Spring AOP
Posted 快鸟
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring AOP相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
(分析基于Spring的版本:version = 4.1.6.RELEASE)
SpringAOP 和 AspectJ 的关系:
它们是两种不同的编程风格, SpringAOP 使用 xml 配置的形式配置 aop。而 AspectJ 使用 AspectJ 的注解来配置 aop
aspect、JoinPoint、Pointcut、Weaving、Advice
JoinPoint: 连接点。表示目标对象中的方法
Pointcut: 切点。表示连接点的集合
Weaving: 织入。把代理逻辑加入到目标对象上的过程叫织入
Advice: 通知。包括 “around”, “before” and “after 等
this、target
this: 产生的代理对象
target: 被代理的原始对象
JoinPoint、ProceedingJoinPoint
JoinPoint 接口可以拿到连接点的相关信息,比如:方法签名、方法参数、this、target
ProceedingJoinPoint 继承自 JoinPoint,它是用来支持环绕(around)通知的,多暴露了一个 proceed() 方法,用来执行目标对象的方法。
Spring AOP工厂: org.springframework.aop.framework.DefaultAopProxyFactory
@Override public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation."); } if (targetClass.isInterface()) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } }
从代码可以看出:
1. 如果AdvisedSupport中没有进行自定义设置,Spring去创建代理的时候,会默认使用JDK动态代理。
2. 如果AdvisedSupport中进行了设置,那么就去判断被代理的类是不是接口,如果是接口的话就使用JDK动态代理,否则才使用Cglib的代理。
(2020.1.17 更新)
从源码看, proxyTargetClass=true 时,如果 targetClass 是接口 or targetClass 是一个代理类型,也有可能走 jdk 动态代理。但是绝大多数情况是不会的。
首先,在源码中找到 targetClass 赋值的地方,可以发现 targetClass 是 bean 的实例的 class,所以通常是一个实体类,不是接口。至于 targetClass 什么时候会是代理类,还不太清楚。
那既然 targetClass 是 bean 的实例的 class 的话,它并不是一个接口,那么当 proxyTargetClass=false 的时候, jdk 怎么来产生代理呢?
答案是,spring 会找到 targetClass 对应的接口来生成代理,如果这个类没有接口的话,会将 proxyTargetClass 设置成 true,从而使用 cglib 来生成代理
Spring 基于JDK动态代理的AOP实现解析:
我们知道,使用JDK的动态代理,主要是实现 java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler#invoke(Object obj, Method method, Object[] aobj)方法。
Spring相关的源码如下:JdkDynamicAopProxy.class
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { MethodInvocation invocation; Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource; Class<?> targetClass = null; Object target = null; try { if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself. return equals(args[0]); } if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself. return hashCode(); } if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() && method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) { // Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config... return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args); } Object retVal; if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { // Make invocation available if necessary. oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } // May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, // in case it comes from a pool. target = targetSource.getTarget(); if (target != null) { targetClass = target.getClass(); } // Get the interception chain for this method. List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); // Check whether we have any advice. If we don\'t, we can fallback on direct // reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation. if (chain.isEmpty()) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does // nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying. retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args); } else { // We need to create a method invocation... invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain. retVal = invocation.proceed(); } // Massage return value if necessary. Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) { // Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method // is type-compatible. Note that we can\'t help if the target sets // a reference to itself in another returned object. retVal = proxy; } else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) { throw new AopInvocationException( "Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method); } return retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { // Must have come from TargetSource. targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } }
从上面可以看出,spring 会先拿到一个 MethodInterceptor 的 chain 。
如果chain为空的话,就直接反射调用原方法;否则,就会根据这个 chain 来生成一个 MethodInvocation ,然后去执行 invocation.proceed() 。
invocation.proceed() 方法的实现,是递归调用 chain 中的 MethodInterceptor。
也就是说,我们所有的AOP拦截,都是通过一连串的 MethodInterceptor 来实现的。
而这个 MethodInterceptor 的 chain 是通过 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); 来生成的。
也就是基于 AdvisedSupport 来生成的。
Spring 对 AdvisedSupport 的注释是:Base class for AOP proxy configuration managers. 也就是说,AdvisedSupport 是产生AOP代理的配置管理者。
AdvisedSupport 中保存了一个List<Advisor> advisors 的集合。
满足条件的Advisor(即:能对此method进行拦截的Advisor),最终会被转换成 MethodInterceptor ,从而添加到chain中。
Spring 基于Cglib的AOP实现解析:
我们知道,使用Cglib实现AOP时,最主要的是要设置Callback来对Method进行拦截,即:void net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer.setCallback(Callback callback) 。
spring生成Callback的源码如下:CglibAopProxy.class
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception { // Parameters used for optimisation choices... boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy(); boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen(); boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic(); // Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls). Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised); .............. }
从上面的代码可以看出,spring在生成 Callback 时,也是基于 AdvisedSupport 来的(同JDK动态代理生成 MethodInterceptor 的chain一样)。
CglibAopProxy$DynamicAdvisedInterceptor.class
private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable { private final AdvisedSupport advised; public DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(AdvisedSupport advised) { this.advised = advised; } @Override public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; Class<?> targetClass = null; Object target = null; try { if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { // Make invocation available if necessary. oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } // May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we // "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool... target = getTarget(); if (target != null) { targetClass = target.getClass(); } List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); Object retVal; // Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is, // no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target. if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly. // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know // it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot // swapping or fancy proxying. retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, args); } else { // We need to create a method invocation... retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed(); } retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal); return retVal; } finally { if (target != null) { releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } } ............... }
不难看出,最终JDK动态代理 与 Cglib代理 对AOP的实现都是基于 AdvisedSupport 的 MethodInterceptor 链。
参考:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/0734ec855183
http://www.cnblogs.com/digdeep/p/4528353.html
http://my.oschina.net/robinyao/blog/649518
http://lgbolgger.iteye.com/blog/2180251
http://www.cnblogs.com/chanedi/p/4552555.html (原码说明)
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable {
Spring 异步@Async也是基于Spring AOP来做的:
在bean创建完成后,会调用 AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 来生成一个代理bean
2018.07.23 add:
编程式使用aop https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26525215/article/details/52422395/
2019.01.11 add:
spring @Transactional 的原理解析:
TransactionAspectSupport#completeTransactionAfterThrowing 对 @Transactional 事务的处理,默认回滚 RuntimeException
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-master-spring-transactional-use/index.html
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/data-access.html#tx-decl-explained
https://doanduyhai.wordpress.com/2011/11/20/spring-transactional-explained/
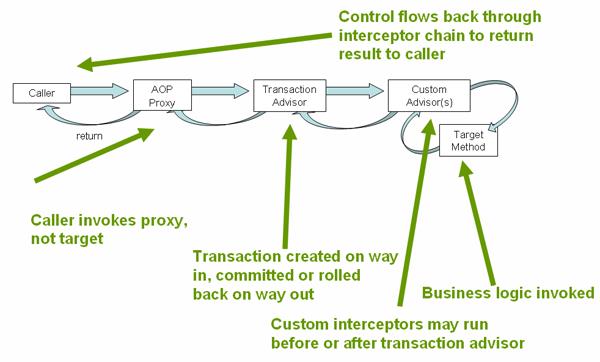
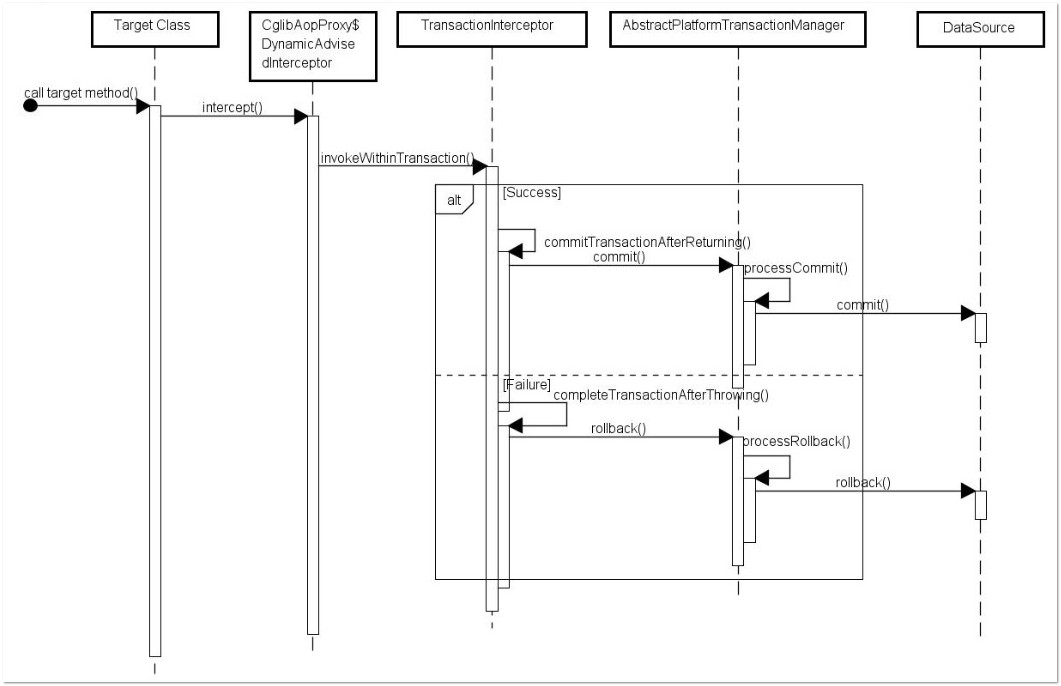
以上是关于Spring AOP的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章