python四则运算2.0
Posted kongweijian
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python四则运算2.0相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
github项目地址: https://github.com/kongkalong/python
|
PSP |
预估耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
|
|
.Estimate |
48*60 |
|
Development |
|
|
.Analysis |
30 |
|
.Design Spec |
30 |
|
.Design Review |
0 |
|
.Coding Standard |
30 |
|
.Design |
60 |
|
.Coding |
24*60 |
|
.Code Reviw |
30 |
|
.Test |
60 |
|
Reporting |
|
|
.Test Report |
0 |
|
.Size Measurement |
0 |
|
.Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
0 |
|
合计 |
4560 |
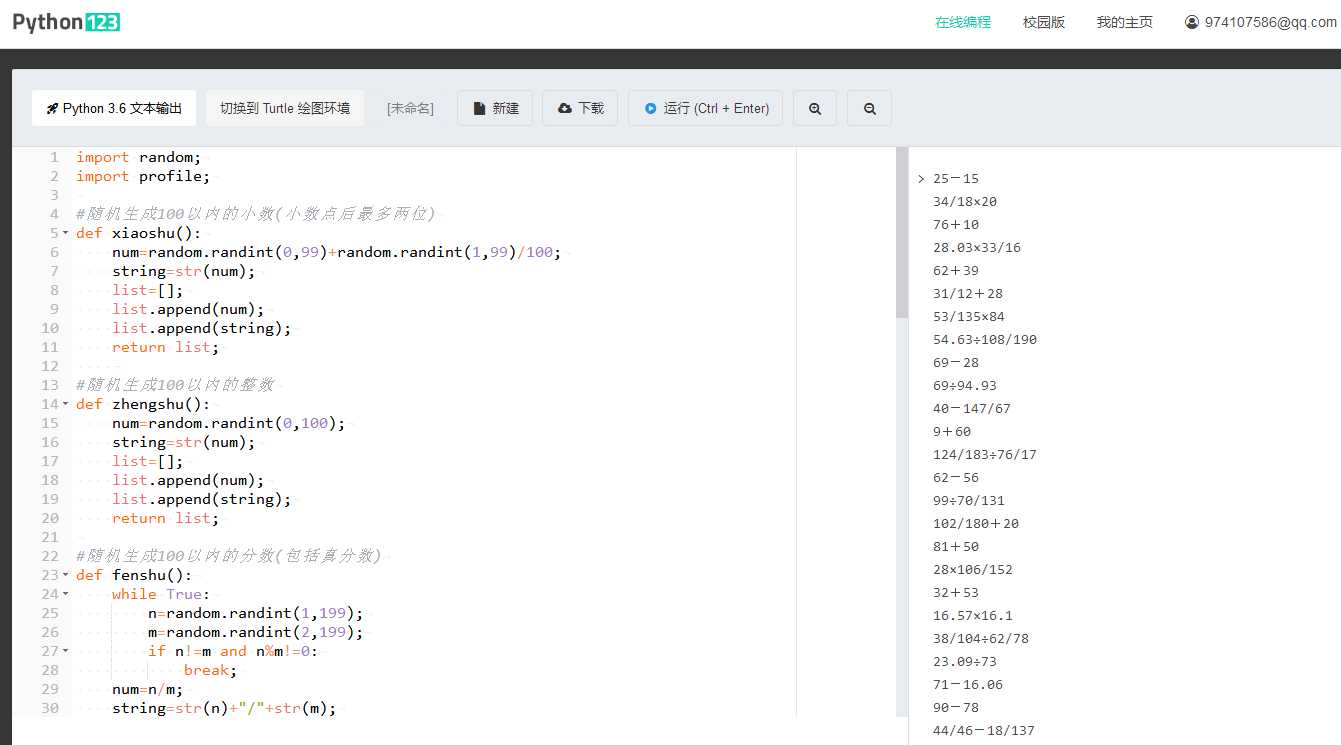
设计实现:函数zhengshu(),fenshu(),xiaoshu()分别随机生成整数,分数(包括真分数)和小数,函数sizeyunsuan()构造四则运算算式的格式为“["数值A","运算符","数值B"]”,函数transform()将数值类型的代表符号转换为实例的数值,如0->整数,函数printresult()将四则运算算式格式输出为“数值A 运算符 数值B”。
代码:
|
import random; |
|
|
import profile; |
|
|
#随机生成100以内的小数(小数点后最多两位) |
|
|
def xiaoshu(): |
|
|
num=random.randint(0,99)+random.randint(1,99)/100; |
|
|
string=str(num); |
|
|
list=[]; |
|
|
list.append(num); |
|
|
list.append(string); |
|
|
return list; |
|
|
|
|
|
#随机生成100以内的整数 |
|
|
def zhengshu(): |
|
|
num=random.randint(0,100); |
|
|
string=str(num); |
|
|
list=[]; |
|
|
list.append(num); |
|
|
list.append(string); |
|
|
return list; |
|
|
#随机生成100以内的分数(包括真分数) |
|
|
def fenshu(): |
|
|
while True: |
|
|
n=random.randint(1,199); |
|
|
m=random.randint(2,199); |
|
|
if n!=m and n%m!=0: |
|
|
break; |
|
|
num=n/m; |
|
|
string=str(n)+"/"+str(m); |
|
|
list=[]; |
|
|
list.append(num); |
|
|
list.append(string); |
|
|
return list; |
|
|
#将0,1,2转换为真实的整数,分数和小数 |
|
|
def transform(num): |
|
|
if num==0: |
|
|
return zhengshu(); |
|
|
if num==1: |
|
|
return fenshu(); |
|
|
if num==2: |
|
|
return xiaoshu(); |
|
|
#构造四则运算算式 |
|
|
def sizeyunsuan(): |
|
|
#四则运算算式的格式用长度为3的列表表示,如1+2相当于["1","+","2"] |
|
|
#数值的类型表示为:0-整数,1-分数,2-小数 |
|
|
#运算符的类型表示为:0-加法,1-减法,2-乘法,3-除法 |
|
|
list=[0,0,0]; #列表初始化为0 |
|
|
list[0]=random.randint(0,2); |
|
|
list[1]=random.randint(0,3); |
|
|
list[2]=random.randint(0,2); |
|
|
return list; |
|
|
|
|
|
#输出四则运算算式 |
|
|
def printresult(listname): |
|
|
if listname[1]==0: |
|
|
n=transform(listname[0]); |
|
|
m=transform(listname[1]); |
|
|
print(n[1]+"+"+m[1]); |
|
|
if listname[1]==1: |
|
|
n=transform(listname[0]); |
|
|
m=transform(listname[2]); |
|
|
#避免出现算式的结果为负数 |
|
|
if n[0]<m[0]: |
|
|
print(m[1]+"-"+n[1]); |
|
|
else: |
|
|
print(n[1]+"-"+m[1]); |
|
|
if listname[1]==2: |
|
|
while True: |
|
|
n=transform(listname[0]); |
|
|
m=transform(listname[2]); |
|
|
#避免出现0×0 |
|
|
if m[0]!=0 or n[0]!=0: |
|
|
break; |
|
|
print(n[1]+"×"+m[1]); |
|
|
if listname[1]==3: |
|
|
n=transform(listname[0]); |
|
|
while True: |
|
|
#避免除数为0 |
|
|
m=transform(listname[2]); |
|
|
if m[0]!=0: |
|
|
break; |
|
|
print(n[1]+"÷"+m[1]); |
|
|
|
|
|
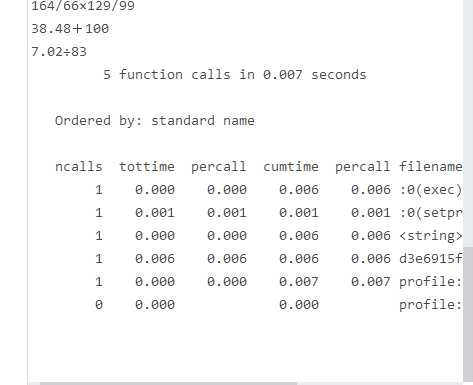
#利用profile性能测试工具进行效能分析 |
|
|
def fun(): |
|
|
for i in range(100000): |
|
|
a=i*i |
|
|
|
|
|
count=0; |
|
|
while count<300: |
|
|
list=sizeyunsuan(); |
|
|
printresult(list); |
|
|
count+=1; |
|
|
#进行效能分析 |
|
|
profile.run("fun()"); |
测试:
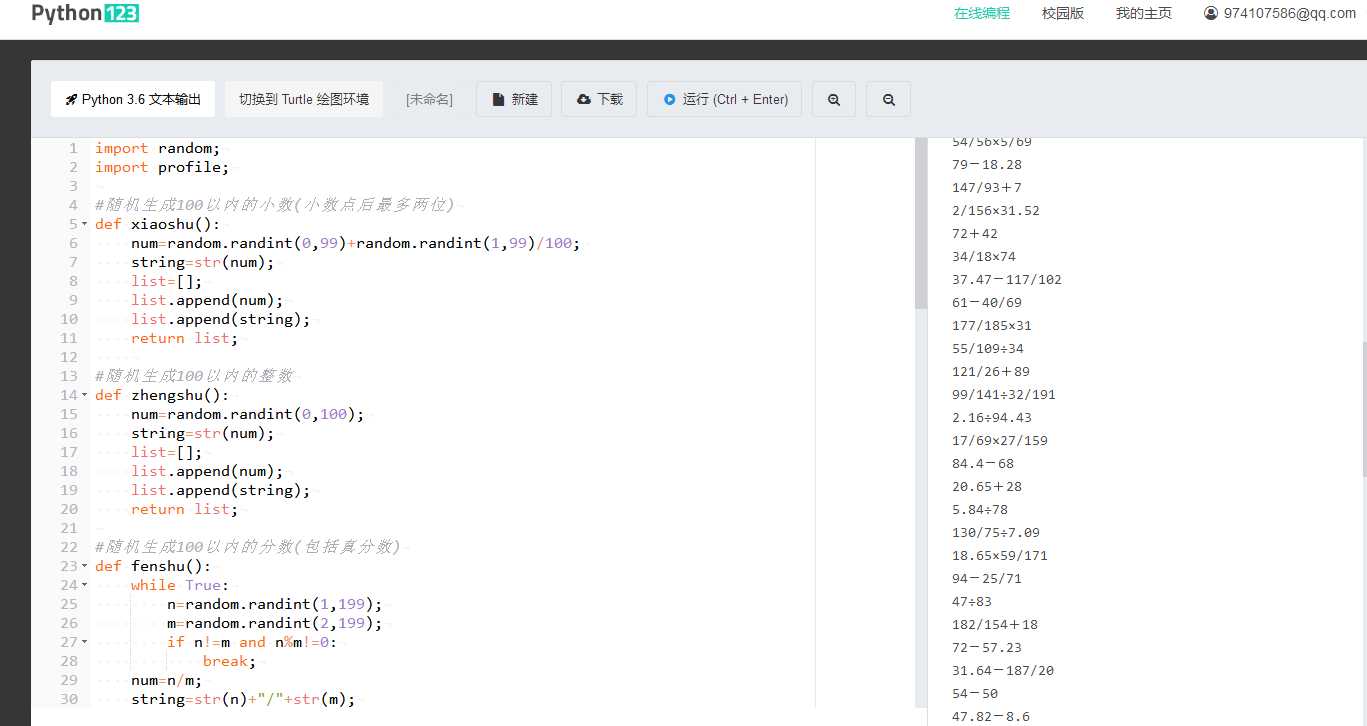
|
PSP |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
|
|
.Estimate |
24*60 |
|
Development |
|
|
.Analysis |
10 |
|
.Design Spec |
15 |
|
.Design Review |
0 |
|
.Coding Standard |
15 |
|
.Design |
20 |
|
.Coding |
2*60 |
|
.Code Reviw |
10 |
|
.Test |
30 |
|
Reporting |
|
|
.Test Report |
0 |
|
.Size Measurement |
0 |
|
.Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
0 |
|
合计 |
1660 |
以上是关于python四则运算2.0的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章