Linux Centos的Inode及Block相关知识
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux Centos的Inode及Block相关知识相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本经验均在CentOSrelease6.7(Final)下操作,如知识有欠缺之处 欢迎批评指正。
linux 的inode及block的相关知识:
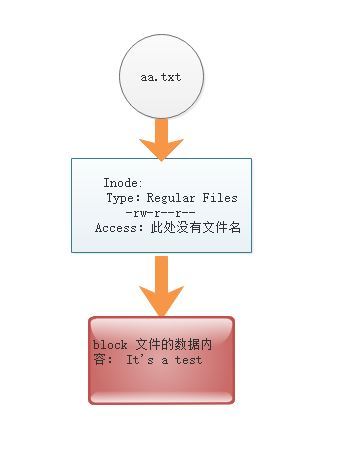
1> Linux系统分区格式化文件系统之后,系统会分为Inode及Block两部分:
1)Inode为系统文件的属性信息(ls -l的结果)及指向文件实体的指针,但是没有存放文件名,一般在上级目录里的Block。
2)Block为存放数据的,ext3/ext4一般为1k,2k,4k,一般默认4k
3)一个文件不论多大至少占用一个Inode和一个Block,一个Block只能存放一个文件的内容,block的数量大于Inode的数量,多个文件可以占用同一个 inode(硬链接) 。
4)访问文件, 通过文件-->inode(验证权限)--->blocks.
5)inode 一般情况默认256B,block大小1k,2k,4k,默认4k,注意,引导分区等特殊分区除外。
6)通过df -i 查看inode的数量及使用情况,dumpe2fs /dev/sda1 查看inode及block的大小和数量。
7)一个block只能 被一个文件使用 ,如果一个文件很小block太大,剩余空间浪费,无法继续被其他文件使用。
8)block不是越大越好,根据业务的文件大小进行选择,一般就是默认 4k。
9)可以在格式化的时候改变inode及block的大小,使用mkfs.ext4 -b 2048 -I 1024 /dev/sdb2
2>Linux中df命令的功能是用来检查linux服务器的文件系统的磁盘空间占用情况。可以利用该命令来获取硬盘被占用了多少空间,目前还剩下多少空间等信息。
1.命令格式:
df [选项] [文件]
2.参数 :
df -i 查看参数多少 个
[[email protected] ~]# df -i Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on /dev/mapper/vg_techw-lv_root 1152816 55846 1096970 5% / tmpfs 125596 1 125595 1% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 128016 38 127978 1% /boot
df -h 查看磁盘大小:
[[email protected] ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/vg_techw-lv_root 18G 1.5G 15G 9% / tmpfs 491M 0 491M 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 477M 36M 416M 8% /boot
查看当前系统分区的Inode及Block的总量及使用量:
[[email protected] ~]# dumpe2fs /dev/sda1 | grep -i "block size" dumpe2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Block size: 1024 [[email protected] ~]# [[email protected] ~]# [[email protected] ~]# dumpe2fs /dev/sda1 | grep -i "inode size" dumpe2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Inode size: 128 ###boot分区为128,常规分区为256 [[email protected] ~]# [[email protected] ~]# [[email protected] ~]# dumpe2fs /dev/sda1 | grep -i "inode count" dumpe2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Inode count: 128016 [[email protected] ~]# [[email protected] ~]# dumpe2fs /dev/sda1 | grep -i "block count" dumpe2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Block count: 512000 Reserved block count: 25600
3>添加一块磁盘,格式化,改变Inode及 Block的大小,挂载查看硬盘的Inode及Block数量:
1)添加一块5G的磁盘,为方便区分设置为/dev/sdb,fdisk分区,然后mkfs.ext4格式化
(虚拟机增加一块5G的硬盘,分区,格式化)
[[email protected] ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x2d37eabe. Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. After that, of course, the previous content won‘t be recoverable. Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite) WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It‘s strongly recommended to switch off the mode (command ‘c‘) and change display units to sectors (command ‘u‘). Command (m for help): n ### add a new partition Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p Partition number (1-4): 2 ### 为做区分,选择2 First cylinder (1-652, default 1): Using default value 1 Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-652, default 652): Using default value 652 Command (m for help): w ### write table to disk and exit The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks. 分区时的参数命令: a toggle a bootable flag b edit bsd disklabel c toggle the dos compatibility flag d delete a partition l list known partition types m print this menu n add a new partition o create a new empty DOS partition table p print the partition table q quit without saving changes s create a new empty Sun disklabel t change a partition‘s system id u change display/entry units v verify the partition table w write table to disk and exit x extra functionality (experts only)
[[email protected] ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb2 mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Filesystem label= OS type: Linux Block size=4096 (log=2) ###默认的Block的大小为4096 Fragment size=4096 (log=2) Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks 327680 inodes, 1309289 blocks 65464 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user First data block=0 Maximum filesystem blocks=1342177280 40 block groups 32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group 8192 inodes per group Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736 Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (32768 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done This filesystem will be automatically checked every 26 mounts or 180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
2)###inode的大小范围为128-2048,block的大小范围为1024-4096####
3)将Block和Inode的大小都改为2048:
[[email protected] ~]# mkfs.ext4 -b 2048 -I 2048 /dev/sdb2 mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Filesystem label= OS type: Linux Block size=2048 (log=1) Fragment size=2048 (log=1) Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks 326400 inodes, 2618578 blocks 130928 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user First data block=0 Maximum filesystem blocks=540016640 160 block groups 16384 blocks per group, 16384 fragments per group 2040 inodes per group Superblock backups stored on blocks: 16384, 49152, 81920, 114688, 147456, 409600, 442368, 802816, 1327104, 2048000 Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (32768 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done This filesystem will be automatically checked every 30 mounts or 180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
4)使用dumpe2fs命令查询Inode和Block的大小:
[[email protected] ~]# dumpe2fs /dev/sdb2 | grep "Inode size" dumpe2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Inode size: 2048 ###大小更改成功 [[email protected] ~]# s /dev/sdb2 | grep "Block size" dumpe2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Block size: 2048 ###大小更改成功
本文出自 “tao” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://xtao16.blog.51cto.com/911643/1785752
以上是关于Linux Centos的Inode及Block相关知识的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
06-Linux基础入门-文件和目录的属性及权限之inode与block