Sorting Algorithm
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Sorting Algorithm相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
sorting 应该是最容易被考到的东西,自己老是学了背,背了忘。为了方便复习,这里进行总结
1. Bubble Sort
定义:每两个两个比较,每扫完一次,当前扫过的最大值放在了末尾。
for i = (n-1) to 1
for j = 0 to i-1
if(A[j] > A[j+1])
swap
Time Complexity:
Best case : O(n) It can occur if the array is already sorted and no swap occurred.
Worse case: O(n^2)
2. Insertion Sort
定义:当前element 的之前所有elements 都已排好序。把当前element 放进之前排好序的数列中的正确位置。(当前的element从后向前比较)
Insertion sort takes advantage of the presorting. It requires fewer comparision than bubble sort
for i = 1 to n -1
j = i
while j >0 and A[j] <A[j-1]
swap(A[j], A[j-1])
j --;
Time Complexity:
Best case : O(n)
Worse case: O(n ^2)
3. Merge Sort
定义:把一个数组打散看成一个一个的单独的,然后每两个两个组一组,merge,新的组合再两个两个组一组,merge
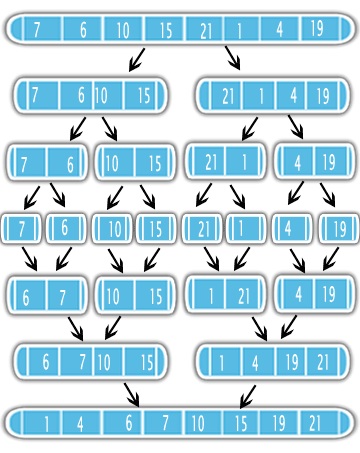
# C = output [length = N]
# A 1st sorted half [N/2]
# B 2nd sorted half [N/2]
i = j = 1
for k = 1 to n
if A[i] < B[j]
C[k] = A[i]
i++
else
C[k] = B[j]
j++
Time Complexity: O(nlgN)
4. Quick sort
定义: 随机选一个pivot( 当然ideally 是 medium), pivot 的左边全是比自己小的数,右边全是比自己大的数
所以有两个指针,一个指头,一个指尾,第一个指针指向第一个elemnt > pivot 的位置, 第二个指针从后往前,指向第一个element 小于pivot的位置
然后swap。如此扫一遍。然后以pivot为界限,array 分为两部分,再分别选一个pivot,继续上面的过程
Quicksort(A as array, low as int, high as int){
if (low < high){
pivot_location = Partition(A,low,high)
Quicksort(A,low, pivot_location)
Quicksort(A, pivot_location + 1, high)
}
}
Partition(A as array, low as int, high as int){
pivot = A[low]
leftwall = low
for i = low + 1 to high{
if (A[i] < pivot) then{
swap(A[i], A[leftwall])
leftwall = leftwall + 1
}
}
swap(A[low],A[leftwall])
return (leftwall)}
Time complexity: O(nlogn)
5. Selection Sort
定义: 选到第一小的,跟第一个element swap, 然后选第二小的,跟第二个element swap
SELECTION-SORT(A) 1. for j ← 1 to n-1 2. smallest ← j 3. for i ← j + 1 to n 4. if A[ i ] < A[ smallest ] 5. smallest ← i 6. Exchange A[ j ] ↔ A[ smallest ]
Complexity: O(n^2)
以上是关于Sorting Algorithm的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
AC日记——Cards Sorting codeforces 830B