mysqlbinlog 数据恢复
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mysqlbinlog 数据恢复相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
mysqlbinlog 数据恢复
mysqlbinlog 支持三种模式:
row level
缺点:
row level模式下,所有的执行的语句当记录到日志中的时候,都将以每行记录的修改来记录,这样可能会产生大量的日志内容,比如有这样一条update语句:update product set user = ‘b’ id = ‘1’,执行之后,日志中记录的不是这条update语句所对应额事件(MySQL以事件的形式来记录bin-log日志),而是这条语句所更新的每一条记录的变化情况,这样就记录成很多条记录被更新的很多个事件。自然,bin-log日志的量就会很大。尤其是当执行alter table之类的语句的时候,产生的日志量是惊人的。因为MySQL对于alter table之类的表结构变更语句的处理方式是整个表的每一条记录都需要变动,实际上就是重建了整个表。那么该表的每一条记录都会被记录到日志中。
优点:
row level模式下,bin-log中可以不记录执行的sql语句的上下文相关的信息,仅仅只需要记录那一条记录被修改了,修改成什么样了。所以row level的日志内容会非常清楚的记录下每一行数据修改的细节。且不会出现某些特定情况下的存储过程,或function,以及 trigger的调用和触发无法被正确复制的问题。
Statement Level
缺点
由于他是记录的执行语句,所以,为了让这些语句在slave端也能正确执行,那么他还必须记录每条语句在执行的时候的一些相关信息,也就是上下文信息,以保证所有语句在slave端杯执行的时候能够得到和在master端执行时候相同的结果。另外就是,由于MySQL现在发展比较快,很多的新功能不断 的加入,使MySQL得复制遇到了不小的挑战,自然复制的时候涉及到越复杂的内容,bug也就越容易出现。在statement level下,目前已经发现的就有不少情况会造成MySQL的复制出现问题,主要是修改数据的时候使用了某些特定的函数或者功能的时候会出现,比如:sleep()函数在有些版本中就不能 真确复制,在存储过程中使用了last_insert_id()函数,可能会使slave和master上得到不一致的id等等。由于row level是基于每一行来记录的变化,所以不会出现类似的问题。
优点
statement level下的优点首先就是解决了row level下的缺点,不需要记录每一行数据的变化,减少bin-log日志量,节约IO,提高性能。因为他只需要记录在Master上所执行的语句的细节,以及执行语句时候的上下文的信息。
Mixed
说明
Mixed模式,可以理解为是前两种模式的结合。
Mixed模式下,MySQL会根据执行的每一条具体的sql语句来区分对待记录的日志形式,也就是在Statement和Row之间选择一种。
新版本中的Statment level还是和以前一样,仅仅记录执行的语句。而新版本的MySQL中队row level模式也被做了优化,并不是所有的修改都会以row level来记录,像遇到表结构变更的时候就会以statement模式来记录,如果sql语句确实就是update或者delete等修改数据的语句,那么还是会记录所有行 的变更。
上述配置可以在/etc/my.cnf 下面进行配置,如下:
log-bin=mysql-bin #binlog_format=”STATEMENT” #binlog_format=”ROW” binlog_format=”MIXED
也可以动态修改
mysql> SET SESSION binlog_format = ‘STATEMENT’; mysql> SET SESSION binlog_format = ‘ROW’; mysql> SET SESSION binlog_format = ‘MIXED’; mysql> SET GLOBAL binlog_format = ‘STATEMENT’; mysql> SET GLOBAL binlog_format = ‘ROW’; mysql> SET GLOBAL binlog_format = ‘MIXED’;
配置完成后可使用如下语句查看状态
show variables like ‘%binlog_format%‘;
基于mysqlbinlog 语句(statement)的恢复
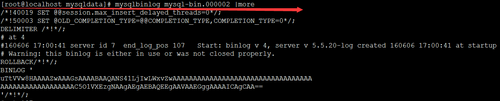
确定需要恢复数据的时间和位置
mysqlbinlog mysql-bin.000002 |more
找出需要恢复的时间和位置
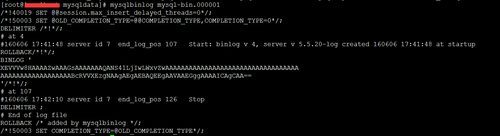
使用mysqlbinlog 已确定的时间恢复出语句文件
可能有多个 mysql-bin.00000x 文件 第一个文件需要确定开始时间,最后一个文件需要确定结束时间。
mysqlbinlog --start-date="2016-06-06 12:30:00" --stop-date="2016-06-06 18:00:00" mysql-bin.000002 >rollbak0606_01.sql、
--start-positon="50" //指定从50位置开始
--stop-postion="100"//指定到100位置结束
处理语句文件并恢复
mysqlbinlog中包含了所有库和表的sql语句。如需要区分库可进行过滤:
grep "insert into xxx" rollbak0606_01.sql >>rollbak0606_del.sql
导入处理后的文件
mysql -uroot -p‘xxxx‘ --default-character-set=utf8 < rollbak0606_del.sql
或者
source ‘filePath‘
基于mysqlbinlog 行(row)的恢复
mysqlbinlog --base64-output=decode-rows -v --start-date=‘2016-06-06 14:00:00‘ --stop-date=‘2016-06-06 14:20:00‘ /opt/mysql/log/mysql-bin.000001 >/opt/mysql_bak/mysqlbinlog_0606.sql
--base64-output=decode-rows 基于行的binlog
-v 用于重构基于行的sql
B. 恢复
mysqlbinlog --start-date="2016-06-06 16:30:00" --stop-date="2016-06-06 17:00:00" --start-positon="50" --stop-postion="100" mysql_bin.000001 |mysql -uroot -p123456
--start-positon="50" //指定从50位置开始
--stop-postion="100"//指定到100位置结束
C. 也可以转换为基于语句的复制
这里需要一个perl 脚本。感谢提供脚本的大神。
#!/usr/lib/perl -w
use strict;
use warnings;
use Class::Struct;
use Getopt::Long qw(:config no_ignore_case); # GetOption
# register handler system signals
use sigtrap ‘handler‘, \&sig_int, ‘normal-signals‘;
# catch signal
sub sig_int(){
my ($signals) = @_;
print STDERR "# Caught SIG$signals.\n";
exit 1;
}
my %opt;
my $srcfile;
my $host = ‘127.0.0.1‘;
my $port = 3306;
my ($user,$pwd);
my ($MYSQL, $MYSQLBINLOG, $ROLLBACK_DML);
my $outfile = ‘/dev/null‘;
my (%do_dbs,%do_tbs);
# tbname=>tbcol, tbcol: @n=>colname,type
my %tbcol_pos;
my $SPLITER_COL = ‘,‘;
my $SQLTYPE_IST = ‘INSERT‘;
my $SQLTYPE_UPD = ‘UPDATE‘;
my $SQLTYPE_DEL = ‘DELETE‘;
my $SQLAREA_WHERE = ‘WHERE‘;
my $SQLAREA_SET = ‘SET‘;
my $PRE_FUNCT = ‘========================== ‘;
# =========================================================
# 基于row模式的binlog,生成DML(insert/update/delete)的rollback语句
# 通过mysqlbinlog -v 解析binlog生成可读的sql文件
# 提取需要处理的有效sql
# "### "开头的行.如果输入的start-position位于某个event group中间,则会导致"无法识别event"错误
#
# 将INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE 的sql反转,并且1个完整sql只能占1行
# INSERT: INSERT INTO => DELETE FROM, SET => WHERE
# UPDATE: WHERE => SET, SET => WHERE
# DELETE: DELETE FROM => INSERT INTO, WHERE => SET
# 用列名替换位置@{1,2,3}
# 通过desc table获得列顺序及对应的列名
# 特殊列类型value做特别处理
# 逆序
#
# 注意:
# 表结构与现在的表结构必须相同[谨记]
# 由于row模式是幂等的,并且恢复是一次性,所以只提取sql,不提取BEGIN/COMMIT
# 只能对INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE进行处理
# ========================================================
sub main{
# get input option
&get_options();
#
&init_tbcol();
#
&do_binlog_rollback();
}
&main();
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : get options and set option flag
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub get_options{
#Get options info
GetOptions(\%opt,
‘help‘, # OUT : print help info
‘f|srcfile=s‘, # IN : binlog file
‘o|outfile=s‘, # out : output sql file
‘h|host=s‘, # IN : host
‘u|user=s‘, # IN : user
‘p|password=s‘, # IN : password
‘P|port=i‘, # IN : port
‘start-datetime=s‘, # IN : start datetime
‘stop-datetime=s‘, # IN : stop datetime
‘start-position=i‘, # IN : start position
‘stop-position=i‘, # IN : stop position
‘d|database=s‘, # IN : database, split comma
‘T|table=s‘, # IN : table, split comma
‘i|ignore‘, # IN : ignore binlog check ddl and so on
‘debug‘, # IN : print debug information
) or print_usage();
if (!scalar(%opt)) {
&print_usage();
}
# Handle for options
if ($opt{‘f‘}){
$srcfile = $opt{‘f‘};
}else{
&merror("please input binlog file");
}
$opt{‘h‘} and $host = $opt{‘h‘};
$opt{‘u‘} and $user = $opt{‘u‘};
$opt{‘p‘} and $pwd = $opt{‘p‘};
$opt{‘P‘} and $port = $opt{‘P‘};
if ($opt{‘o‘}) {
$outfile = $opt{‘o‘};
# 清空 outfile
`echo ‘‘ > $outfile`;
}
#
$MYSQL = qq{mysql -h$host -u$user -p‘$pwd‘ -P$port};
&mdebug("get_options::MYSQL\n\t$MYSQL");
# 提取binlog,不需要显示列定义信息,用-v,而不用-vv
$MYSQLBINLOG = qq{mysqlbinlog -v};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " --start-position=".$opt{‘start-position‘} if $opt{‘start-position‘};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " --stop-position=".$opt{‘stop-position‘} if $opt{‘stop-postion‘};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " --start-datetime=‘".$opt{‘start-datetime‘}."‘" if $opt{‘start-datetime‘};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " --stop-datetime=‘$opt{‘stop-datetime‘}‘" if $opt{‘stop-datetime‘};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " $srcfile";
&mdebug("get_options::MYSQLBINLOG\n\t$MYSQLBINLOG");
# 检查binlog中是否含有 ddl sql: CREATE|ALTER|DROP|RENAME
&check_binlog() unless ($opt{‘i‘});
# 不使用mysqlbinlog过滤,USE dbname;方式可能会漏掉某些sql,所以不在mysqlbinlog过滤
# 指定数据库
if ($opt{‘d‘}){
my @dbs = split(/,/,$opt{‘d‘});
foreach my $db (@dbs){
$do_dbs{$db}=1;
}
}
# 指定表
if ($opt{‘T‘}){
my @tbs = split(/,/,$opt{‘T‘});
foreach my $tb (@tbs){
$do_tbs{$tb}=1;
}
}
# 提取有效DML SQL
$ROLLBACK_DML = $MYSQLBINLOG." | grep ‘^### ‘";
# 去掉注释: ‘### ‘ -> ‘‘
# 删除首尾空格
$ROLLBACK_DML .= " | sed ‘s/###\\s*//g;s/\\s*\$//g‘";
&mdebug("rollback dml\n\t$ROLLBACK_DML");
# 检查内容是否为空
my $cmd = "$ROLLBACK_DML | wc -l";
&mdebug("check contain dml sql\n\t$cmd");
my $size = `$cmd`;
chomp($size);
unless ($size >0){
&merror("binlog DML is empty:$ROLLBACK_DML");
};
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : check binlog contain DDL
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub check_binlog{
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT check_binlog");
my $cmd = "$MYSQLBINLOG ";
$cmd .= " | grep -E -i ‘^(CREATE|ALTER|DROP|RENAME)‘ ";
&mdebug("check binlog has DDL cmd\n\t$cmd");
my $ddlcnt = `$cmd`;
chomp($ddlcnt);
my $ddlnum = `$cmd | wc -l`;
chomp($ddlnum);
my $res = 0;
if ($ddlnum>0){
# 在ddl sql前面加上前缀<DDL>
$ddlcnt = `echo ‘$ddlcnt‘ | sed ‘s/^/<DDL>/g‘`;
&merror("binlog contain $ddlnum DDL:$MYSQLBINLOG. ddl sql:\n$ddlcnt");
}
return $res;
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : init all table column order
# if input --database --table params, only get set table column order
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub init_tbcol{
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT init_tbcol");
# 提取DML语句
my $cmd .= "$ROLLBACK_DML | grep -E ‘^(INSERT|UPDATE|DELETE)‘";
# 提取表名,并去重
#$cmd .= " | awk ‘{if (\$1 ~ \"^UPDATE\") {print \$2}else {print \$3}}‘ | uniq ";
$cmd .= " | awk ‘{if (\$1 ~ \"^UPDATE\") {print \$2}else {print \$3}}‘ | sort | uniq ";
&mdebug("get table name cmd\n\t$cmd");
open ALLTABLE, "$cmd | " or die "can‘t open file:$cmd\n";
while (my $tbname = <ALLTABLE>){
chomp($tbname);
#if (exists $tbcol_pos{$tbname}){
# next;
#}
&init_one_tbcol($tbname) unless (&ignore_tb($tbname));
}
close ALLTABLE or die "can‘t close file:$cmd\n";
# init tb col
foreach my $tb (keys %tbcol_pos){
&mdebug("tbname->$tb");
my %colpos = %{$tbcol_pos{$tb}};
foreach my $pos (keys %colpos){
my $col = $colpos{$pos};
my ($cname,$ctype) = split(/$SPLITER_COL/, $col);
&mdebug("\tpos->$pos,cname->$cname,ctype->$ctype");
}
}
};
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : init one table column order
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub init_one_tbcol{
my $tbname = shift;
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT init_one_tbcol");
# 获取表结构及列顺序
my $cmd = $MYSQL." --skip-column-names --silent -e ‘desc $tbname‘";
# 提取列名,并拼接
$cmd .= " | awk -F\‘\\t\‘ \‘{print NR\"$SPLITER_COL`\"\$1\"`$SPLITER_COL\"\$2}‘";
&mdebug("get table column infor cmd\n\t$cmd");
open TBCOL,"$cmd | " or die "can‘t open desc $tbname;";
my %colpos;
while (my $line = <TBCOL>){
chomp($line);
my ($pos,$col,$coltype) = split(/$SPLITER_COL/,$line);
&mdebug("linesss=$line\n\t\tpos=$pos\n\t\tcol=$col\n\t\ttype=$coltype");
$colpos{$pos} = $col.$SPLITER_COL.$coltype;
}
close TBCOL or die "can‘t colse desc $tbname";
$tbcol_pos{$tbname} = \%colpos;
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : rollback sql: INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub do_binlog_rollback{
my $binlogfile = "$ROLLBACK_DML ";
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT do_binlog_rollback");
# INSERT|UPDATE|DELETE
my $sqltype;
# WHERE|SET
my $sqlarea;
my ($tbname, $sqlstr) = (‘‘, ‘‘);
my ($notignore, $isareabegin) = (0,0);
# output sql file
open SQLFILE, ">> $outfile" or die "Can‘t open sql file:$outfile";
# binlog file
open BINLOG, "$binlogfile |" or die "Can‘t open file: $binlogfile";
while (my $line = <BINLOG>){
chomp($line);
if ($line =~ /^(INSERT|UPDATE|DELETE)/){
# export sql
if ($sqlstr ne ‘‘){
$sqlstr .= ";\n";
print SQLFILE $sqlstr;
&mdebug("export sql\n\t".$sqlstr);
$sqlstr = ‘‘;
}
if ($line =~ /^INSERT/){
$sqltype = $SQLTYPE_IST;
$tbname = `echo ‘$line‘ | awk ‘{print \$3}‘`;
chomp($tbname);
$sqlstr = qq{DELETE FROM $tbname};
}elsif ($line =~ /^UPDATE/){
$sqltype = $SQLTYPE_UPD;
$tbname = `echo ‘$line‘ | awk ‘{print \$2}‘`;
chomp($tbname);
$sqlstr = qq{UPDATE $tbname};
}elsif ($line =~ /^DELETE/){
$sqltype = $SQLTYPE_DEL;
$tbname = `echo ‘$line‘ | awk ‘{print \$3}‘`;
chomp($tbname);
$sqlstr = qq{INSERT INTO $tbname};
}
# check ignore table
if(&ignore_tb($tbname)){
$notignore = 0;
&mdebug("<BINLOG>#IGNORE#:line:".$line);
$sqlstr = ‘‘;
}else{
$notignore = 1;
&mdebug("<BINLOG>#DO#:line:".$line);
}
}else {
if($notignore){
&merror("can‘t get tbname") unless (defined($tbname));
if ($line =~ /^WHERE/){
$sqlarea = $SQLAREA_WHERE;
$sqlstr .= qq{ SET};
$isareabegin = 1;
}elsif ($line =~ /^SET/){
$sqlarea = $SQLAREA_SET;
$sqlstr .= qq{ WHERE};
$isareabegin = 1;
}elsif ($line =~ /^\@/){
$sqlstr .= &deal_col_value($tbname, $sqltype, $sqlarea, $isareabegin, $line);
$isareabegin = 0;
}else{
&mdebug("::unknown sql:".$line);
}
}
}
}
# export last sql
if ($sqlstr ne ‘‘){
$sqlstr .= ";\n";
print SQLFILE $sqlstr;
&mdebug("export sql\n\t".$sqlstr);
}
close BINLOG or die "Can‘t close binlog file: $binlogfile";
close SQLFILE or die "Can‘t close out sql file: $outfile";
# 逆序
# 1!G: 只有第一行不执行G, 将hold space中的内容append回到pattern space
# h: 将pattern space 拷贝到hold space
# $!d: 除最后一行都删除
my $invert = "sed -i ‘1!G;h;\$!d‘ $outfile";
my $res = `$invert`;
&mdebug("inverter order sqlfile :$invert");
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : transfer column pos to name
# deal column value
#
# &deal_col_value($tbname, $sqltype, $sqlarea, $isareabegin, $line);
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub deal_col_value($$$$$){
my ($tbname, $sqltype, $sqlarea, $isareabegin, $line) = @_;
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT deal_col_value");
&mdebug("input:tbname->$tbname,type->$sqltype,area->$sqlarea,areabegin->$isareabegin,line->$line");
my @vals = split(/=/, $line);
my $pos = substr($vals[0],1);
my $valstartpos = length($pos)+2;
my $val = substr($line,$valstartpos);
my %tbcol = %{$tbcol_pos{$tbname}};
my ($cname,$ctype) = split(/$SPLITER_COL/,$tbcol{$pos});
&merror("can‘t get $tbname column $cname type") unless (defined($cname) || defined($ctype));
&mdebug("column infor:cname->$cname,type->$ctype");
# join str
my $joinstr;
if ($isareabegin){
$joinstr = ‘ ‘;
}else{
# WHERE 被替换为 SET, 使用 , 连接
if ($sqlarea eq $SQLAREA_WHERE){
$joinstr = ‘, ‘;
# SET 被替换为 WHERE 使用 AND 连接
}elsif ($sqlarea eq $SQLAREA_SET){
$joinstr = ‘ AND ‘;
}else{
&merror("!!!!!!The scripts error");
}
}
#
my $newline = $joinstr;
# NULL value
if (($val eq ‘NULL‘) && ($sqlarea eq $SQLAREA_SET)){
$newline .= qq{ $cname IS NULL};
}else{
# timestamp: record seconds
if ($ctype eq ‘timestamp‘){
$newline .= qq{$cname=from_unixtime($val)};
# datetime: @n=yyyy-mm-dd hh::ii::ss
}elsif ($ctype eq ‘datetime‘){
$newline .= qq{$cname=‘$val‘};
}else{
$newline .= qq{$cname=$val};
}
}
&mdebug("\told>$line\n\tnew>$newline");
return $newline;
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : check is ignore table
# params: IN table full name # format:`dbname`.`tbname`
# RETURN:
# 0 not ignore
# 1 ignore
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub ignore_tb($){
my $fullname = shift;
# 删除`
$fullname =~ s/`//g;
my ($dbname,$tbname) = split(/\./,$fullname);
my $res = 0;
# 指定了数据库
if ($opt{‘d‘}){
# 与指定库相同
if ($do_dbs{$dbname}){
# 指定表
if ($opt{‘T‘}){
# 与指定表不同
unless ($do_tbs{$tbname}){
$res = 1;
}
}
# 与指定库不同
}else{
$res = 1;
}
}
#&mdebug("Table check ignore:$fullname->$res");
return $res;
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : print debug msg
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub mdebug{
my (@msg) = @_;
print "<DEBUG>@msg\n" if ($opt{‘debug‘});
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : print error msg and exit
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub merror{
my (@msg) = @_;
print "<Error>:@msg\n";
&print_usage();
exit(1);
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : print usage
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub print_usage{
print <<EOF;
==========================================================================================
Command line options :
--help # OUT : print help info
-f, --srcfile # IN : binlog file. [required]
-o, --outfile # OUT : output sql file. [required]
-h, --host # IN : host. default ‘127.0.0.1‘
-u, --user # IN : user. [required]
-p, --password # IN : password. [required]
-P, --port # IN : port. default ‘3306‘
--start-datetime # IN : start datetime
--stop-datetime # IN : stop datetime
--start-position # IN : start position
--stop-position # IN : stop position
-d, --database # IN : database, split comma
-T, --table # IN : table, split comma. [required] set -d
-i, --ignore # IN : ignore binlog check contain DDL(CREATE|ALTER|DROP|RENAME)
--debug # IN : print debug information
Sample :
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f ‘mysql-bin.000001‘ -o ‘/tmp/t.sql‘ -u ‘user‘ -p ‘pwd‘
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f ‘mysql-bin.000001‘ -o ‘/tmp/t.sql‘ -u ‘user‘ -p ‘pwd‘ -i
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f ‘mysql-bin.000001‘ -o ‘/tmp/t.sql‘ -u ‘user‘ -p ‘pwd‘ --debug
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f ‘mysql-bin.000001‘ -o ‘/tmp/t.sql‘ -h ‘192.168.1.2‘ -u ‘user‘ -p ‘pwd‘ -P 3307
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f ‘mysql-bin.000001‘ -o ‘/tmp/t.sql‘ -u ‘user‘ -p ‘pwd‘ --start-position=107
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f ‘mysql-bin.000001‘ -o ‘/tmp/t.sql‘ -u ‘user‘ -p ‘pwd‘ --start-position=107 --stop-position=10000
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f ‘mysql-bin.000001‘ -o ‘/tmp/t.sql‘ -u ‘user‘ -p ‘pwd‘ -d ‘db1,db2‘
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f ‘mysql-bin.0000*‘ -o ‘/tmp/t.sql‘ -u ‘user‘ -p ‘pwd‘ -d ‘db1,db2‘ -T ‘tb1,tb2‘
==========================================================================================
EOF
exit;
}
1;
脚本谨慎使用。
例子:
perl binlog-rollback.pl -f ‘mysql-bin.000001‘ -o ‘/tmp/t.sql‘ -h ‘192.168.1.2‘ -u ‘user‘ -p ‘pwd‘ -P 3307
提供用户名和密码是为了确定表结构,其他用法可参考案例。
得到的结果为事物的反向语句。delete--->insert,insert--->delete 如下:
INSERT INTO cqdata.cq_herodata SET `id`=23, `serverId`=1, `userId`=2, `tempId`=2, `starArr`=‘way‘, `gemArr`=‘wa‘, `wingArr`=‘way‘, `equipData`=‘way‘, `sex`=2, `combat`=4327896, `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:03‘; INSERT INTO cqdata.cq_herodata SET `id`=22, `serverId`=1, `userId`=2, `tempId`=2, `starArr`=‘way‘, `gemArr`=‘wa‘, `wingArr`=‘way‘, `equipData`=‘way‘, `sex`=2, `combat`=4327896, `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:03‘; INSERT INTO cqdata.cq_herodata SET `id`=21, `serverId`=1, `userId`=2, `tempId`=2, `starArr`=‘way‘, `gemArr`=‘wa‘, `wingArr`=‘way‘, `equipData`=‘way‘, `sex`=2, `combat`=4327896, `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:02‘; INSERT INTO cqdata.cq_herodata SET `id`=20, `serverId`=1, `userId`=2, `tempId`=2, `starArr`=‘way‘, `gemArr`=‘wa‘, `wingArr`=‘way‘, `equipData`=‘way‘, `sex`=2, `combat`=4327896, `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:02‘; INSERT INTO cqdata.cq_herodata SET `id`=19, `serverId`=1, `userId`=2, `tempId`=2, `starArr`=‘way‘, `gemArr`=‘wa‘, `wingArr`=‘way‘, `equipData`=‘way‘, `sex`=2, `combat`=4327896, `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:01‘; INSERT INTO cqdata.cq_herodata SET `id`=18, `serverId`=1, `userId`=2, `tempId`=2, `starArr`=‘way‘, `gemArr`=‘wa‘, `wingArr`=‘way‘, `equipData`=‘way‘, `sex`=2, `combat`=4327896, `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:01‘; INSERT INTO cqdata.cq_herodata SET `id`=17, `serverId`=1, `userId`=2, `tempId`=2, `starArr`=‘way‘, `gemArr`=‘wa‘, `wingArr`=‘way‘, `equipData`=‘way‘, `sex`=2, `combat`=4327896, `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:00‘; INSERT INTO cqdata.cq_herodata SET `id`=16, `serverId`=1, `userId`=2, `tempId`=2, `starArr`=‘way‘, `gemArr`=‘wa‘, `wingArr`=‘way‘, `equipData`=‘way‘, `sex`=2, `combat`=4327896, `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:00‘; DELETE FROM cqdata.cq_herodata WHERE `id`=23 AND `serverId`=1 AND `userId`=2 AND `tempId`=2 AND `starArr`=‘way‘ AND `gemArr`=‘wa‘ AND `wingArr`=‘way‘ AND `equipData`=‘way‘ AND `sex`=2 AND `combat`=4327896 AND `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:03‘; DELETE FROM cqdata.cq_herodata WHERE `id`=22 AND `serverId`=1 AND `userId`=2 AND `tempId`=2 AND `starArr`=‘way‘ AND `gemArr`=‘wa‘ AND `wingArr`=‘way‘ AND `equipData`=‘way‘ AND `sex`=2 AND `combat`=4327896 AND `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:03‘; DELETE FROM cqdata.cq_herodata WHERE `id`=21 AND `serverId`=1 AND `userId`=2 AND `tempId`=2 AND `starArr`=‘way‘ AND `gemArr`=‘wa‘ AND `wingArr`=‘way‘ AND `equipData`=‘way‘ AND `sex`=2 AND `combat`=4327896 AND `recordTime`=‘2016-06-06 15:37:02‘;
`insert into XXX` 实际上为删除了该条记录。`delete from XXX ` 实际为插入了这条语句。对文件按照库名表名进行处理。导入mysql即可按照要求恢复数据。
本文出自 “hanchengway” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://hanchengway.blog.51cto.com/10974268/1786689
以上是关于mysqlbinlog 数据恢复的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章