第7章:栈
Posted 木子识时务
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第7章:栈相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- 栈概览
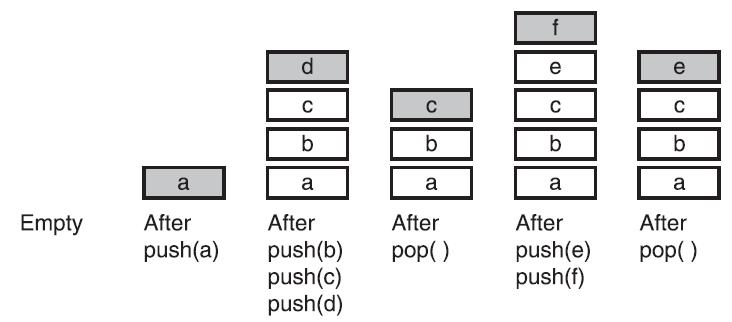
- 栈是线性集合,遵从后进先出原则( Last - in first - out , LIFO )原则
- 栈常用的操作包括压入( push ) 和弹出( pop )
- 栈的应用
- 将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,并且计算后缀表达式的值
- 回溯算法
- 管理计算机内存以支持函数和方法调用
- 支持应用程序中的撤消功能
- 维护Web浏览器访问链接的历史记录
- 使用栈
- 栈不是Python的内建类型,可以用列表代替,但是列表可以在任何位置插入,删除,替换元素,这些违背了栈作为一种抽象数据类型的本意,因此需要为栈定义一种更为严格的接口
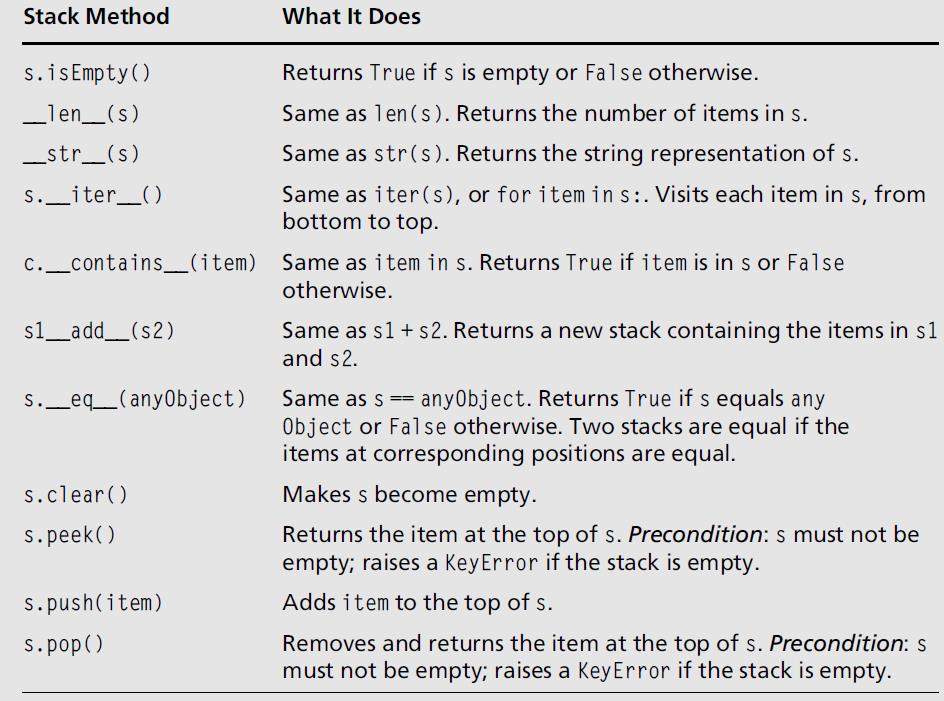
- 栈接口
- 初始化一个栈
-
s1 = ArrayStack()
s2 = LinkedStack( [20, 40, 60] )
- 示例应用程序:匹配括号
- 步骤
- 扫描表达式,将开始的括号压入栈中
- 当遇到一个结束的括号时,如果栈为空,或者如果栈项的项不是相同的类型开始括号,括号不匹配
- 如果是正确类型的括号,从栈顶弹出一项,继续扫描表达式
- 当到达表达式未尾时,栈应为空,否则括号不匹配
- 代码
- index 方法返回列表中项的位置
- 可以自定义括号的类型
-
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
"""
File: brackets.py
Checks expressions for matching brackets.
"""
from linkedstack import LinkedStack
def bracketsBalance( exp, startBracketList = [\'(\', \'[\'], endBracketList = [\')\', \']\'] ):
"""exp is a string that represents the expressions.
startBracketList is the list of start brackets list.
endBracketList is the list of end brackets list.
precondition: startBracketList must have the same length of endBracketList.
raise: Exception if startBracketList don\'t have the same length of endBracketList."""
if len( startBracketList ) != len( endBracketList ):
raise Exception( "The startBracketList must have the same length with the endBracketList." )
stk = LinkedStack()
for ch in exp:
if ch in startBracketList:
stk.push( ch )
elif ch in endBracketList:
if stk.isEmpty():
return False
chFromStack = stk.pop()
if chFromStack != startBracketList[ endBracketList.index( ch ) ]:
return False
return stk.isEmpty()
def main():
"""Test the bracketsBalance function."""
while True:
exp = input( "Enter a brackets expressions: ")
if exp == "":
break
if bracketsBalance(exp,[\'(\',\'[\', \'{\'],[\')\', \']\', \'}\'] ):
print("OK!")
else:
print( "Not OK!" )
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- 栈的 3 种应用
- 计算算术表达式
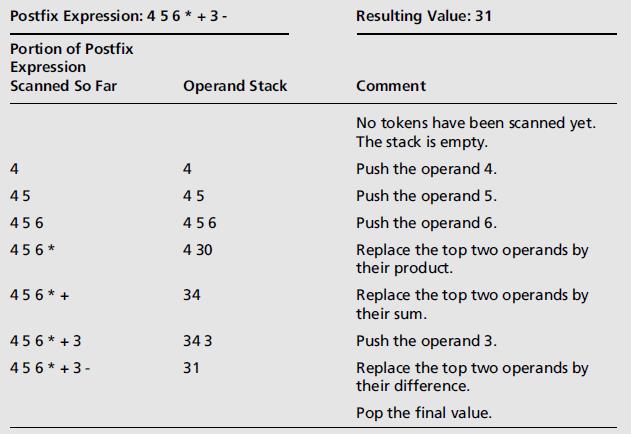
- 计算后缀表达式
- 步骤(需要一个数字栈)
- 从左到右的遍历表达式,遇到运算数,则将其压入数字栈中
- 碰到一个运算符时,从数字栈中弹出两个运算数,对其应用运算符,并将所得的结果压入数字栈
- 继续遍历,直到到达表达式的未尾,此时,数字栈中只剩表达式的值
- 示例
- 时间复杂度为 O(n)
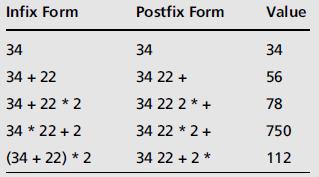
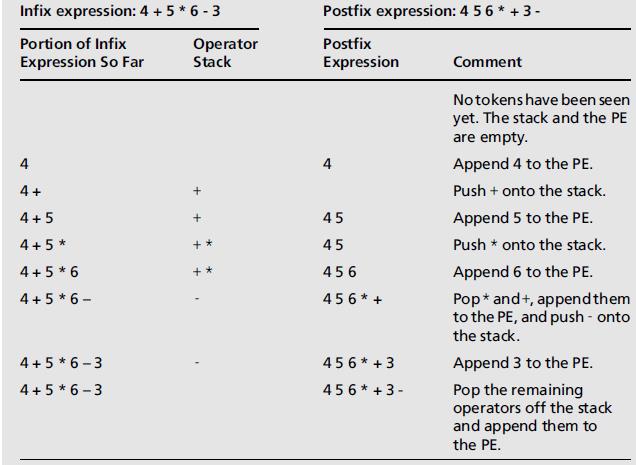
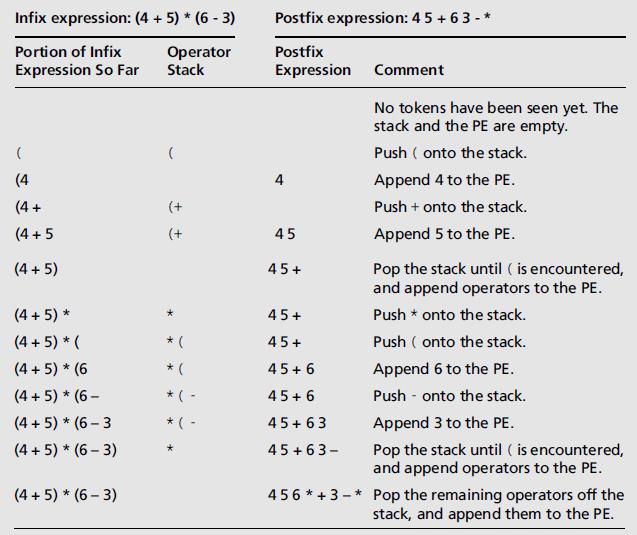
- 将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式
- 步骤
- 开始时,有一个空的后缀表达式和一个空的栈,栈用来保存运算符和左圆括号
- 从左到右,扫描中缀表达式
- 遇到一个运算数时,将其添加到后缀表达式中
- 遇到一个左圆括号时,将其压入栈中
- 遇到一个运算符,从栈中弹出和它具有相等或更高优先级的所有运算符,并将其依次添加到后缀表达式中
- 遇到一个右圆括号时,将运算符从栈中移动到后缀表达式中,直到碰到与之匹配的左圆括号,并将其丢弃
- 遇到中缀表达式的结束时,将栈中剩余的运算符全部转移到后缀表达式中
- 示例
- 时间复杂度为 O(n)
- 回溯算法
- 描述
- 回溯算法从一个预定义的起始状态开始,随后从一个状态移动到另一个状态,以搜索想要的最终状态。
- 在任何状态下,如果有多个选择,则会随机选取一种状态,然后继续
- 如果算法到达了不希望结果的一个状态,它会回到上一个拥有一个末探索的、可替代选项的位置,并尝试这个可替代选项。
- 最后,要么算法到达了想要的结果,要么穷尽了对所有算法的搜索
- 栈的作用是在每一个关头记住可替代的状态
- 伪代码
-
Create an empty stack
Push the starting state onto the stack
while the stack in not empty:
Pop the stack and eaxmine the state
if the state represents an ending state
return SUCCESSFUL CONCLUSION
elif the state hasn\'t been visited previously
Mark the state as visited
Push onto the stack all unvisited adjacent states.
return UNSUCCESSFUL CONCLUSION
- 算法整体复杂度为 O(n)
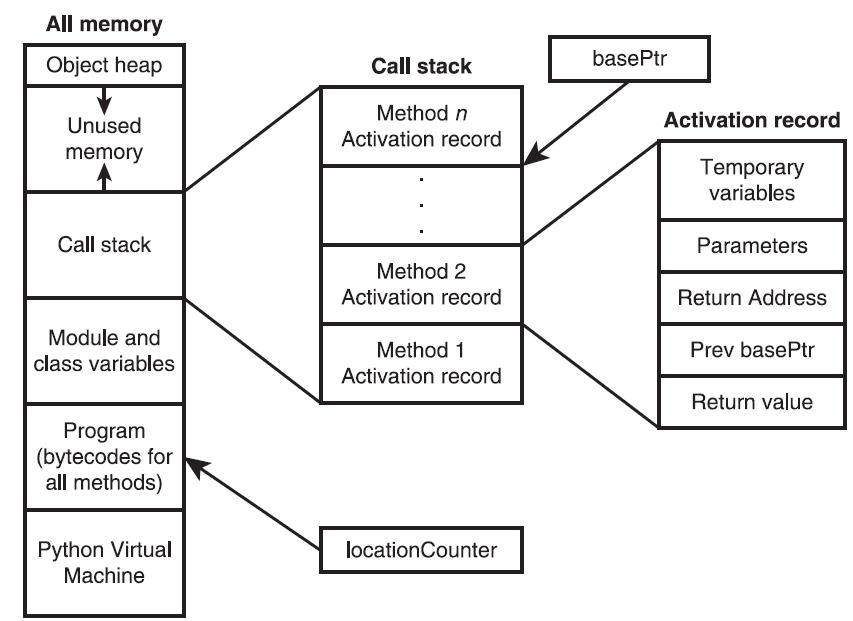
- 内存管理