Android Fragment用法详解--静态使用Fragment
Posted _Vincent
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android Fragment用法详解--静态使用Fragment相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
先说明一下,本例子是运行在android Studio下面的。同样的代码复制粘贴到Eclipse运行却会报错。具体原因我也没有细查。知道的哥们,留言通知下呗。
Fragment,也就是碎片,本意是为了适配大屏幕的安卓设备而生的。但是出现后,很多安卓开发者都非常喜欢这个东西。这个东西很好用,但是也不是很容易用。下面我来来细细解说Android中的Fragment。
1、Fragment产生的缘由
运行Android的设备繁多,屏幕大小更是多种多样。针对不同屏幕尺寸,通常情况下,开发者都是先针对手机开发一套源代码,然后拷贝一份,修改布局以适应大屏幕设备,或平板,电视等。为了决解这样的麻烦,Google推出了Fragment。你可以把Fragment当成Activity的一个界面的一个组成部分,甚至Activity的界面可以完全有不同的Fragment组成,Fragment拥有自己的生命周期和接收、处理用户的事件,这样就不必在Activity写一堆控件的事件处理的代码了。更为重要的是,你可以动态的添加、替换和移除某个Fragment。
2、Fragment的生命周期
Fragment必须是依存与Activity而存在的,因此Activity的生命周期会直接影响到Fragment的生命周期。官网这张图很好的说明了两者生命周期的关系:
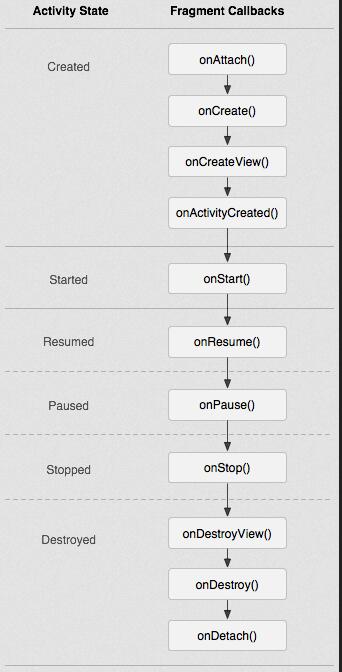
可以看到Fragment比Activity多了几个额外的生命周期回调方法:
onAttach(Activity)
当Fragment与Activity发生关联时调用。
onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup,Bundle)
创建该Fragment的视图
onActivityCreated(Bundle)
当Activity的onCreate方法返回时调用
onDestoryView()
与onCreateView想对应,当该Fragment的视图被移除时调用
onDetach()
与onAttach相对应,当Fragment与Activity关联被取消时调用
注意:除了onCreateView,其他的所有方法如果你重写了,必须调用父类对于该方法的实现,
3、静态的使用Fragment
这是使用Fragment最简单的一种方式,把Fragment当成普通的控件,直接写在Activity的布局文件中。步骤:
1、继承Fragment,重写onCreateView决定Fragemnt的布局
2、在Activity中声明此Fragment,就当和普通的View一样
下面展示一个例子(我使用2个Fragment作为Activity的布局,一个Fragment用于标题布局,一个Fragment用于内容布局):
TitleFragment的布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:background="@android:color/darker_gray" android:layout_height="45dp"> <ImageButton android:id="@+id/im_button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@android:drawable/star_on" /> <TextView android:textSize="25sp" android:textColor="@android:color/holo_red_dark" android:gravity="center" android:text="Fragment制作标题栏" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </RelativeLayout>
ContentFragment布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:gravity="center" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:gravity="center" android:textSize="25sp" android:text="Fragment当作主面板" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </RelativeLayout>
MainActivity布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <fragment android:id="@+id/fg_title" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="45dp" android:name="app.linfeng.com.myapplication.TitleFragment" /> <fragment android:layout_below="@id/fg_title" android:id="@+id/fg_content" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:name="app.linfeng.com.myapplication.ContentFragment" /> </RelativeLayout>
TitleFragment源代码
package app.linfeng.com.myapplication; import android.os.Bundle; import android.support.v4.app.Fragment; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import android.widget.ImageButton; import android.widget.Toast; public class TitleFragment extends Fragment { private ImageButton im_button; @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.title_fragment_layout,container,false); im_button = (ImageButton) view.findViewById(R.id.im_button); im_button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Toast.makeText(getContext(),"业务逻辑写在Fragment上,Activity是不是很整洁了?",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }); return view; } }
ContentFragment源代码
package app.linfeng.com.myapplication; import android.os.Bundle; import android.support.v4.app.Fragment; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; public class ContentFragment extends Fragment { @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.content_fragment_layout,container,false); return view; } }
MainActivity源代码
package app.linfeng.com.myapplication; import android.os.Bundle; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; /** * 因为Android Studio新建Activity是自动继承AppCompatActivity,所以我也没有改成 * Activity,这个和本案例没有关系哈。 */ public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE); //因为继承的是AppCompatActivity,所以requestWindowFeature()失效了 getSupportActionBar().hide(); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } }
最后我们看看运行效果

静态使用Fragment其实就是把Fragment当成普通的View一样声明在Activity的布局文件中,然后所有控件的事件处理等代码都由各自的Fragment去处理,瞬间觉得Activity好干净有木有~~代码的可读性、复用性以及可维护性是不是瞬间提升了
以上是关于Android Fragment用法详解--静态使用Fragment的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章