SpringMVC深入理解
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringMVC深入理解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
核心类与接口
- DispatcherServlet 前置控制器
- HandlerMapping 请求映射(到Controller)
- HandlerAdapter 请求映射(到Controller类的方法上)
- Controller 控制器
- HandlerIntercepter 拦截器
- ViewResolver 视图映射
- View 视图处理
启动过程
Spring MVC启动过程大致分为两个过程:
- ContextLoaderListener初始化,读取context-param中的contextConfigLocation指定的配置文件,创建ROOT Context,通过调用继承自ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext方法实例化Spring IoC容器,并将此容器实例注册到ServletContext中
- ContextLoaderListener初始化完毕后,开始初始化web.xml中配置的DispatcherServlet,DispatcherServlet的初始化又包括了视图管理器、异常处理器、映射管理等等;
1 /**
2 * Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
3 * <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
4 */
5 protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
6 initMultipartResolver(context);
7 initLocaleResolver(context);
8 initThemeResolver(context);
9 initHandlerMappings(context);
10 initHandlerAdapters(context);
11 initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
12 initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
13 initViewResolvers(context);
14 initFlashMapManager(context);
15 }
ContextLoaderListener初始化的是 WebApplicationContext, 创建后可以从ServletContext中获取,WebApplicationContext是应用程序内共享的,最多只有一个,如果寻求简单也可以不初始化此容器。与之不同 DispatcherServlet可以有多个,并共享一个WebApplicationContext容器,每一个DispatcherServlet有不同的配置,控制不同的WEB访问。一般将 DAO、Service 层Bean共享的放在ContextLoaderListener配置的容器中,将WEB层的Bean放在特定的DispatcherServlet配置的容器中。
SpringMVC利用Spring的注入特性初始化资源文件,只需要调用setPropertyValues方法就可将contextConfigLocation属性设置到对应实例中,也就是以依赖注入的方式初始化属性。
时序图如下(盗图):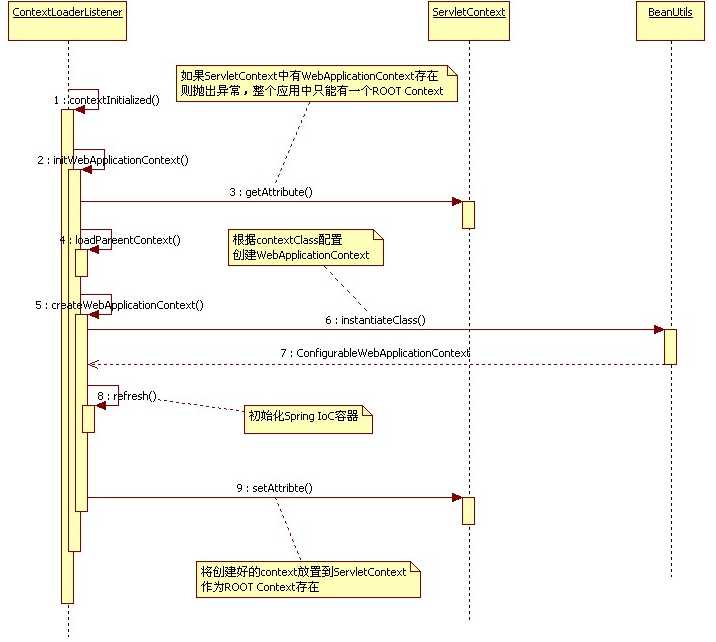
请求处理流程
官网上的图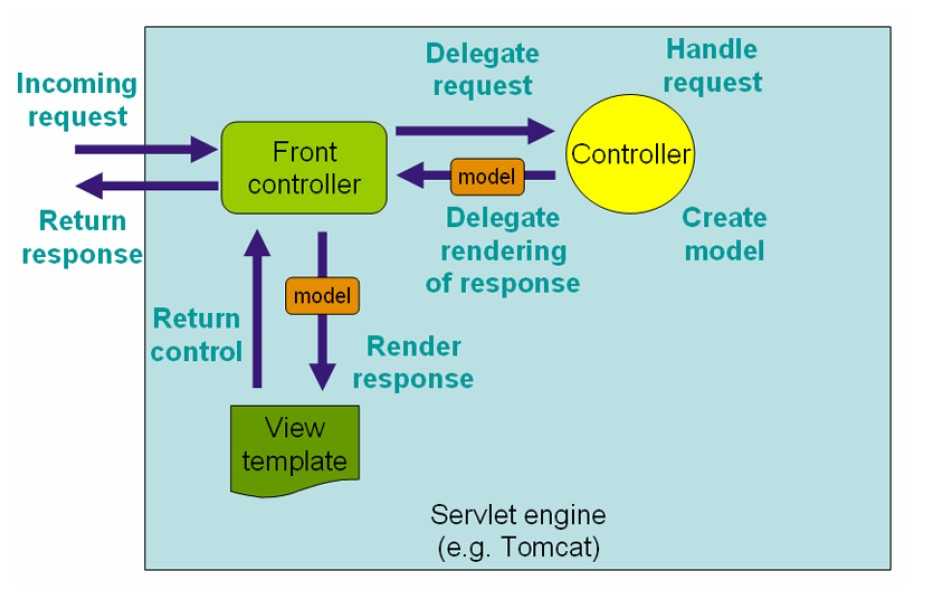
涉及到核心类与接口的过程描述:
客户端浏览器发送http请求,被`DispatcherServlet`捕获,调用关键的doDispatch方法,遍历所有注册为`Controller`的bean,为请求寻找关联映射,其中遍历查找的函数getHandler和getHandlerAdapter的源码:
1 /**
2 * Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request.
3 * <p>Tries all handler mappings in order.
4 * @param request current HTTP request
5 * @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found
6 */
7 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
8 for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
9 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
10 logger.trace(
11 "Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘");
12 }
13 HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
14 if (handler != null) {
15 return handler;
16 }
17 }
18 return null;
19 }
20
21
22 /**
23 * Return the HandlerAdapter for this handler object.
24 * @param handler the handler object to find an adapter for
25 * @throws ServletException if no HandlerAdapter can be found for the handler. This is a fatal error.
26 */
27 protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
28 for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
29 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
30 logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
31 }
32 if (ha.supports(handler)) {
33 return ha;
34 }
35 }
36 throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
37 "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
38 }
找到匹配的映射后`HandlerAdapter`会依次调用preHandle、handle(返回ModelAndView)、postHandle方法,所有步骤完成后调用processDispatchResult函数处理结果,并返回View给客户端。postDispatchResult函数和其中调用的render函数源码如下:
1 /**
2 * Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is
3 * either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView.
4 */
5 private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
6 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception {
7
8 boolean errorView = false;
9
10 if (exception != null) {
11 if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
12 logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
13 mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
14 }
15 else {
16 Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
17 mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
18 errorView = (mv != null);
19 }
20 }
21
22 // Did the handler return a view to render?
23 if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
24 render(mv, request, response);
25 if (errorView) {
26 WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
27 }
28 }
29 else {
30 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
31 logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() +
32 "‘: assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
33 }
34 }
35
36 if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
37 // Concurrent handling started during a forward
38 return;
39 }
40
41 if (mappedHandler != null) {
42 mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
43 }
44 }
45
46
47 /**
48 * Render the given ModelAndView.
49 * <p>This is the last stage in handling a request. It may involve resolving the view by name.
50 * @param mv the ModelAndView to render
51 * @param request current HTTP servlet request
52 * @param response current HTTP servlet response
53 * @throws ServletException if view is missing or cannot be resolved
54 * @throws Exception if there‘s a problem rendering the view
55 */
56 protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
57 // Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
58 Locale locale = this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request);
59 response.setLocale(locale);
60
61 View view;
62 if (mv.isReference()) {
63 // We need to resolve the view name.
64 view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
65 if (view == null) {
66 throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name ‘" + mv.getViewName() +
67 "‘ in servlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘");
68 }
69 }
70 else {
71 // No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
72 view = mv.getView();
73 if (view == null) {
74 throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
75 "View object in servlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘");
76 }
77 }
78
79 // Delegate to the View object for rendering.
80 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
81 logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘");
82 }
83 try {
84 if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
85 response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
86 }
87 view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
88 }
89 catch (Exception ex) {
90 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
91 logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" +
92 getServletName() + "‘", ex);
93 }
94 throw ex;
95 }
96 }
这就是一个完整的处理http请求的过程。盗图一张: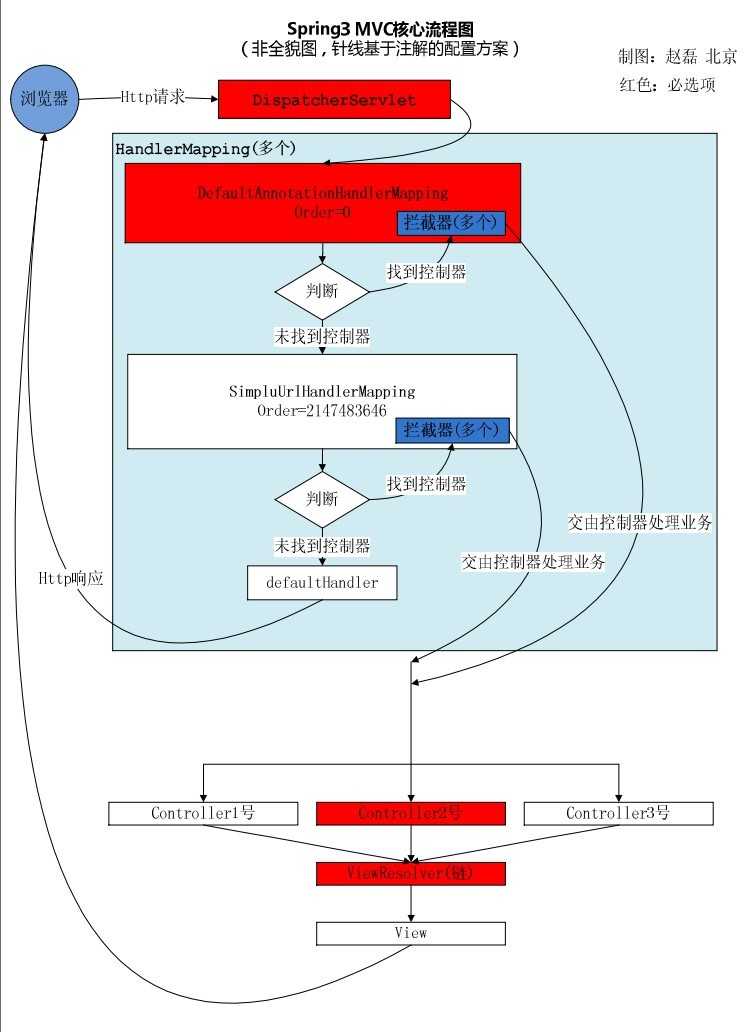
时序图如下(来源:http://neoremind.com/2016/02/springmvc%E7%9A%84%E4%B8%80%E4%BA%9B%E5%B8%B8%E7%94%A8%E6%9C%80%E4%BD%B3%E5%AE%9E%E8%B7%B5/):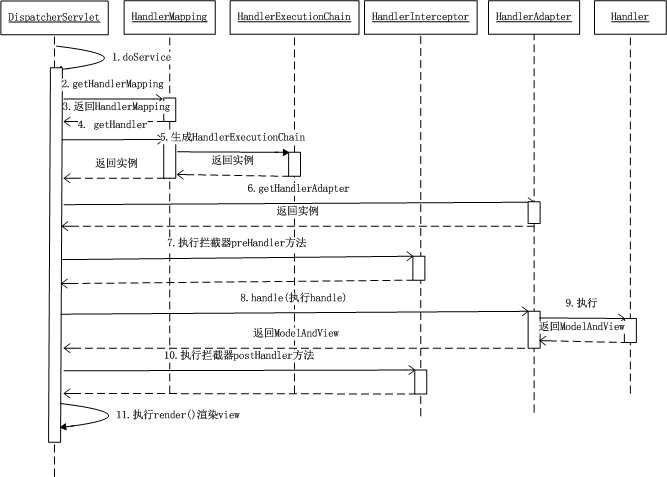
配置实例
这里放的是最简单的配置,可以通过这个简单的配置实例回顾一下上面的过程。
目录结构
-SpringMVCDemo
-src
-me.cyan
-WelcomeController
-web
-WEB-INF
-applicationContext.xml
-dispatcher-servlet.xml
-web.xml
-index.jsp
-pom.xml
pom.xml
引入的包
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
4 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
5 <groupId>me.cyan</groupId>
6 <artifactId>SpringMVCDemo</artifactId>
7 <name>SpringMVCDemo</name>
8 <packaging>war</packaging>
9 <version>1.0.0</version>
10
11 <properties>
12 <spring-version>4.2.6.RELEASE</spring-version>
13 </properties>
14
15 <dependencies>
16 <dependency>
17 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
18 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
19 <version>${spring-version}</version>
20 </dependency>
21 <dependency>
22 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
23 <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
24 <version>${spring-version}</version>
25 </dependency>
26 <dependency>
27 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
28 <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
29 <version>${spring-version}</version>
30 </dependency>
31 <dependency>
32 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
33 <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
34 <version>${spring-version}</version>
35 </dependency>
36 <dependency>
37 <groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
38 <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
39 <version>1.2</version>
40 </dependency>
41 <dependency>
42 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
43 <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
44 <version>${spring-version}</version>
45 </dependency>
46 <dependency>
47 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
48 <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
49 <version>${spring-version}</version>
50 </dependency>
51 <dependency>
52 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
53 <artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
54 <version>${spring-version}</version>
55 </dependency>
56 </dependencies>
57 </project>
web.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" 5 version="3.1"> 6 7 <!--配置文件路径--> 8 <context-param> 9 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 10 <param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value> 11 </context-param> 12 <listener> 13 <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> 14 </listener> 15 16 <!--SpringMVC核心servlet--> 17 <servlet> 18 <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> 19 <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> 20 <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 21 </servlet> 22 <servlet-mapping> 23 <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> 24 <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> 25 </servlet-mapping> 26 </web-app>
dispatcher-servlet.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" 4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> 6 7 <!-- 默认的注解映射的支持 --> 8 <mvc:annotation-driven /> 9 10 <!-- 自动扫描的包名 --> 11 <context:component-scan base-package="me.cyan" /> 12 13 </beans>
WelcomeController
1 package me.cyan;
2
3 import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
4 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
5 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
6
7 /**
8 * Created by cyan on 16/5/23.
9 */
10
11 @Controller
12 public class welcomeController {
13
14 @RequestMapping("/hello")
15 public @ResponseBody String sayhello(){
16 return "hello Spring MVC!";
17 }
18 }
运行结果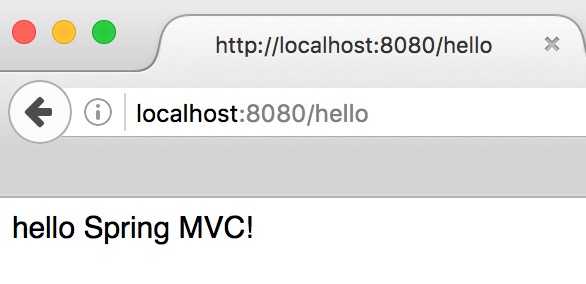
文章出自:http://www.cnblogs.com/verlen11/p/5521536.html
以上是关于SpringMVC深入理解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Java基础__慕课网学习(24):深入理解抽象类与接口(转)
