小型web服务器
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了小型web服务器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
HTTP是一个属于应用层的面向对象的协议,由于其简捷、快速的方式,适用于分布式超媒体信息系统。HTTP协议的主要特点可概括如下:
1.支持客户/服务器模式。
2.简单快速:客户向服务器请求服务时,只需传送请求方法和路径。请求方法常用的有GET、HEAD、POST。每种方法规定了客户与服务器联系的类型不同。由于HTTP协议简单,使得HTTP服务器的程序规模小,因而通信速度很快。
3.灵活:HTTP允许传输任意类型的数据对象。正在传输的类型由Content-Type加以标记。
4.无连接:无连接的含义是限制每次连接只处理一个请求。服务器处理完客户的请求,并收到客户的应答后,即断开连接。采用这种方式可以节省传输时间。
5.无状态:HTTP协议是无状态协议。无状态是指协议对于事务处理没有记忆能力。缺少状态意味着如果后续处理需要前面的信息,则它必须重传,这样可能导致每次连接传送的数据量增大。另一方面,在服务器不需要先前信息时它的应答就较快。
http(超文本传输协议)是一个基于请求与响应模式的、无状态的、应用层的协议,常基于TCP的连接方式,HTTP1.1版本中给出一种持续连接的机制,绝大多数的Web开发,都是构建在HTTP协议之上的Web应用。
HTTP URL (URL是一种特殊类型的URI,包含了用于查找某个资源的足够的信息)的格式如下:
http://host[":"port][abs_path]
http表示要通过HTTP协议来定位网络资源;host表示合法的Internet主机域名或者IP地址;port指定一个端口号,为空则使用缺省端口80;abs_path指定请求资源的URI;如果URL中没有给出abs_path,那么当它作为请求URI时,必须以“/”的形式给出,通常这个工作浏览器自动帮我们完成。
1.http请求由三部分组成,分别是:请求行、消息报头
请求行以一个方法符号开头,以空格分开,后面跟着请求的URI和协议的版本,格式如下:Method Request-URI HTTP-Version CRLF 其中 Method表示请求方法;Request-URI是一个统一资源标识符;HTTP-Version表示请求的HTTP协议版本;CRLF表示回车和换行(除了作为结尾的CRLF外,不允许出现单独的CR或LF字符)。
在接收和解释请求消息后,服务器返回一个HTTP响应消息。
2.HTTP响应也是由三个部分组成,分别是:状态行、消息报头、响应正文
状态行格式如下:
HTTP-Version Status-Code Reason-Phrase CRLF
其中,HTTP-Version表示服务器HTTP协议的版本;Status-Code表示服务器发回的响应状态代码;Reason-Phrase表示状态代码的文本描述。
状态代码有三位数字组成,第一个数字定义了响应的类别,且有五种可能取值:
1xx:指示信息--表示请求已接收,继续处理
2xx:成功--表示请求已被成功接收、理解、接受
3xx:重定向--要完成请求必须进行更进一步的操作
4xx:客户端错误--请求有语法错误或请求无法实现
5xx:服务器端错误--服务器未能实现合法的请求
常见状态代码、状态描述、说明:
200 OK //客户端请求成功
400 Bad Request //客户端请求有语法错误,不能被服务器所理解
401 Unauthorized //请求未经授权,这个状态代码必须和WWW-Authenticate报头域一起使用
403 Forbidden //服务器收到请求,但是拒绝提供服务
404 Not Found //请求资源不存在,eg:输入了错误的URL
500 Internal Server Error //服务器发生不可预期的错误
503 Server Unavailable //服务器当前不能处理客户端的请求,一段时间后可能恢复正常
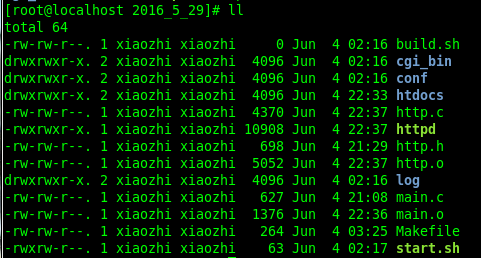
当前目录下文件如上图所示。
http.h http.c main.c 为主要源文件
conf,cgi_bin,log,build.sh暂时没使用
htdocs文件夹里存储网页数据来源:
1.jpg和一张html
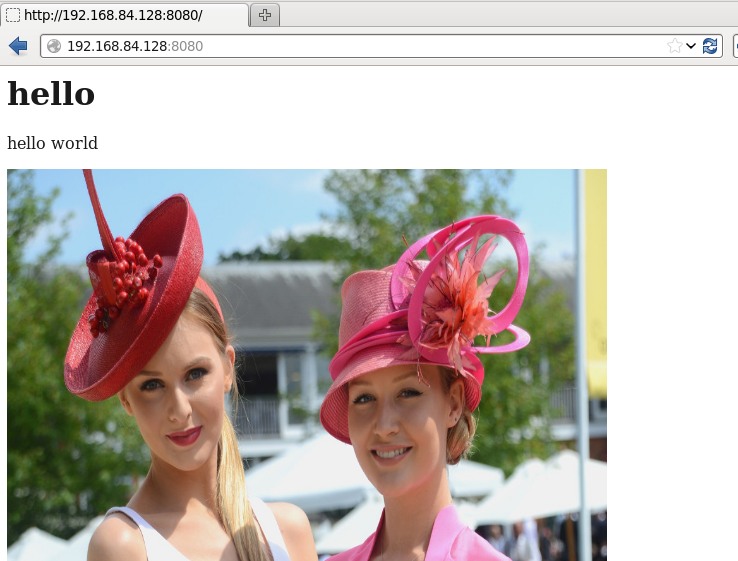
<html> <head> <h1>hello</h1> </head> <body> <p>hello world</p> <img src="1.jpg" height="500" width="600"/> </body> </html>
Makefile:
ROOT_PATH=$(shell pwd) LDFLAGS=-lpthread FLAGS=#_DEBUG1_ CC=gcc BIN=httpd SRC=$(shell ls *.c) OBJ=$(SRC:.c=.o) $(BIN):$(OBJ) $(CC) -o [email protected] $^ $(LDFLAGS) %.o:%.c $(CC) -c $< .PHONY:clean clean: rm -f $(OBJ) $(BIN) .PHONY:debug debug: @echo $(SRC) @echo $(OBJ)
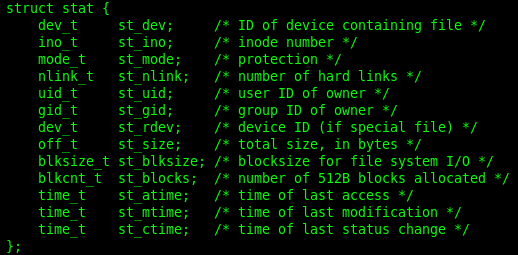
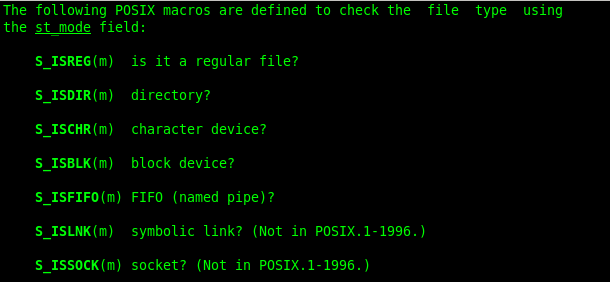
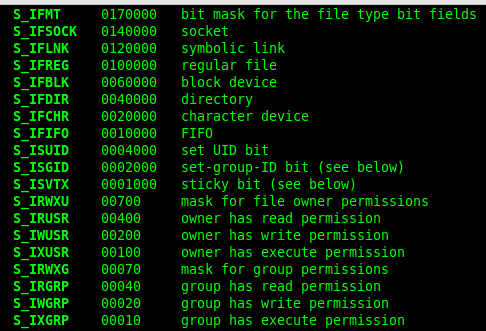
所用函数:
返回值:成功0;失败:-1,置错误码
st.st_mode:
返回值:成功:写到outfd的字节数;失败:-1,置错误码
//http.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<sys/sendfile.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<errno.h>
#define _DEF_PAGE_ "index.html"
#define _SIZE_ 1024
static void printLog(const char* const str,const char* const fun,int line);
void usage(const char* const proc);
int startup(char* ip,int port);
void echo_error(int sock,int errno);
int get_line(int sock,char* buf,int size);
void clear_head(int sock);
void echo_html(int sock,char* path,ssize_t size);
void accept_request(int sock);
void* handle_client(void* arg);
//http.c
#include"http.h"
//打印错误消息
static void printLog(const char* const str,const char* const fun,int line)
{
printf("%s:%s:%d\n",str,fun,line);
}
void usage(const char* const proc)
{
assert(proc);
printLog(proc,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
}
//创建套接字,完成绑定,设置为连接状态
int startup(char* ip,int port)
{
assert(ip);
int sock=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
if(sock<0)
{
printLog(strerror(errno),__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
exit(1);
}
int opt=1;
setsockopt(sock,SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,&opt,sizeof(opt));
struct sockaddr_in local;
local.sin_family=AF_INET;
local.sin_port=htons(port);
if(strncmp(ip,"any",3)==0)
{
local.sin_addr.s_addr= INADDR_ANY;
}
else
{
local.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(ip);
}
if(bind(sock,(struct sockaddr*)&local,sizeof(local))<0)
{
printLog(strerror(errno),__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
exit(1);
}
if(listen(sock,5)<0)
{
printLog(strerror(errno),__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
exit(1);
}
return sock;
}
void echoErr(int sock,int errno)
{
return;
}
//每次读取一行
int get_line(int sock,char* buf,int size)
{
assert(buf);
int i=0;
ssize_t _s=-1;
char ch=‘\0‘;
// printf("getLine");
while(i<size-1&&ch!=‘\n‘)
{
_s=recv(sock,&ch,1,0);
if(_s>0)
{
if(ch==‘\r‘)
{
if((_s=recv(sock,&ch,1,MSG_PEEK)))
{
if(_s>0&&ch==‘\n‘)
recv(sock,&ch,1,0);
}
}
buf[i++]=ch;
}
else
{
buf[i++]=‘\n‘;
break;
}
}
// printf("endddddddddddd");
buf[i]=‘\0‘;
return i;
}
//清除sock报文头部
void clear_head(int sock)
{
char buf[_SIZE_];
buf[0]=‘\0‘;
ssize_t _s=1;
while(_s>0&&strcmp(buf,"\n")!=0)
{
_s=get_line(sock,buf,sizeof(buf));
}
}
//发回响应
void echo_html(int sock,char* path,ssize_t size)
{
// printf("echo_htmlllllllllll\n");
// printf("path:%s\n",path);
int fd=open(path,O_RDONLY);
if(fd<0)
{
printLog(strerror(errno),__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
exit(1);
}
// printf("fd:%d\n",fd);
char* status_line="HTTP/1.0 200 ok\r\n\r\n";
send(sock,status_line,strlen(status_line),0);
// printf("sock success,size:%d\n",size);
if(sendfile(sock,fd,NULL,size)<0)
{
printf("error");
}
// printf("sendfile success");
close(fd);
}
//处理请求
void accept_request(int sock)
{
char buf[_SIZE_];
// int ret;
// while((ret=get_line(sock,buf,sizeof(buf)))>0)
// {
// if(ret==0)
// {
// printLog(strerror(errno),__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
// break;
// }
// printf("%s",buf);
// }
int ret=-1;
int i=0,j=0;
char method[_SIZE_/2];
char url[_SIZE_];
char path[_SIZE_];
memset(method,‘\0‘,sizeof(method));
memset(buf,‘\0‘,sizeof(buf));
memset(path,‘\0‘,sizeof(path));
memset(url,‘\0‘,sizeof(url));
if(get_line(sock,buf,sizeof(buf))==0)
{
printLog("errno",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
return;
}
// printf("%s",buf);
i=j=0;
while(!isspace(buf[i])&&i<strlen(buf)&&j<sizeof(method)-1)
{
method[j]=buf[i];//get method
++i;
++j;
}
method[j]=‘\0‘;
// printf("method:%s\n",method);
j=0;
while(isspace(buf[i]))
{
++i;
}
while(!isspace(buf[i])&&i<strlen(buf)&&j<sizeof(url)-1)
{
url[j]=buf[i];
++j;
++i;
}
url[j]=‘\0‘;
// printf("url:%s\n",url);
int cgi=0;
if(strcasecmp(method,"POST")!=0&&strcasecmp(method,"GET")!=0)
{
printf("error\n");
// echoErr(sock,1);
return;
}
// printf("success\n");
if(strcasecmp(method,"POST")==0)
{
cgi=1;
}
if(strcasecmp(method,"GET")==0)
{
// printf("getttttttttttttttttttt\n");
char* query_string=url;
while(*query_string!=‘\0‘&&*query_string!=‘?‘)
{
++query_string;
}
if(*query_string==‘?‘)
{
*query_string=‘\0‘;
cgi=1;
}
++query_string;
sprintf(path,"htdocs%s",url);//sprintf
// printf("path:%s\n",path);
if(path[strlen(path)-1]==‘/‘)
{
strcat(path,_DEF_PAGE_);
}
// printf("cgi=0,path:%s\n",path);
struct stat st;
if(stat(path,&st)<0)//not exist
{
printf("error");
return;
}
else if(S_IFDIR&st.st_mode)//dir
{
// printf("dirrrrrrrrrrr\n");
if(strcmp(path,"htdocs/_DEF_PAGE_")!=0)
{
strcpy(path,"htdocs/");
strcat(path,_DEF_PAGE_);
// printf("hhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh");
}
}
else if((st.st_mode&S_IXUSR)||(st.st_mode&S_IXGRP)||(st.st_mode&S_IXOTH))
{
// printf("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx\n");
cgi=1;
}
if(cgi)
{
//execute_cgi(sock,path,method,query_string);
}
else
{
// printf("echo_html\n");
fflush(stdout);
clear_head(sock);
echo_html(sock,path,st.st_size);
}
}
close(sock);
}
void* handle_client(void* arg)
{
int sock=(int)arg;
accept_request(sock);
return NULL;
}
//main.c
#include"http.h"
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
if(argc!=3)
{
usage(argv[0]);
return 1;
}
char* ip=argv[1];
int port=atoi(argv[2]);
int listen_sock=startup(ip,port);
struct sockaddr_in client;
socklen_t len=sizeof(client);
fflush(stdout);
while(1)
{
// printf("kkkkkkkkkkk");
// fflush(stdout);
int new_sock=accept(listen_sock,(struct sockaddr*)&client,&len);
if(new_sock<0)
{
printf("no client");
fflush(stdout);
continue;
}
pthread_t id;
// printf("con");
pthread_create(&id,NULL,handle_client,(void*)new_sock);
pthread_detach(id);//set detach return val:0/errno
}
return 0;
}注:注释为了测试,没实际意义。
运行截图
本文出自 “小止” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://10541556.blog.51cto.com/10531556/1786248
以上是关于小型web服务器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章