name ; private Integer age ; private Date birthday ; private Teacher teacher ; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } public Teacher getTeacher() { return teacher; } public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) { this.teacher = teacher; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\\‘‘ + ", age=" + age + ", birthday=" + birthday + ", teacher=" + teacher + ‘}‘; } /** * 浅拷贝 * @return * @throws CloneNotSupportedException */ @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } // // /** // * 深度拷贝 // * @return // * @throws CloneNotSupportedException // */ // @Override // protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { // Student student = (Student) super.clone(); // student.setTeacher((Teacher) student.getTeacher().clone()); // student.setBirthday((Date) student.getBirthday().clone()); // return student ; // } }
Teacher 类:
package com.dsx.design.prototype; public class Teacher implements Cloneable{ private String name ; private Integer age ; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Teacher{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\\‘‘ + ", age=" + age + ‘}‘; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
Test 类:
package com.dsx.design.prototype; import java.util.Date; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student student = new Student(); Date date = new Date(666666L); student.setName("zhangsan"); student.setBirthday(date); Teacher teacher = new Teacher(); teacher.setName("李老师"); teacher.setAge(38); student.setTeacher(teacher); Student clone = (Student) student.clone(); teacher.setAge(40); System.out.println(student); } }
以上是关于设计模式-原型模式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章