Hadoop InputFormat源码分析
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Hadoop InputFormat源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
平时我们写MapReduce程序的时候,在设置输入格式的时候,总会调用形如job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class)来保证输入文件按照我们想要的格式被读取。所有的输入格式都继承于InputFormat,这是一个抽象类,其子类有专门用于读取普通文件的FileInputFormat,用来读取数据库的DBInputFormat等等。
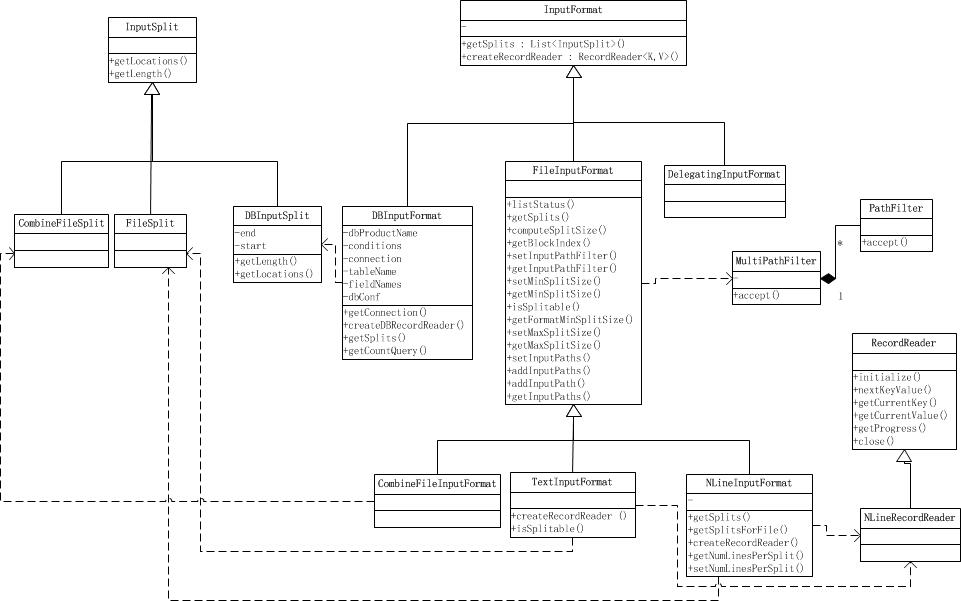
不同的InputFormat都会按自己的实现来读取输入数据并产生输入分片,一个输入分片会被单独的MapTask作为数据源,下面我们先看看这些输入分片(InputSplit)是什么样的。
InPutSplit:
我们知道Mapper的输入是一个一个的输入分片,称为InputSplit。InputSplit是一个抽象类,它在逻辑上包含了提供给处理这个InputSplit的Mapper的所有K-V对。
- public abstract class InputSplit {
- public abstract long getLength() throws IOException, InterruptedException;
- public abstract
- String[] getLocations() throws IOException, InterruptedException;
- }
getLength()用来获取InputSplit的大小,以支持对InputSplit进行排序,而getLocations()则用来获取存储分片的位置列表。
我们来看一个简单的InputSplit子类:FileSplit,源码如下:
- public class FileSplit extends InputSplit implements Writable {
- private Path file;
- private long start;
- private long length;
- private String[] hosts;
- FileSplit() {}
- /** Constructs a split with host information
- *
- * @param file the file name
- * @param start the position of the first byte in the file to process
- * @param length the number of bytes in the file to process
- * @param hosts the list of hosts containing the block, possibly null
- */
- public FileSplit(Path file, long start, long length, String[] hosts) {
- this.file = file;
- this.start = start;
- this.length = length;
- this.hosts = hosts;
- }
- /** The file containing this split‘s data. */
- public Path getPath() { return file; }
- /** The position of the first byte in the file to process. */
- public long getStart() { return start; }
- /** The number of bytes in the file to process. */
- @Override
- public long getLength() { return length; }
- @Override
- public String toString() { return file + ":" + start + "+" + length; }
- ////////////////////////////////////////////
- // 序列化和反序列化
- ////////////////////////////////////////////
- @Override
- public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
- Text.writeString(out, file.toString());
- out.writeLong(start);
- out.writeLong(length);
- }
- @Override
- public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
- file = new Path(Text.readString(in));
- start = in.readLong();
- length = in.readLong();
- hosts = null;
- }
- @Override
- public String[] getLocations() throws IOException {
- if (this.hosts == null) {
- return new String[]{};
- } else {
- return this.hosts;
- }
- }
- }
从上面的源码我们可以看到,一个FileSplit是由文件路径,分片开始位置,分片大小和存储分片数据的hosts列表组成,由这些信息我们就可以从输入文件中切分出提供给单个Mapper的输入数据。这些属性会在Constructor设置,我们在后面会看到这会在InputFormat的getSplits()构造这些分片。
我们再来看看CombinerFileSplit的源码:
- @InterfaceAudience.Public
- @InterfaceStability.Stable
- public class CombineFileSplit extends InputSplit implements Writable {
- private Path[] paths;
- private long[] startoffset;
- private long[] lengths;
- private String[] locations;
- private long totLength;
- /**
- * default constructor
- */
- public CombineFileSplit() {}
- public CombineFileSplit(Path[] files, long[] start,
- long[] lengths, String[] locations) {
- initSplit(files, start, lengths, locations);
- }
- public CombineFileSplit(Path[] files, long[] lengths) {
- long[] startoffset = new long[files.length];
- for (int i = 0; i < startoffset.length; i++) {
- startoffset[i] = 0;
- }
- String[] locations = new String[files.length];
- for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
- locations[i] = "";
- }
- initSplit(files, startoffset, lengths, locations);
- }
- private void initSplit(Path[] files, long[] start,
- long[] lengths, String[] locations) {
- this.startoffset = start;
- this.lengths = lengths;
- this.paths = files;
- this.totLength = 0;
- this.locations = locations;
- for(long length : lengths) {
- totLength += length;
- }
- }
- /**
- * Copy constructor
- */
- public CombineFileSplit(CombineFileSplit old) throws IOException {
- this(old.getPaths(), old.getStartOffsets(),
- old.getLengths(), old.getLocations());
- }
- public long getLength() {
- return totLength;
- }
- /** Returns an array containing the start offsets of the files in the split*/
- public long[] getStartOffsets() {
- return startoffset;
- }
- /** Returns an array containing the lengths of the files in the split*/
- public long[] getLengths() {
- return lengths;
- }
- /** Returns the start offset of the i<sup>th</sup> Path */
- public long getOffset(int i) {
- return startoffset[i];
- }
- /** Returns the length of the i<sup>th</sup> Path */
- public long getLength(int i) {
- return lengths[i];
- }
- /** Returns the number of Paths in the split */
- public int getNumPaths() {
- return paths.length;
- }
- /** Returns the i<sup>th</sup> Path */
- public Path getPath(int i) {
- return paths[i];
- }
- /** Returns all the Paths in the split */
- public Path[] getPaths() {
- return paths;
- }
- /** Returns all the Paths where this input-split resides */
- public String[] getLocations() throws IOException {
- return locations;
- }
- public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
- totLength = in.readLong();
- int arrLength = in.readInt();
- lengths = new long[arrLength];
- for(int i=0; i<arrLength;i++) {
- lengths[i] = in.readLong();
- }
- int filesLength = in.readInt();
- paths = new Path[filesLength];
- for(int i=0; i<filesLength;i++) {
- paths[i] = new Path(Text.readString(in));
- }
- arrLength = in.readInt();
- startoffset = new long[arrLength];
- for(int i=0; i<arrLength;i++) {
- startoffset[i] = in.readLong();
- }
- }
- public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
- out.writeLong(totLength);
- out.writeInt(lengths.length);
- for(long length : lengths) {
- out.writeLong(length);
- }
- out.writeInt(paths.length);
- for(Path p : paths) {
- Text.writeString(out, p.toString());
- }
- out.writeInt(startoffset.length);
- for(long length : startoffset) {
- out.writeLong(length);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
- for (int i = 0; i < paths.length; i++) {
- if (i == 0 ) {
- sb.append("Paths:");
- }
- sb.append(paths[i].toUri().getPath() + ":" + startoffset[i] +
- "+" + lengths[i]);
- if (i < paths.length -1) {
- sb.append(",");
- }
- }
- if (locations != null) {
- String locs = "";
- StringBuffer locsb = new StringBuffer();
- for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
- locsb.append(locations[i] + ":");
- }
- locs = locsb.toString();
- sb.append(" Locations:" + locs + "; ");
- }
- return sb.toString();
- }
- }
与FileSPlit类似,CombineFileSplit同样包含文件路径,分片起始位置,分片大小和存储分片数据的host列表,由于CombineFileSplit是针对小文件的,它把很多小文件包在一个InputSplit中,这样一个Mapper就可以处理很多小文件。要知道我们上面的FileSplit是对应一个输入文件的也就是说如果用FileSplit对应的FileInputFormat来作为输入格式。那么即使文件特别小,也是单独计算成一个分片来处理的。当我们的输入是由大量小文件组成的,就会导致同样大量的InputSplit,从而需要同样大量的Mapper来处理,这将很慢,想想一堆Map Task要运行(运行一个新的MapTask可是要启动虚拟机的),这是不符合Hadoop的设计理念的,所以使用CombineFileSplit可以优化Hadoop处理众多小文件的场景。
最后介绍TagInputSplit,这个类就是封装了一个InputSplit,然后加了一些tags在里面满足我们需要这些tags数据的情况,我们从下面就可以一目了然。
- class TaggedInputSplit extends InputSplit implements Configurable, Writable {
- private Class<? extends InputSplit> inputSplitClass;
- private InputSplit inputSplit;
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- private Class<? extends InputFormat> inputFormatClass;
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- private Class<? extends Mapper> mapperClass;
- private Configuration conf;
- public TaggedInputSplit() {
- // Default constructor.
- }
- /**
- * Creates a new TaggedInputSplit.
- *
- * @param inputSplit The InputSplit to be tagged
- * @param conf The configuration to use
- * @param inputFormatClass The InputFormat class to use for this job
- * @param mapperClass The Mapper class to use for this job
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public TaggedInputSplit(InputSplit inputSplit, Configuration conf,
- Class<? extends InputFormat> inputFormatClass,
- Class<? extends Mapper> mapperClass) {
- this.inputSplitClass = inputSplit.getClass();
- this.inputSplit = inputSplit;
- this.conf = conf;
- this.inputFormatClass = inputFormatClass;
- this.mapperClass = mapperClass;
- }
- /**
- * Retrieves the original InputSplit.
- *
- * @return The InputSplit that was tagged
- */
- public InputSplit getInputSplit() {
- return inputSplit;
- }
- /**
- * Retrieves the InputFormat class to use for this split.
- *
- * @return The InputFormat class to use
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public Class<? extends InputFormat> getInputFormatClass() {
- return inputFormatClass;
- }
- /**
- * Retrieves the Mapper class to use for this split.
- *
- * @return The Mapper class to use
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public Class<? extends Mapper> getMapperClass() {
- return mapperClass;
- }
- public long getLength() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- return inputSplit.getLength();
- }
- public String[] getLocations() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- return inputSplit.getLocations();
- }
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
- inputSplitClass = (Class<? extends InputSplit>) readClass(in);
- inputFormatClass = (Class<? extends InputFormat<?, ?>>) readClass(in);
- mapperClass = (Class<? extends Mapper<?, ?, ?, ?>>) readClass(in);
- inputSplit = (InputSplit) ReflectionUtils
- .newInstance(inputSplitClass, conf);
- SerializationFactory factory = new SerializationFactory(conf);
- Deserializer deserializer = factory.getDeserializer(inputSplitClass);
- deserializer.open((DataInputStream)in);
- inputSplit = (InputSplit)deserializer.deserialize(inputSplit);
- }
- private Class<?> readClass(DataInput in) throws IOException {
- String className = Text.readString(in);
- try {
- return conf.getClassByName(className);
- } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
- throw new RuntimeException("readObject can‘t find class", e);
- }
- }
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
- Text.writeString(out, inputSplitClass.getName());
- Text.writeString(out, inputFormatClass.getName());
- Text.writeString(out, mapperClass.getName());
- SerializationFactory factory = new SerializationFactory(conf);
- Serializer serializer =
- factory.getSerializer(inputSplitClass);
- serializer.open((DataOutputStream)out);
- serializer.serialize(inputSplit);
- }
- public Configuration getConf() {
- return conf;
- }
- public void setConf(Configuration conf) {
- this.conf = conf;
- }
- }
InputFormat:
通过使用InputFormat,MapReduce框架可以做到:
1.验证作业输入的正确性。
2.将输入文件切分成逻辑的InputSplits,一个InputSplit将被分配给一个单独的MapTask。
3.提供RecordReader的实现,这个RecordReader会从InputSplit中正确读出一条一条的K-V对供Mapper使用。
- public abstract class InputFormat<K, V> {
- public abstract
- List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext context
- ) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
- public abstract
- RecordReader<K,V> createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
- TaskAttemptContext context
- ) throws IOException,
- InterruptedException;
- }
上面是InputFormat的源码,getSplits()是用来获取由输入文件计算出来的InputSplits,我们在后面会看到计算InputSplit的时候会考虑到输入文件是否可分割、文件存储时分块的大小和文件大小等因素;而createRecordReader()提供了前面第三点所说的RecordReader的实现,以将K-V对从InputSplit中正确读取出来,比如LineRecordReader就以偏移值为key,一行数据为value的形式读取分片的。
FileInputFormat:
PathFilter被用来进行文件刷选,这样我们就可以控制哪些文件要被作为输入,哪些不作为输入,PathFIlter有一个accept(Path)方法,当接收的Path要被包含进来,就返回true,否则返回false。可以通过设置mapred.input.pathFIlter.class来设置用户自定义的PathFilter。
- public interface PathFilter {
- /**
- * Tests whether or not the specified abstract pathname should be
- * included in a pathname list.
- *
- * @param path The abstract pathname to be tested
- * @return <code>true</code> if and only if <code>pathname</code>
- * should be included
- */
- boolean accept(Path path);
- }
FileInputFormat是InputFormat的子类,它包含了一个MultiPathFilter,这个MultiPathFilter由一个过滤隐藏文件(名字前缀‘-‘或‘.‘)的PathFilter和一些可能存在的用户自定义的PathFilter组成,MultiPathFilter会在listStatus()方法中使用,而listStatus()方法又被getSplits()方法用来获取输入文件,也就是说实现了在获取输入分片前进行文件过滤。
- private static class MultiPathFilter implements PathFilter {
- private List<PathFilter> filters;
- public MultiPathFilter() {
- this.filters = new ArrayList<PathFilter>();
- }
- public MultiPathFilter(List<PathFilter> filters) {
- this.filters = filters;
- }
- public void add(PathFilter one) {
- filters.add(one);
- }
- public boolean accept(Path path) {
- for (PathFilter filter : filters) {
- if (filter.accept(path)) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- public String toString() {
- StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
- buf.append("[");
- for (PathFilter f: filters) {
- buf.append(f);
- buf.append(",");
- }
- buf.append("]");
- return buf.toString();
- }
- }
这些PathFilter会在listStatus()方法中用到,listStatus()是用来获取输入数据列表的。
下面是FileInputFormat的getSplits()方法,它首先得到分片的最小值minSize和最大值maxSize,它们会被用来计算分片的大小。可以通过设置mapred.min.split.size和mapred.max.split.size来设置。splits集合可以用来存储计算得到的输入分片,files则存储作为由listStatus()获取的输入文件列表。然后对于每个输入文件,判断是否可以分割,通过computeSplits()计算出分片大小splitSize,计算方法是:Math.max(minSize,Math.min(maxSize,blockSize));也就是保证在minSize和maxSize之间,且如果minSize<=blockSize<=maxSize,则设blockSize。然后根据这个splitSize计算出每个文件的InputSplit集合,然后加入到列表splits集合中。注意到我们生成InputSplit的时候按上面说的使用文件路径,分片起始位置,分片大小和存放这个文件爱你的hosts列表来创建。最后我们还设置了输入文件数量:mapreduce.input.num.files。
- public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job
- ) throws IOException {
- long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job));
- long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
- // generate splits
- List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>();
- List<FileStatus>files = listStatus(job);
- for (FileStatus file: files) {
- Path path = file.getPath();
- FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration());
- long length = file.getLen();
- BlockLocation[] blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length);
- if ((length != 0) && isSplitable(job, path)) {
- long blockSize = file.getBlockSize();
- long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize);
- long bytesRemaining = length;
- while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
- int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
- splits.add(new FileSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize,
- blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts()));
- bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
- }
- if (bytesRemaining != 0) {
- splits.add(new FileSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining,
- blkLocations[blkLocations.length-1].getHosts()));
- }
- } else if (length != 0) {
- splits.add(new FileSplit(path, 0, length, blkLocations[0].getHosts()));
- } else {
- //Create empty hosts array for zero length files
- splits.add(new FileSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0]));
- }
- }
- // Save the number of input files in the job-conf
- job.getConfiguration().setLong(NUM_INPUT_FILES, files.size());
- LOG.debug("Total # of splits: " + splits.size());
- return splits;
- }
就这样,我们利用FileInputFormat的getSplits()方法,我们就计算出了我们作业的所有输入分片了。
那这些计算出来的分片是怎么被map读出来的呢?就是InputFormat中的另一个方法createRecordReader(),FileInputFormat并没有对这个方法做具体的要求,而是交给子类自行去实现它。
RecordReader:
RecordReader是用来从一个输入分片中读取一个一个的K-V对的抽象类,我们可以将其看做是在InputSplit上的迭代器。我们从类图中可以看到它的一些方法,最主要的方法就是nextKeyValue()方法,由它获取分片上的下一个K-V对。
我们呢再来看看RecordReader的一个子类:LineRecordReader,这也是我们用的最多的。
LineRecordReader由一个FileSplit构造出来,start是这个FileSplit的起始位置,pos是当前读取分片的位置,end是分片结束位置,in是打开一个读取这个分片的输入流,它是使用这个FIleSplit对应的文件名来打开的。key和value则分别是每次读取的K-V对。然后我们还看到可以利用getProgress()来跟踪读取分片的进度,这个函数就是根据已经读取的K-V对占总K-V对的比例显示进度的。
- public class LineRecordReader extends RecordReader<LongWritable, Text> {
- private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(LineRecordReader.class);
- private CompressionCodecFactory compressionCodecs = null;
- private long start;
- private long pos;
- private long end;
- private LineReader in;
- private int maxLineLength;
- private LongWritable key = null;
- private Text value = null;
- private Seekable filePosition;
- private CompressionCodec codec;
- private Decompressor decompressor;
- public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit,
- TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
- FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit;
- Configuration job = context.getConfiguration();
- this.maxLineLength = job.getInt("mapred.linerecordreader.maxlength",
- Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- start = split.getStart();
- end = start + split.getLength();
- final Path file = split.getPath();
- compressionCodecs = new CompressionCodecFactory(job);
- codec = compressionCodecs.getCodec(file);
以上是关于Hadoop InputFormat源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章