死磕Spring AOP系列4:剖析AOP schema方式原理
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了死磕Spring AOP系列4:剖析AOP schema方式原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这个是《死磕Spring AOP系列》第4个。已经讲过的内容
死磕Spring AOP系列3:剖析Bean处理器之DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
死磕Spring AOP系列2:剖析Bean处理器之BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
死磕Spring AOP系列1:编程式实现AOP
通过前3篇,大家应该可以清楚的知道:AOP代理原理有3元素
BeanPostProcessor,作为代理对象初始入口
Advisor&Pointcut&MethodMatcher完成匹配
Advice的声明及链式结构维护
三个问题在前面的讲解中已经讲解了。其中:
Advice的链式结构,是通过ProxyFactory统一维护的管理的,在《编程式实现AOP》中已说明;
匹配在前面系列2及系列3中也做了说明;
代理对象初始入口也在系列第3讲中进行了讲解。
本文,主要从这3各方面入手,对常用的aop schema做一个全方位的剖析。主要内容
使用aop schema方式做一个简单的演示demo
确认并剖析相关的BeanPostProcessor
确认并剖析相关的Advisor,PointCut
1.使用aop schema方式做一个简单的演示demo
例子代码来源于http://www.tutorialspoint.com/spring/schema_based_aop_appoach.htm
//1 切面类
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Logging {
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* before a selected method execution.
*/
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("Going to setup student profile.");
}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* after a selected method execution.
*/
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("Student profile has been setup.");
}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* when any method returns.
*/
public void afterReturningAdvice(Object retVal){
System.out.println("Returning:" + retVal.toString() );
}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* if there is an exception raised.
*/
public void AfterThrowingAdvice(IllegalArgumentException ex){
System.out.println("There has been an exception: " + ex.toString());
}
}
//2 业务模拟类
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
System.out.println("Age : " + age );
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("Name : " + name );
return name;
}
public void printThrowException(){
System.out.println("Exception raised");
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}XML(Beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd "> <aop:config> <aop:aspect id="log" ref="logging"> <aop:pointcut id="selectAll" expression="execution(* com.tutorialspoint.*.*(..))"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="selectAll" method="beforeAdvice"/> <aop:after pointcut-ref="selectAll" method="afterAdvice"/> <aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="selectAll" returning="retVal" method="afterReturningAdvice"/> <aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="selectAll" throwing="ex" method="AfterThrowingAdvice"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> <!-- Definition for student bean --> <bean id="student" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student"> <property name="name" value="Zara" /> <property name="age" value="11"/> </bean> <!-- Definition for logging aspect --> <bean id="logging" class="com.tutorialspoint.Logging"/> </beans>
Main
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/tutorialspoint/Beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
student.getName();
student.getAge();
// student.printThrowException();
}
}执行结果
Going to setup student profile.
Name : Zara
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:Zara
Going to setup student profile.
Age : 11
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:11
通过查看日志,可以捕获到以下信息,为咱们剖析源码找到了分析点。
...
DEBUG: org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator - Creating implicit proxy for bean ‘student‘ with 0 common interceptors and 5 specific interceptors
DEBUG: org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy - Creating CGLIB proxy: target source is SingletonTargetSource for target object [[email protected]]
DEBUG: org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy - Unable to apply any optimisations to advised method: public java.lang.String com.tutorialspoint.Student.getName()
2.找寻aop schema对应的BeanPostProcessor
aop的schema 对应的spring beanPostProcessor,是Spring自动指派的,对我们是透明的,这一点和以前讲到的BeanNameAutoProxyCreator和DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator不同,咱们没有声明。
首先,aop是客制化的标签(不是bean标签,都是客制化标签),要找到这个位置。熟悉spring自定义标签的朋友应该都知道,需要找到aop标签*.handler文件.位置在$base/spring-aop\src\main\resources\META-INF\spring.handlers.
内容如下
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/aop=org.springframework.aop.config.AopNamespaceHandler
2.1 分析AopNamespaceHandler
public class AopNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
/**
完成一些解析器
* Register the {@link BeanDefinitionParser BeanDefinitionParsers} for the
*
*/
public void init() {
// In 2.0 XSD as well as in 2.1 XSD.
//负责解析<aop:config>
registerBeanDefinitionParser("config", new ConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
//负责即系<aspectj-autoproxy>
registerBeanDefinitionParser("aspectj-autoproxy", new AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionDecorator("scoped-proxy", new ScopedProxyBeanDefinitionDecorator());
// Only in 2.0 XSD: moved to context namespace as of 2.1
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
//接下来关注的重点是ConfigBeanDefinitionParser
class ConfigBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef =
new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), parserContext.extractSource(element));
parserContext.pushContainingComponent(compositeDef);
//配置the auto proxy creator
configureAutoProxyCreator(parserContext, element);
//接下来解析xml节点元素
List<Element> childElts = DomUtils.getChildElements(element);
for (Element elt: childElts) {
String localName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(elt);
if (POINTCUT.equals(localName)) {
parsePointcut(elt, parserContext);
}
else if (ADVISOR.equals(localName)) {
parseAdvisor(elt, parserContext);
}
else if (ASPECT.equals(localName)) {
parseAspect(elt, parserContext);
}
}
parserContext.popAndRegisterContainingComponent();
return null;
}
private void configureAutoProxyCreator(ParserContext parserContext, Element element) {
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAspectJAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
}
}
--------------------
public abstract class AopNamespaceUtils {
public static void registerAspectJAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
ParserContext parserContext, Element sourceElement) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
parserContext.getRegistry(), parserContext.extractSource(sourceElement));
useClassProxyingIfNecessary(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement);
registerComponentIfNecessary(beanDefinition, parserContext);
}
}
--------------------
public abstract class AopConfigUtils {
public static final String AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME =
"org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator";
//AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator注册到spring容器
public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
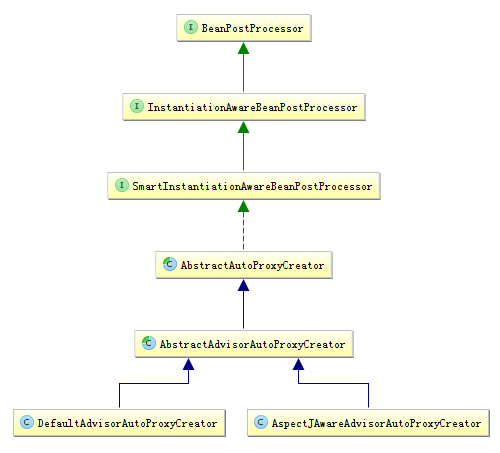
}到这儿,任务也算完成了。AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator就是我们苦苦寻找的BeanPostProcessor.
真巧它和DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator是兄弟。接下来,就是剖析AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator。
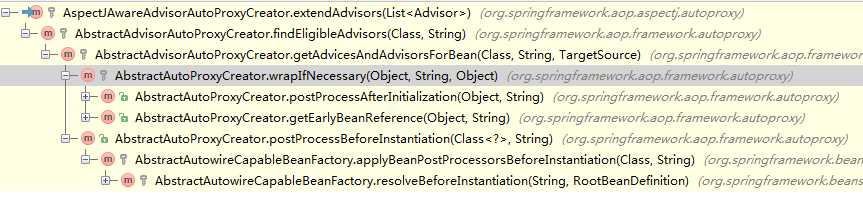
结合《死磕Spring AOP系列3》,可以将getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean作为分析的起点,以前说过该方法是AbstractAutoProxyCreator的抽象方法,由子类实现。
public abstract class AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator {
...
@Override
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) {
List advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
//查找适合的Advisors
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class beanClass, String beanName) {
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);//交给子类实现扩展
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
}2.3剖析AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.extendAdvisors方法
public class AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator extends AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator {
//添加 ExposeInvocationInterceptor to the beginning of the advice chain
protected void extendAdvisors(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors) {
AspectJProxyUtils.makeAdvisorChainAspectJCapableIfNecessary(candidateAdvisors);
}
}
public abstract class AspectJProxyUtils {
public static boolean makeAdvisorChainAspectJCapableIfNecessary(List<Advisor> advisors) {
// Don‘t add advisors to an empty list; may indicate that proxying is just not required
if (!advisors.isEmpty()) {
boolean foundAspectJAdvice = false;
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
// Be careful not to get the Advice without a guard, as
// this might eagerly instantiate a non-singleton AspectJ aspect
if (isAspectJAdvice(advisor)) {
foundAspectJAdvice = true;
}
}
if (foundAspectJAdvice && !advisors.contains(ExposeInvocationInterceptor.ADVISOR)) {
advisors.add(0, ExposeInvocationInterceptor.ADVISOR);//添加到链
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
*判断是不是AspectJAdvice
* Determine whether the given Advisor contains an AspectJ advice.
* @param advisor the Advisor to check
*/
private static boolean isAspectJAdvice(Advisor advisor) {
return (advisor instanceof InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor ||
advisor.getAdvice() instanceof AbstractAspectJAdvice ||
(advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor &&
((PointcutAdvisor) advisor).getPointcut() instanceof AspectJExpressionPointcut));
}
}
//就做一件事,对外曝光MethodInvocation,放到ThreadLocal中
public class ExposeInvocationInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Ordered, Serializable {
/** Singleton instance of this class */
public static final ExposeInvocationInterceptor INSTANCE = new ExposeInvocationInterceptor();
private static final ThreadLocal<MethodInvocation> invocation =
new NamedThreadLocal<MethodInvocation>("Current AOP method invocation");private ExposeInvocationInterceptor() {
} public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 1;
}
}3.剖析Spring pointcut匹配逻辑
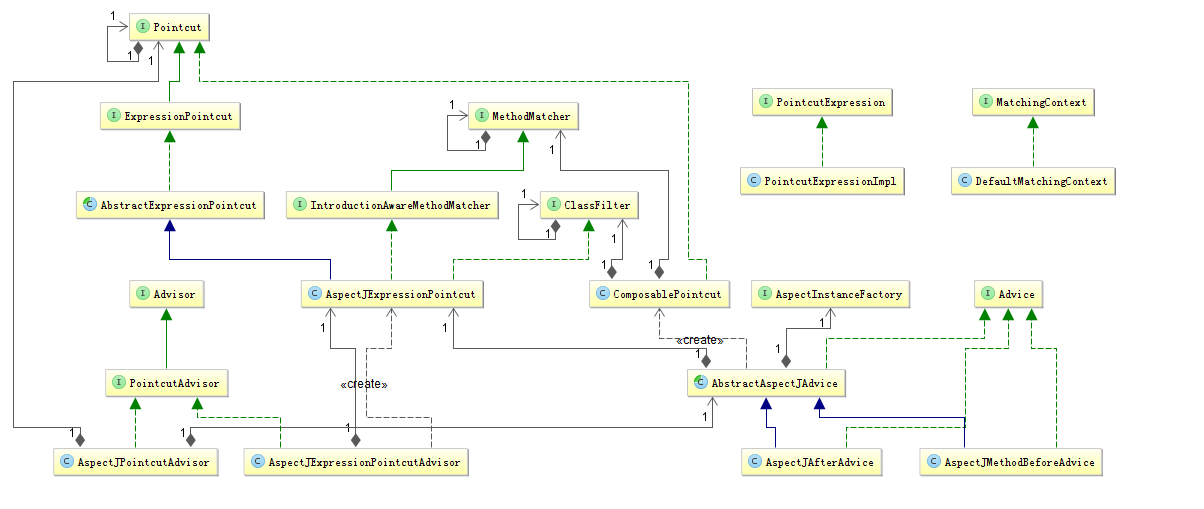
如图
重点关注AspectJExpressionPointcut.该类同时实现了MethodMatcher和ClassFilter两个接口。
public class AspectJExpressionPointcut extends AbstractExpressionPointcut
implements ClassFilter, IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher, BeanFactoryAware {
//ClassFilter实现
public boolean matches(Class targetClass) {
checkReadyToMatch();
try {
return this.pointcutExpression.couldMatchJoinPointsInType(targetClass);
} catch (ReflectionWorldException e) {
logger.debug("PointcutExpression matching rejected target class", e);
}
}
//MethodMatcher实现
public boolean matches(Method method, Class targetClass, boolean beanHasIntroductions) {
checkReadyToMatch();
Method targetMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
ShadowMatch shadowMatch = getShadowMatch(targetMethod, method);
// Special handling for this, target, @this, @target, @annotation
// in Spring - we can optimize since we know we have exactly this class,
// and there will never be matching subclass at runtime.
if (shadowMatch.alwaysMatches()) {
return true;
}
else if (shadowMatch.neverMatches()) {
return false;
}
else {
// the maybe case
return (beanHasIntroductions || matchesIgnoringSubtypes(shadowMatch) || matchesTarget(shadowMatch, targetClass));
}
}
}
public class PointcutExpressionImpl implements PointcutExpression {
//AspectJExpressionPointcut 实现ClassFilter接口时候调用。
public boolean couldMatchJoinPointsInType(Class aClass) {
ResolvedType matchType = world.resolve(aClass.getName());
ReflectionFastMatchInfo info = new ReflectionFastMatchInfo(matchType, null, this.matchContext, world);
boolean couldMatch = pointcut.fastMatch(info).maybeTrue();
if (MATCH_INFO) {
System.out.println("MATCHINFO: fast match for ‘" + this.expression + "‘ against ‘" + aClass.getName() + "‘: "
+ couldMatch);
}
return couldMatch;
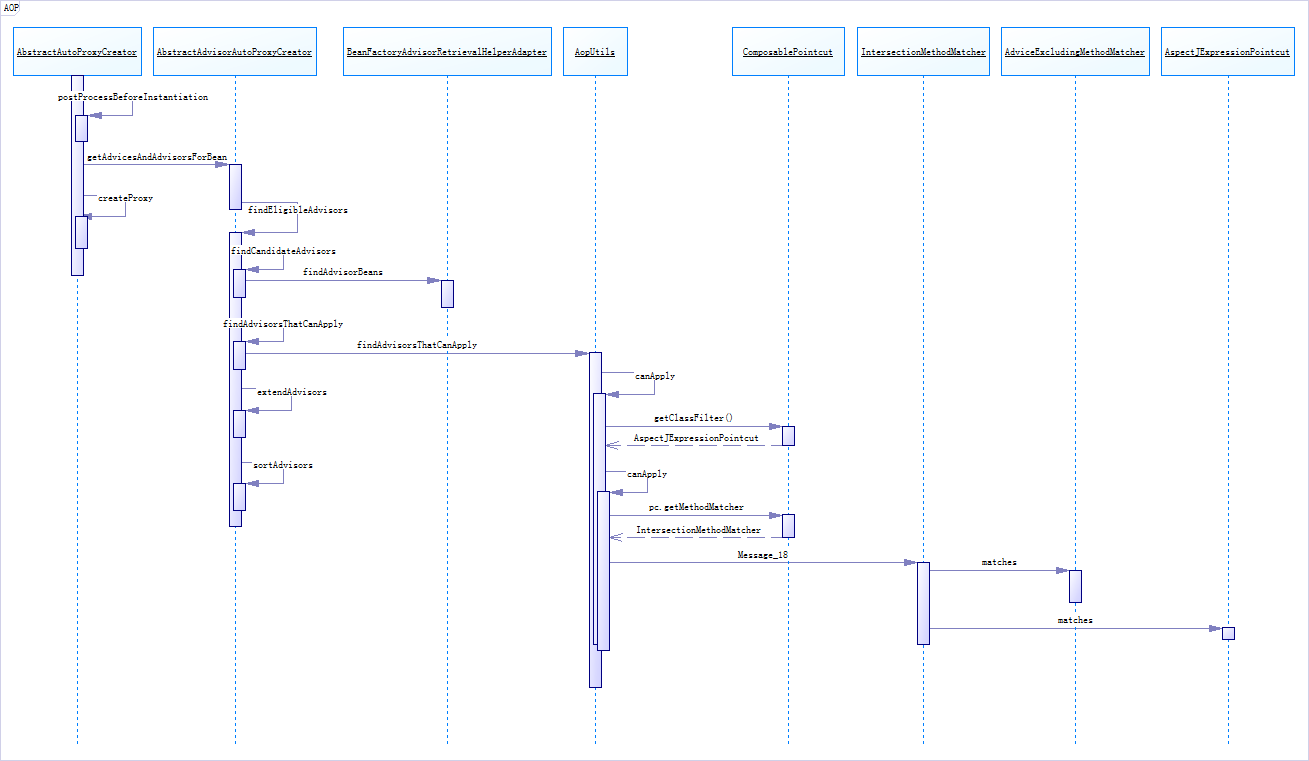
}}4序列图
5.总结
截止到现在已经讲解了BeanNameAutoProxyCreator,DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator及今天的AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator。虽然复杂度有所区别,但底层设计本质是一样的。Spring 在AbstractAutoProxyCreator进行了抽象处理,实现了扩展性。
本文出自 “简单” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://dba10g.blog.51cto.com/764602/1786117
以上是关于死磕Spring AOP系列4:剖析AOP schema方式原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
死磕Spring AOP系列3:剖析Bean处理器之DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator