死锁,线程协作(同步,阻塞队列,Condition,管道流)
Posted ^sun^
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了死锁,线程协作(同步,阻塞队列,Condition,管道流)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
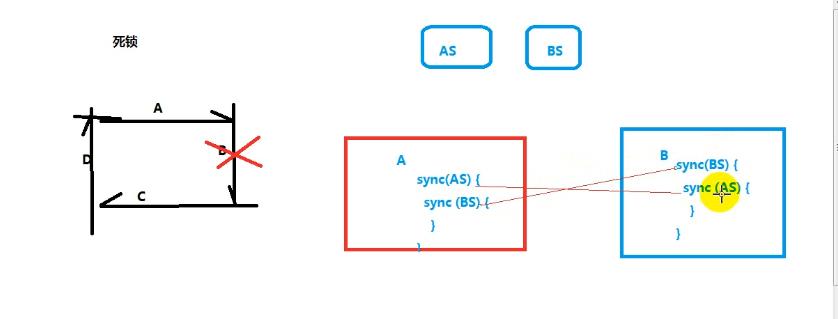
synchronized死锁
package com.thread.demo.deadlock; public class DeadLock { private static Object lock1 = new Object(); private static Object lock2 = new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建线程1 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized (lock1) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到lock1这把锁"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "等待lock2锁.........."); synchronized (lock2) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到lock2这把锁"); } } } } }, "A线程").start(); // 创建的线程2 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized (lock2) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到lock2这把锁"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "等待lock1锁.........."); synchronized (lock1) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到lock1这把锁"); } } } } }, "B线程").start(); } }
ReentrantLock死锁
package com.thread.demo.deadlock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class ReentrantDeadLock { private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(new MyRunnable(lock), "一线程").start(); new Thread(new MyRunnable(lock), "二线程").start(); } } class MyRunnable implements Runnable { private Lock lock; private static int count = 0; public MyRunnable(Lock lock) { this.lock = lock; } @Override public void run() { lock.lock(); try { for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) { count++; if (i == 100000) { throw new RuntimeException(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":count=" + count); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
wait,notify,notifyAll 必须结合synchronized关键字使用
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; /** * wait,notify,notifyAll 必须结合synchronized关键字使用 * * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建共享池 Container container = new Container(); new MyThread(container).start(); new MyThread(container).start(); new MyThread(container).start(); new MyThread1(container).start(); new MyThread1(container).start(); new MyThread1(container).start(); } } class MyThread extends Thread { private Container container; public MyThread(Container container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { container.get(); } } class MyThread1 extends Thread { private Container container; public MyThread1(Container container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { container.put(); } } class Container { boolean flag = true; public synchronized void put() { while (true) { if (!flag) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "放入内容......."); flag = false; // 唤醒拿内容线程 notifyAll(); } } public synchronized void get() { while (true) { if (flag) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿出内容......."); flag = true; notifyAll(); } } }
使用synchronized实现生产消费者模式
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; /** * 使用synchronized实现生产消费者模式 * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { AppleContainer container = new AppleContainer(); new Thread(new Producer(container),"AA").start(); new Thread(new Consumer(container),"BB").start(); } } // 生产者 class Producer implements Runnable { private AppleContainer container; public Producer(AppleContainer container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { System.out.println("生产----------------------苹果:" + (i+1)); Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); } container.increace(); } } } // 消费者 class Consumer implements Runnable { private AppleContainer container; public Consumer(AppleContainer container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费----------------------苹果:" + (i+1)); Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); } container.decreace(); } } } class AppleContainer { private int apple; public synchronized void increace() { if (apple == 5) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } apple++; System.out.println("生产有苹果:"+apple); notifyAll(); } public synchronized void decreace() { if (apple == 0) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } apple--; System.out.println("消费有苹果:"+apple); notifyAll(); } }
使用阻塞队列实现生产消费者模式
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; /** * 使用阻塞队列实现生产消费者模式 * @author Administrator * */ public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建阻塞队列(先进先出) BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(4); new Thread(new ProducerQueue(proQueue),"AA").start(); new Thread(new ConsumerQueue(proQueue),"BB").start(); } } class ProducerQueue implements Runnable { private BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue; public ProducerQueue(BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue) { this.proQueue = proQueue; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println("生产了编号为:"+i); try { Thread.sleep(1000); proQueue.put(i); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } class ConsumerQueue implements Runnable { private BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue; public ConsumerQueue(BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue) { this.proQueue = proQueue; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { System.out.println("消费了编号为:"+proQueue.take()); Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
lock实现生产消费者模式
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { Basket b = new Basket(); Product p = new Product(b); ConsumerCondition c = new ConsumerCondition(b); ConsumerCondition c1 = new ConsumerCondition(b); new Thread(p,"生产者1").start(); new Thread(c,"消费者1").start(); new Thread(c1,"消费者2").start(); } } // 馒头 class ManTou { int id; public ManTou(int id) { this.id = id; } @Override public String toString() { return "ManTou" + id; } } // 装馒头的篮子 class Basket { int max = 6; LinkedList<ManTou> manTous = new LinkedList<ManTou>(); Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); // 锁对象 Condition full = lock.newCondition(); // 用来监控篮子是否满的Condition实例 Condition empty = lock.newCondition(); // 用来监控篮子是否空的Condition实例 // 往篮子里面放馒头 public void push(ManTou m) { lock.lock(); try { while (max == manTous.size()) { System.out.println("篮子是满的,待会儿再生产..."); full.await(); // wait } manTous.add(m); empty.signalAll(); // notfiy } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } // 往篮子里面取馒头 public ManTou pop() { ManTou m = null; lock.lock(); try { while (manTous.size() == 0) { System.out.println("篮子是空的,待会儿再吃..."); empty.await(); } m = manTous.removeFirst(); full.signalAll(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } return m; } } // 生产者 class Product implements Runnable { Basket basket; public Product(Basket basket) { this.basket = basket; } public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ManTou m = new ManTou(i); basket.push(m); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产了" + m); try { Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 2000)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } // 消费者 class ConsumerCondition implements Runnable { Basket basket; public ConsumerCondition(Basket basket) { this.basket = basket; } public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 2000)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } ManTou m = basket.pop(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费了" + m); } } }
管道输入输出流实现生产消费者模式
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PipedInputStream; import java.io.PipedOutputStream; public class Demo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 创建管道输出流 */ PipedOutputStream pos = new PipedOutputStream(); /** * 创建管道输入流 */ PipedInputStream pis = new PipedInputStream(); try { /** * 将管道输入流与输出流连接 此过程也可通过重载的构造函数来实现 */ pos.connect(pis); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } /** * 创建生产者线程 */ PipeProducer p = new PipeProducer(pos, "CCC"); /** * 创建消费者线程 */ PipeProducerConsumer c1 = new PipeProducerConsumer(pis, "AAA"); PipeProducerConsumer c2 = new PipeProducerConsumer(pis, "BBB"); /** * 启动线程 */ p.start(); c1.start(); c2.start(); } } /** * 生产者线程(与一个管道输入流相关联) * */ class PipeProducer extends Thread { private PipedOutputStream pos; public PipeProducer(PipedOutputStream pos, String name) { super(name); this.pos = pos; } public void run() { int i = 0; try { while (true) { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "product:" + i); pos.write(i); i++; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 消费者线程(与一个管道输入流相关联) * */ class PipeProducerConsumer extends Thread { private PipedInputStream pis; public PipeProducerConsumer(PipedInputStream pis, String name) { super(name); this.pis = pis; } public void run() { try { while (true) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "consumer1:" + pis.read()); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
以上是关于死锁,线程协作(同步,阻塞队列,Condition,管道流)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
线程阻塞唤醒 waitnotify 及 condition死锁原理分析
Java并发编程:线程间协作的两种方式:waitnotifynotifyAll和Condition
Java并发编程:线程间协作的两种方式:waitnotifynotifyAll和Condition
线程阻塞唤醒 waitnotify 及 condition死锁原理分析