跟王老师学注解:利用反射读取注解信息
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了跟王老师学注解:利用反射读取注解信息相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
跟王老师学注解(五):读取注解信息
主讲教师:王少华 QQ群号:483773664
一、注解被读取
(一)条件
当一个注解类型被定义为运行时注解后,该注解才是运行时可以见,当class文件被装载时被保存在class文件中的注解才会被Java虚拟机所读取。
要把@Retention注解的value成员变量的值设为RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME
(二)办法
我们已知所有的注解都是继承的java.lang.Annotation接口,也就是说Annotation是所有接口的父接口。除此之外,在java.lang.reflect包下的新增了AnnotatedElement接口,该接口代表程序中可以接受注解的程序元素,
1、该接口有如下几个实现类,分别是:
Class:类定义
Constructor:构造方法定义
Field:类的成员变量定义
Method:类的方法定义
Package:类的包定义

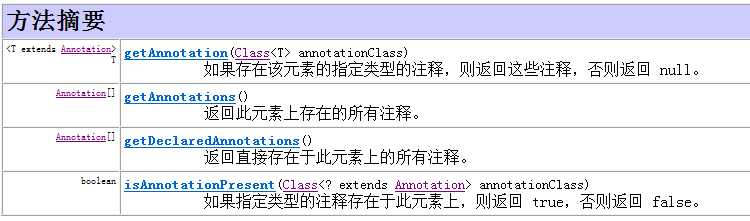
2、java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement接口是所有程序元素的父接口,程序通过反射获得某个类的AnnotatedElement对象,调用该对象的3个方法就可以来访问注解信息。
getAnnotation()方法:用于返回该程序元素上存在的、指定类型的注解,如果该类型的注解不存在,则返回null
getAnnotations():用来返回该程序元素上存在的所有注解。
isAnnotationPresent():用来判断该程序元素上是否包含指定类型的注解,如果存在返回true,否则返回false.
二、示例
(一)输出类方法上的所有注解
1、自定义的annotation
12345678 @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE })@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface MyAnnotation { String name() default "Jack"; int age() default 20;}
2、使用自定义Annotation
12345678 public class Person { private String name; private int age; @MyAnnotation public void setInfo(){ }}
3、测试
12345678910 public class AnnotationTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { Class<Person> personClass = (Class<Person>) Class.forName("chapter10_04.Person"); Method method = personClass.getMethod("setInfo"); Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annotations) { System.out.println(annotation); } }}
(二)获取某个注解里的元数据
123456789101112131415161718 public class AnnotationTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { Class<Person> personClass = (Class<Person>) Class.forName("chapter10_04.Person"); Method method = personClass.getMethod("setInfo"); Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annotations) { //如果类型是MyAnnotation if (annotation instanceof MyAnnotation) { System.out.println(annotation); //强制类型转换 MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation; //输出值 System.out.println("myAnnotation.name:"+myAnnotation.name()); System.out.println("myAnnotation.age:"+myAnnotation.age()); } } }}
三、@Inherited
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE })@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface MyAnnotation { String name() default "Jack"; int age() default 20;} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | public class Person { private String name; private int age; @MyAnnotation public void setInfo(){ }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | public class AnnotationTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { Class<Person> personClass = (Class<Person>) Class.forName("chapter10_04.Person"); Method method = personClass.getMethod("setInfo"); Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annotations) { System.out.println(annotation); } }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public class AnnotationTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { Class<Person> personClass = (Class<Person>) Class.forName("chapter10_04.Person"); Method method = personClass.getMethod("setInfo"); Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annotations) { //如果类型是MyAnnotation if (annotation instanceof MyAnnotation) { System.out.println(annotation); //强制类型转换 MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation; //输出值 System.out.println("myAnnotation.name:"+myAnnotation.name()); System.out.println("myAnnotation.age:"+myAnnotation.age()); } } }} |
@Inherited : 在您定义注解后并使用于程序代码上时,预设上父类别中的注解并不会被继承至子类别中,您可以在定义注解时加上java.lang.annotation.Inherited 限定的Annotation,这让您定义的Annotation型别被继承下来。注意注解继承只针对class 级别注解有效。
(一)改造MyAnnotation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE })@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Inheritedpublic @interface MyAnnotation { String name() default "Jack"; int age() default 20;} |
(二)继承类及使用自定义注解
1 2 3 4 | @MyAnnotationpublic class Fruit {} |
1 2 3 | public class Apple extends Fruit{ } |
(三)获得父类的annotaion
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | public class AnnotationTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { Class<Apple> appleClass = (Class<Apple>) Class.forName("chapter10_04.Apple"); Annotation[] annotations = appleClass.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annotations) { System.out.println(annotation); } }} |
以上是关于跟王老师学注解:利用反射读取注解信息的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章