varnish与squid缓存效率对比实例
Posted dannylinux
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了varnish与squid缓存效率对比实例相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前提:安装varnish、squid、webbench(压测工具)
注:varnish和squid机都未安装其他多余服务,服务器绑定域名为www.dannylinux.top (为同一台服务器,测试其中一个时,另一个服务停掉)
varnish和squid监听端口都为80,方便测试时不用防火墙端口转发配置
1.varnish配置
#使用varnish版本4的格式. vcl 4.0; # 加载后端轮询模块 import directors; #######################健康检查策略区域########################### # 名为www_probe的健康检查策略 probe www_probe { .request = "GET /html/test.html HTTP/1.1" # 健康检查url为/html/test.html 协议为http1.1 "Host: www.xxxxx.com" # 访问的域名为www.xxxxx.com "Connection: close"; # 检查完关闭连接 #其他参数 如 超时时间 检查间隔 等 均使用默认 } ################################################################## #######################配置后端区域################################ backend backend_16 { .host = "111.111.111.16"; .port = "80"; .probe = www_probe; # 使用名为www_probe的健康检查策略 } backend backend_17 { .host = "111.111.111.17"; .port = "80"; .probe = www_probe; # 使用名为www_probe的健康检查策略 } #默认后端 backend default { .host = "测试web服务器IP"; #此处实验没用集群,只用了这个 .port = "80"; } ################################################################### # 配置后端集群事件 sub vcl_init { # 后端集群有4种模式 random, round-robin, fallback, hash # random 随机 # round-robin 轮询 # fallback 后备 # hash 固定后端 根据url(req.http.url) 或 用户cookie(req.http.cookie) 或 用户session(req.http.sticky)(这个还有其他要配合) # 把backend_16 和 backend_17配置为轮询集群 取名为www_round_robin new www_round_robin = directors.round_robin(); www_round_robin.add_backend(backend_16); www_round_robin.add_backend(backend_17); # 把backend_16 和 backend_17配置为随机选择集群 取名为www_random new www_random = directors.random(); www_random.add_backend(backend_16,10); # 设置backend_16后端的权重为10 www_random.add_backend(backend_17,5); # 设置backend_17后端的权重为5 # 把backend_16 和 backend_17配置为固定后端集群 取名为www_hash 在recv调用时还需要添加东西 看recv例子 new www_hash = directors.hash(); www_hash.add_backend(backend_16,1); # 设置backend_16后端的权重为1 www_hash.add_backend(backend_17,1); # 设置backend_17后端的权重为1 } #定义允许清理缓存的IP acl purge { # For now, I‘ll only allow purges coming from localhost "127.0.0.1"; "localhost"; } # 请求入口 这里一般用作路由处理 判断是否读取缓存 和 指定该请求使用哪个后端 sub vcl_recv { ##############################指定后端区域########################### # 域名为 www.xxxxx.com 的请求 指定使用名为www_round_robin的后端集群 在集群名后加上 .backend() 如只使用单独后端 直接写后端名字即可 如 = backend_16; if (req.http.host ~ "www.xxxxx.com") { set req.backend_hint = www_round_robin.backend(); } # 使用固定后端集群例子 使用名为www_hash的集群 if (req.http.host ~ "3g.xxxxx.com") { set req.backend_hint = www_hash.backend(req.http.cookie); # 根据用户的cookie来分配固定后端 可以指定其他分配规则 } # 其他将使用default默认后端 ##################################################################### # 把真实客户端IP传递给后端服务器 后端服务器日志使用X-Forwarded-For来接收 if (req.restarts == 0) { if (req.http.X-Forwarded-For) { set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = req.http.X-Forwarded-For + ", " + client.ip; } else { set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = client.ip; } } # 匹配清理缓存的请求 if (req.method == "PURGE") { # 如果发起请求的客户端IP 不是在acl purge里面定义的 就拒绝 if (!client.ip ~ purge) { return (synth(405, "This IP is not allowed to send PURGE requests.")); } # 是的话就执行清理 return (purge); } # 如果不是正常请求 就直接穿透没商量 if (req.method != "GET" && req.method != "HEAD" && req.method != "PUT" && req.method != "POST" && req.method != "TRACE" && req.method != "OPTIONS" && req.method != "PATCH" && req.method != "DELETE") { /* Non-RFC2616 or CONNECT which is weird. */ return (pipe); } # 如果不是GET和HEAD就跳到pass 再确定是缓存还是穿透 if (req.method != "GET" && req.method != "HEAD") { return (pass); } # 缓存通过上面所有判断的请求 (只剩下GET和HEAD了) return (hash); } # pass事件 sub vcl_pass { # 有fetch,synth or restart 3种模式. fetch模式下 全部都不会缓存 return (fetch); } # hash事件(缓存事件) sub vcl_hash { # 根据以下特征来判断请求的唯一性 并根据此特征来缓存请求的内容 特征为&关系 # 1. 请求的url # 2. 请求的servername 如没有 就记录请求的服务器IP地址 # 3. 请求的cookie hash_data(req.url); if (req.http.host) { hash_data(req.http.host); } else { hash_data(server.ip); } # 返回lookup , lookup不是一个事件(就是 并非指跳去sub vcl_lookup) 他是一个操作 他会检查有没有缓存 如没有 就会创建缓存 return (lookup); } # 缓存命中事件 在lookup操作后自动调用 官网文档说 如没必要 一般不需要修改 sub vcl_hit { # 可以在这里添加判断事件(if) 可以返回 deliver restart synth 3个事件 # deliver 表示把缓存内容直接返回给用户 # restart 重新启动请求 不建议使用 超过重试次数会报错 # synth 返回状态码 和原因 语法:return(synth(status code,reason)) # 这里没有判断 所有缓存命中直接返回给用户 return (deliver); } # 缓存不命中事件 在lookup操作后自动调用 官网文档说 如没必要 一般不需要修改 sub vcl_miss { # 此事件中 会默认给http请求加一个 X-Varnish 的header头 提示: nginx可以根据此header来判断是否来自varnish的请求(就不用起2个端口了) # 要取消此header头 只需要在这里添加 unset bereq.http.x-varnish; 即可 # 这里所有不命中的缓存都去后端拿 没有其他操作 fetch表示从后端服务器拿取请求内容 return (fetch); } # 返回给用户的前一个事件 通常用于添加或删除header头,如通过curl -I返回头中添加一个返回值,如下: sub vcl_deliver { # 例子 # set resp.http.* 用来添加header头 如 set resp.http.xxxxx = "haha"; unset为删除 # set resp.status 用来设置返回状态 如 set resp.status = 404; # obj.hits 会返回缓存命中次数 用于判断或赋值给header头 # req.restarts 会返回该请求经历restart事件次数 用户判断或赋值给header头 # 根据判断缓存时间来设置xxxxx-Cache header头 if (obj.hits > 0) { set resp.http.X-Cache = "cached from " + client.ip; #如果命中,则显示Hit from +客户端IP } else { set resp.http.X-Cache = "uncached"; #未命中则显示"Miss" 具体效果图在最底部 } #取消显示php框架版本的header头 unset resp.http.X-Powered-By; #取消显示nginx版本、Via(来自varnish)等header头 为了安全 unset resp.http.Server; unset resp.http.X-Drupal-Cache; unset resp.http.Via; unset resp.http.Link; unset resp.http.X-Varnish; #显示请求经历restarts事件的次数 set resp.http.X-restarts_count = req.restarts; #显示该资源缓存的时间 单位秒 set resp.http.X-Age = resp.http.Age; #显示该资源命中的次数 set resp.http.X-hit_count = obj.hits; #取消显示Age 为了不和CDN冲突 unset resp.http.Age; #返回给用户 return (deliver); } #处理对后端返回结果的事件(设置缓存、移除cookie信息、设置header头等) 在fetch事件后自动调用 sub vcl_backend_response { #后端返回如下错误状态码 则不缓存 if (beresp.status == 499 || beresp.status == 404 || beresp.status == 502) { set beresp.uncacheable = true; } #如请求php或jsp 则不缓存 if (bereq.url ~ "\\.(php|jsp)(\\?|$)") { set beresp.uncacheable = true; #php和jsp以外的请求 }else{ #如请求html 则缓存5分钟 if (bereq.url ~ "\\.html(\\?|$)") { set beresp.ttl = 300s; unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie; #其他缓存1小时 如css js等 }else{ set beresp.ttl = 1h; unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie; } } #开启grace模式 表示当后端全挂掉后 即使缓存资源已过期(超过缓存时间) 也会把该资源返回给用户 资源最大有效时间为6小时 set beresp.grace = 6h; #返回给用户 return (deliver); } #返回给用户前的事件 可以在这里自定义输出给用户的内容 sub vcl_deliver { }
2.squid配置
# # Recommended minimum configuration: # # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt to list your (internal) IP networks from where browsing # should be allowed #acl localnet src xx.xx.xx.0/24 #acl localnet src 172.31.16.128/32 acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines acl SSL_ports port 443 acl Safe_ports port 80 # http acl Safe_ports port 21 # ftp acl Safe_ports port 443 # https acl Safe_ports port 70 # gopher acl Safe_ports port 210 # wais acl Safe_ports port 1025-65535 # unregistered ports acl Safe_ports port 280 # http-mgmt acl Safe_ports port 488 # gss-http acl Safe_ports port 591 # filemaker acl Safe_ports port 777 # multiling http acl CONNECT method CONNECT # # Recommended minimum Access Permission configuration: # # Deny requests to certain unsafe ports http_access deny !Safe_ports # Deny CONNECT to other than secure SSL ports http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports # Only allow cachemgr access from localhost http_access allow localhost manager http_access deny manager # We strongly recommend the following be uncommented to protect innocent # web applications running on the proxy server who think the only # one who can access services on "localhost" is a local user #http_access deny to_localhost # # INSERT YOUR OWN RULE(S) HERE TO ALLOW ACCESS FROM YOUR CLIENTS # forwarded_for off via off # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt localnet in the ACL section to list your (internal) IP networks # from where browsing should be allowed http_access allow localnet http_access allow localhost # And finally deny all other access to this proxy http_access allow all #http_access deny all # Squid normally listens to port 3128 #http_port 3128 http_port 80 accel vhost vport #设置squid监听端口,方便域名直接访问 cache_peer web测试服务器IP parent 80 0 no-query no-digest originserver name=www cache_peer_domain www www.dannylinux.top dannylinux.top # Uncomment and adjust the following to add a disk cache directory. cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256 # Leave coredumps in the first cache dir coredump_dir /var/spool/squid # # Add any of your own refresh_pattern entries above these. # refresh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080 refresh_pattern ^gopher: 1440 0% 1440 refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/|\\?) 0 0% 0 refresh_pattern . 0 20% 4320 refresh_pattern -i \\.css$ 360 50% 2880 reload-into-ims refresh_pattern -i \\.js$ 1440 50% 2880 reload-into-ims refresh_pattern -i \\.html$ 720 50% 1440 reload-into-ims refresh_pattern -i \\.jpg$ 1440 90% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.gif$ 1440 90% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.swf$ 1440 90% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.jpg$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.png$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.bmp$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.doc$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.ppt$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.xls$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.pdf$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.rar$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.zip$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload refresh_pattern -i \\.txt$ 1440 50% 2880 ignore-reload
3.测试
1)varnish测试结果
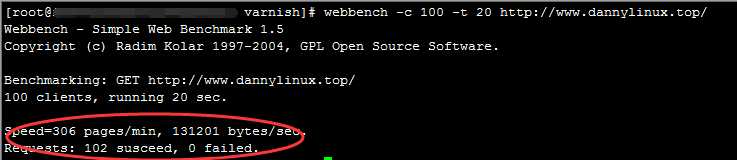
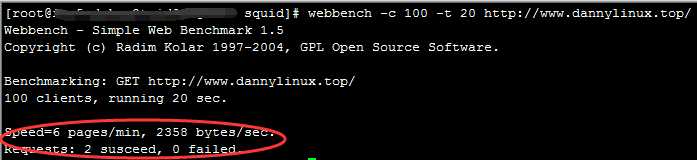
2)squid测试结果
4.结论
就算是排除我squid配置文件缓存没有配置好的原因,但是这差距还真不是一般的大啊,squid差varnish不是一点半点啊。
以上是关于varnish与squid缓存效率对比实例的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章